Understanding Rotator Cuff Injuries
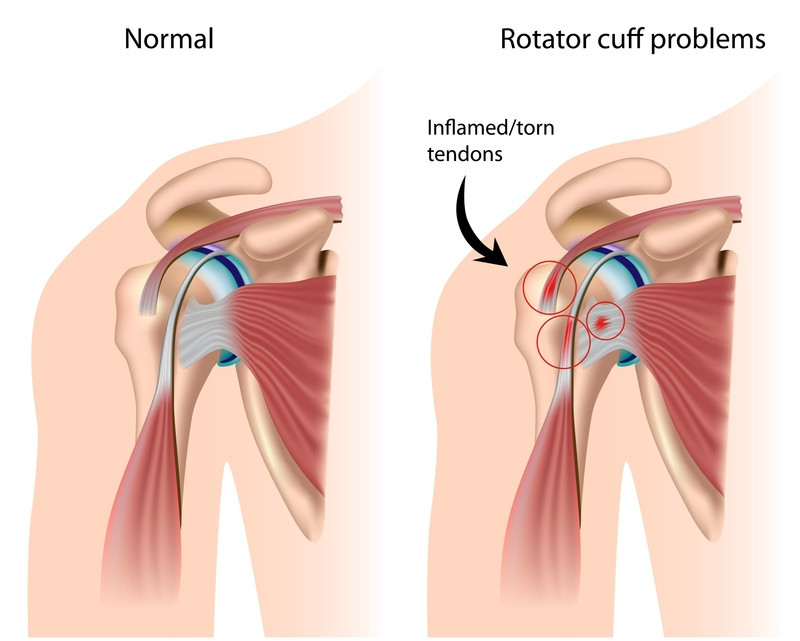
The shoulder is one of the most complex and mobile joints in the human body.
This ball-and-socket connection is supported by a group of muscles and tendons collectively known as the rotator cuff, which facilitates a remarkable range of three-dimensional movements.
The rotator cuff is comprised of four muscles and their tendons that surround the shoulder joint, helping to stabilize it while enabling lifting and rotating movements of the arm.
Unfortunately, this complex structure is particularly vulnerable to injury.
Whether through acute trauma, repetitive stress, or age-related degeneration, rotator cuff tears are a common orthopedic condition affecting individuals across Singapore and worldwide.
Read more: Best Orthopedic Doctor in JB for Singaporeans
What Exactly Is a Rotator Cuff Tear?
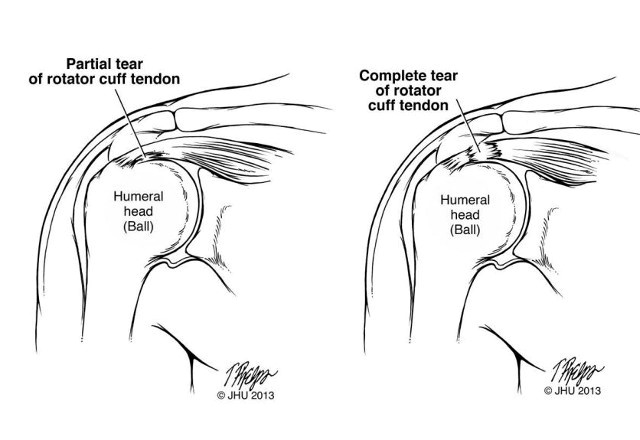
A rotator cuff tear occurs when one or more of the tendons or muscles of the rotator cuff become damaged or torn. These tears can be classified into two main categories:
- Partial Tear: When the tendon is frayed or damaged but not completely severed. The muscle remains partially attached to the bone.
- Complete Tear: When the damage extends through the entire tendon or pulls the tendon completely off the bone, resulting in a hole in the tendon.
Interestingly, not all rotator cuff tears cause symptoms.
Research suggests that only about one-third of rotator cuff tears result in pain, with some individuals being completely unaware of the injury.
This is because pain often localizes in the upper arm rather than the shoulder itself, making self-diagnosis challenging.
You might like: ACL Reconstruction Surgery in Singapore: Causes, Costs
Common Causes of Rotator Cuff Tears
Rotator cuff tears typically occur through two primary mechanisms:
- Acute Traumatic Tears: These result from a sudden injury, such as a fall onto an outstretched arm or lifting a heavy object with a jerking motion. Athletes participating in contact sports or individuals involved in accidents may experience acute tears.
- Degenerative Tears: These develop gradually over time due to repeated stress and wear and tear on the tendon. As we age, the blood supply to the rotator cuff tendons decreases, impairing the body’s natural ability to repair tendon damage. Continuous overhead motions in certain occupations or sports can accelerate this degeneration.
Who Is Most at Risk for Rotator Cuff Injuries?
Certain demographics and lifestyle factors increase the risk of developing rotator cuff problems.
Adults over 40 are particularly susceptible as tendons naturally weaken with age.
Athletes involved in sports requiring repetitive overhead movements such as swimming, tennis, baseball, and volleyball often develop rotator cuff issues over time.
Bodybuilders may experience problems due to heavy lifting and potential overtraining of shoulder muscles.
Additionally, genetic factors play a role, as those with a family history of rotator cuff injuries tend to have increased susceptibility to similar problems.
Related article: Frozen Shoulder Treatment in Singapore: Symptoms, Recovery, Prevention
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Rotator Cuff Tear
While some rotator cuff tears can be asymptomatic, many present with distinctive signs that should prompt medical evaluation.
Patients commonly experience a dull, aching pain in the shoulder, which may worsen when lying on the affected side.
Difficulty and weakness when lifting or rotating the arm is another typical symptom, along with the inability to perform previously manageable tasks, such as reaching behind the back.
Many patients report audible clicking or popping sensations during certain shoulder movements.
Progressive weakness in the shoulder and arm often develops over time, and pain may radiate from the shoulder down the arm.
Sleep disturbances are common, as lying on the affected shoulder can exacerbate discomfort.
Limited range of motion in the shoulder joint becomes increasingly apparent as the condition progresses.
It’s important to note that untreated rotator cuff tears can lead to more serious conditions like frozen shoulder or shoulder arthritis, making early intervention crucial.
You might like: Shoulder Pain in Singapore: Causes, Treatments, Recovery
Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Injuries in Singapore
Singapore’s orthopedic specialists follow a comprehensive approach to diagnosing rotator cuff tears. The process typically includes:
- Detailed Medical History: Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, past injuries, work activities, and recreational pursuits that might contribute to shoulder problems.
- Physical Examination: The physician will assess your shoulder’s range of motion, strength, and specific movements that provoke pain or discomfort.
- Imaging Studies: These are essential for confirming the diagnosis and determining the extent of the injury:
- X-rays: While they don’t directly show rotator cuff tears, they can reveal bone spurs or other structural abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The gold standard for visualizing soft tissue injuries, providing detailed images of the rotator cuff.
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive, dynamic imaging technique that can assess the rotator cuff in motion.
Since shoulder pain can also result from conditions like bone spurs, arthritis, or other joint issues, a thorough diagnostic process is crucial for proper treatment planning.
You might be interested: Tennis Elbow Treatment in Singapore: Causes, Symptoms, Recovery
Non-Surgical Treatment Options in Singapore
For many patients with partial tears (particularly those less than 5mm in size) or mild injuries, conservative management can be effective.
Non-surgical approaches commonly employed in Singapore include:
Rest and Activity Modification
Temporarily limiting activities that exacerbate symptoms, especially overhead movements, can provide relief and allow natural healing processes to begin.
Related article: Golfers Elbow Treatment in Singapore: Causes, Symptoms, Cost
Pain Management
Various pain control strategies may be recommended:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and swelling
- Ice therapy to minimize inflammation
- Heat therapy to improve blood circulation and promote healing
Physical Therapy
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in recovery from rotator cuff injuries. Singapore offers excellent physiotherapy services that focus on:
- Restoring shoulder mobility through gentle stretching exercises
- Strengthening the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles
- Improving scapular (shoulder blade) stability
- Teaching proper body mechanics to prevent re-injury
You might like: Scoliosis Treatment in Singapore: Causes and Symptoms
Corticosteroid Injections
For patients with significant inflammation and pain, corticosteroid injections into the shoulder joint can provide temporary relief.
However, these are typically limited to a few injections per year as excessive use may weaken tendons.
Shockwave Therapy
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) has gained popularity in Singapore as a non-invasive treatment option for rotator cuff injuries. This approach uses acoustic waves that:
- Stimulate blood vessel formation
- Enhance collagen synthesis
- Break down calcified deposits that may accumulate in chronic rotator cuff conditions
- Improve blood circulation in the tendon-bone junctions
ESWT is particularly effective for treating chronic calcific tendonitis in the rotator cuff and is often used as a first-line treatment before considering surgical options.
When Surgery Becomes Necessary
Despite conservative treatment, some rotator cuff injuries require surgical intervention. Surgery is typically recommended in Singapore when:
- The tear is large (more than 3cm) or involves multiple tendons
- The patient experiences persistent pain despite non-surgical management
- There is significant weakness affecting daily activities
- The tear resulted from an acute, traumatic injury, especially in younger, active individuals
- The patient has specific occupational demands requiring full shoulder function
Surgical Options for Rotator Cuff Repair in Singapore
Singapore’s orthopedic surgeons are highly skilled in various surgical techniques for rotator cuff repair, with the appropriate approach depending on multiple factors including tear size, location, patient age, and activity level.
The city-state’s advanced healthcare system offers access to the full spectrum of surgical options, from minimally invasive techniques to complex reconstructive procedures.
Arthroscopic Repair
Arthroscopic repair has become the gold standard for many rotator cuff repairs in Singapore due to its minimally invasive nature and excellent outcomes.
This technique is performed through small incisions, each less than 1 centimeter in length, which significantly reduces tissue trauma compared to traditional open approaches.
During the procedure, a tiny camera called an arthroscope provides clear visualization of the shoulder joint interior, while specialized instruments are used to repair the torn tendon with precision.
This approach results in less post-operative pain and faster recovery times compared to more invasive techniques.
Arthroscopic repair is particularly suitable for tears smaller than 3 centimeters and requires less tissue disruption than open surgery, making it an ideal choice for many patients.
Mini-Open Repair
The mini-open repair technique represents a hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both arthroscopic and open surgical methods.
The procedure begins with initial assessment and preparation performed arthroscopically, followed by creation of a small incision measuring 3-5 centimeters that allows direct access to repair the tear.
This approach offers direct visualization of the repair site while minimizing tissue damage and scarring.
Mini-open repair is well-suited for more complex tears or situations where additional procedures are needed during the same surgery.
The technique provides an excellent compromise between optimal visualization and tissue preservation, making it valuable for intermediate-complexity cases.
Open Surgical Repair
Traditional open surgery remains necessary in certain situations where less invasive approaches are insufficient.
This technique is typically used for large, complex tears that require extensive reconstruction and cannot be adequately addressed through smaller incisions.
Open repair provides complete visualization of the entire tear and surrounding anatomy, allowing surgeons to employ more robust repair techniques when needed.
This approach is required when tendon quality is poor, when previous repairs have failed and revision surgery is needed, or when tendon grafting becomes necessary to restore function.
Despite being more invasive, open repair remains an essential option for the most challenging cases.
Tendon Transfer
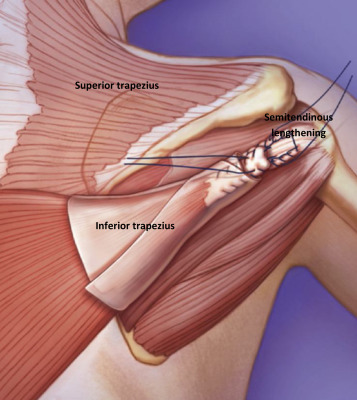
When a torn rotator cuff tendon is too severely damaged for direct repair, tendon transfer procedures offer an alternative solution.
During this procedure, a nearby healthy tendon, often from the latissimus dorsi or pectoralis major muscle, is surgically transferred to replace the function of the damaged rotator cuff tendon.
This technique provides an alternative mechanism for shoulder function when the original tendon cannot be salvaged.
Tendon transfer is typically reserved for irreparable tears, especially in younger patients who require maintained shoulder function for work or recreational activities.
These procedures require specialized surgical expertise and careful patient selection to achieve optimal outcomes.
Reverse Shoulder Replacement
In cases involving massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears combined with arthritis, a condition known as cuff tear arthropathy, reverse shoulder replacement offers a definitive solution.
This innovative procedure reverses the normal ball-and-socket anatomy of the shoulder joint.
The ball component is attached to the shoulder blade (scapula), while the socket component is placed on the upper arm bone (humerus).
This anatomical reversal enables the deltoid muscle to compensate for the non-functioning rotator cuff, restoring functional movement to the shoulder.
Reverse shoulder replacement is primarily reserved for older patients who have both significant arthritis and massive rotator cuff tears that cannot be repaired through other means.
Financial Considerations: Medisave and Insurance Coverage
For Singaporeans and Permanent Residents, rotator cuff repair procedures may be eligible for Medisave claims. The exact amount covered depends on the complexity of the procedure and the surgical approach used.
Integrated Shield Plans can provide additional coverage, potentially reducing out-of-pocket expenses for private healthcare services. Patients are encouraged to consult with their insurance providers and the hospital’s financial counselors to understand their coverage options.
The Recovery Journey After Rotator Cuff Repair
Recovery from rotator cuff surgery is a gradual process that requires patience and commitment. The typical timeline in Singapore includes:
Immediate Post-operative Phase (0-6 weeks)
- Wearing a sling to immobilize and protect the repaired tendon
- Pain management through prescribed medications
- Limited movement to prevent disruption of the repair
- Initial gentle pendulum exercises as directed by the physiotherapist
Early Rehabilitation Phase (6-12 weeks)
- Progressive removal of the sling
- Passive range of motion exercises guided by a physiotherapist
- Gradual introduction of active-assisted movements
- Focus on regaining mobility without stressing the repair
Intermediate Rehabilitation Phase (3-6 months)
- Active strengthening exercises
- Functional training specific to daily activities
- Sport or occupation-specific rehabilitation as appropriate
- Continued monitoring of healing through follow-up appointments
Advanced Rehabilitation and Return to Activity (6-12 months)
- Progressive resistance training
- Return to full daily activities
- Sport-specific training for athletes
- Maintenance exercises to prevent re-injury
It’s important to note that full recovery can take up to a year, with professional athletes potentially requiring even longer to return to pre-injury performance levels. Studies indicate that approximately 50% of professional athletes with rotator cuff repairs return to their previous competitive level.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, rotator cuff repair carries certain risks.
In Singapore, these complications are rare when the surgery is performed by experienced orthopedic surgeons, but patients should be aware of potential issues.
Infection at the surgical site can occur, though strict sterile techniques minimize this risk. Some patients develop stiffness or frozen shoulder, particularly if rehabilitation is delayed or inadequate.
Re-tear of the repaired tendon is a concern, especially in larger tears and older patients.
Nerve or blood vessel damage is uncommon but possible during the procedure. Some individuals experience persistent pain or weakness despite technically successful repairs.
Reactions to anesthesia, while rare, can occur in susceptible individuals. In open repairs, there’s a small risk of deltoid muscle detachment affecting shoulder function.
The risk of re-tearing depends on several factors, including age, tear size, and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Even with some re-tears, many patients still experience significant pain relief and functional improvement.
Emerging Technologies in Rotator Cuff Treatment
Singapore is at the forefront of adopting innovative approaches to rotator cuff treatment, incorporating cutting-edge technologies and techniques that improve patient outcomes and accelerate recovery times.
Singapore is at the forefront of adopting innovative approaches to rotator cuff treatment. Some emerging technologies include:
Biological Augmentation
Modern rotator cuff treatment increasingly utilizes biological enhancement techniques to optimize healing and improve long-term outcomes.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injections concentrate the patient’s own healing factors to enhance tissue repair processes at the injury site.
Stem cell therapy represents an advanced approach that promotes tissue regeneration by introducing cells capable of differentiating into the specific tissue types needed for tendon repair.
Growth factor applications are being used to strengthen the critical tendon-bone interface, which is often the weakest point in rotator cuff healing and the most common site of re-injury.
These biological augmentation techniques work by harnessing the body’s natural healing mechanisms and amplifying them to achieve better repair quality.
Advanced Imaging and Surgical Planning
Technological advances in imaging and surgical planning have revolutionized the precision and effectiveness of rotator cuff procedures.
Three-dimensional modeling allows surgeons to create detailed pre-operative plans by visualizing the exact anatomy and pathology before entering the operating room, leading to more targeted and efficient surgical interventions.
Computer-assisted surgery provides improved accuracy during procedures by offering real-time guidance and precise instrument positioning.
Enhanced visualization techniques during arthroscopy utilize high-definition cameras and specialized lighting systems to provide surgeons with clearer, more detailed views of the surgical field, enabling more precise tissue handling and repair techniques.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation Technologies
Recovery and rehabilitation following rotator cuff surgery have been enhanced through the integration of advanced therapeutic technologies.
Shockwave therapy utilizes focused acoustic waves to stimulate healing processes and reduce pain during the post-surgical recovery phase, potentially accelerating the return of function and strength.
INDIBA® Activ therapy represents a non-invasive approach that uses radiofrequency energy to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation at the cellular level.
Advanced motion analysis systems allow rehabilitation specialists to create optimized rehabilitation protocols by precisely measuring movement patterns and identifying specific deficits that need to be addressed during the recovery process.
These technological advances collectively contribute to improved surgical outcomes, faster recovery times, and reduced risk of complications for patients undergoing rotator cuff treatment in Singapore’s advanced healthcare system.
Preventing Rotator Cuff Injuries
While not all rotator cuff tears can be prevented, several strategies can reduce the risk.
Proper warm-up before physical activities is essential to prepare the shoulder muscles for exertion.
Developing balanced strength in all shoulder muscles helps maintain proper biomechanics and joint stability.
Using correct technique during sports and occupational tasks reduces abnormal stress on the tendons.
It’s advisable to avoid repetitive overhead activities when fatigued, as muscle fatigue can lead to poor mechanics and increased tendon strain.
Taking regular breaks during prolonged overhead work allows tissues to recover from stress.
Maintaining good posture and shoulder alignment during daily activities minimizes unnecessary strain on the rotator cuff.
Perhaps most importantly, paying prompt attention to minor shoulder discomfort before it progresses can prevent small issues from developing into serious problems.
Choosing the Right Specialist in Singapore
Singapore boasts world-class orthopedic care for rotator cuff injuries. When selecting a specialist, consider:
- Experience and specialization in shoulder surgery
- Proficiency in both arthroscopic and open techniques
- Access to comprehensive rehabilitation services
- Hospital accreditation and facilities
- Patient reviews and testimonials
- Communication style and willingness to answer questions
FAQ Section
What is the success rate of rotator cuff repair surgery in Singapore?
Success rates for rotator cuff repairs in Singapore are generally high, with most patients experiencing significant pain relief and improved function.
Complete healing of the tendon, confirmed by MRI, occurs in approximately 70-90% of cases, depending on tear size, patient age, and surgical technique.
Even in cases where the tendon does not completely heal, many patients still report substantial symptom improvement and better quality of life.
How long does rotator cuff repair surgery take?
A typical rotator cuff repair procedure in Singapore takes between 1 to 2 hours to complete.
This duration can vary based on the complexity of the tear, the surgical technique used, and whether additional procedures (such as removal of bone spurs) are performed simultaneously.
Arthroscopic procedures may take longer than open surgery due to the technical precision required.
Will I need to wear a sling after surgery, and for how long?
Yes, patients are typically required to wear a protective sling for 4 to 6 weeks following rotator cuff repair surgery.
The exact duration depends on the size of the tear and the surgeon’s assessment of the repair’s stability.
During this period, you may be allowed to remove the sling briefly for hygiene purposes and certain prescribed exercises, but strict adherence to wearing the sling is crucial for proper healing.
When can I return to work after rotator cuff surgery?
Return to work timelines vary significantly based on occupation demands. Patients with sedentary desk jobs may return to work within 2 to 4 weeks, often while still wearing the sling.
Those with physically demanding jobs involving lifting, overhead work, or manual labor typically require 3 to 6 months before resuming full duties.
Your surgeon and physiotherapist will provide specific guidance based on your individual recovery progress and occupational requirements.
Can a rotator cuff tear heal without surgery?
Small partial tears (less than 5mm) often heal without surgical intervention through appropriate conservative treatment.
This includes a combination of rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and possible corticosteroid injections.
However, larger tears, complete tears, or tears that have displaced significantly typically do not heal well without surgical repair.
The natural healing capacity of tendons is limited by their relatively poor blood supply, especially in older adults.
What are the signs that my rotator cuff injury requires surgical treatment?
Indicators that surgery might be necessary include persistent pain despite 3-6 months of conservative treatment, significant weakness affecting daily activities, tears larger than 3cm confirmed by imaging studies, acute tears from traumatic injuries (especially in younger patients), night pain that interrupts sleep despite medication, and progressive worsening of symptoms over time.
Additionally, if your occupation or recreational activities demand full shoulder strength and mobility, surgery may be recommended sooner.
How long will I need physiotherapy after rotator cuff surgery?
Most patients require supervised physiotherapy for 3 to 6 months following rotator cuff repair. Initially, sessions may be scheduled 2-3 times weekly, gradually decreasing in frequency as you progress.
However, a home exercise program typically continues for 6 to 12 months post-surgery.
The duration and intensity of physiotherapy depend on factors such as the extent of the repair, your baseline level of function, and your compliance with the rehabilitation program.
What can I do to prevent re-tearing my rotator cuff after surgery?
To minimize the risk of re-injury, follow your surgeon’s and physiotherapist’s instructions carefully during recovery.
Avoid premature return to heavy lifting or overhead activities. Maintain the strength and flexibility exercises recommended by your physiotherapist even after formal rehabilitation ends.
Use proper body mechanics during daily activities and sports. Consider modifying high-risk activities that place excessive stress on the shoulder.
Maintain overall fitness and healthy body weight to reduce joint stress, and address any early signs of shoulder discomfort promptly.
Is Shockwave Therapy effective for rotator cuff injuries?
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) has shown promising results for certain rotator cuff conditions, particularly calcific tendinitis.
Research indicates it can effectively break down calcium deposits, improve blood circulation to the affected area, and stimulate the body’s natural healing processes.
While it may not replace surgery for complete tears, it can be an effective non-invasive option for partial tears and tendinopathy.
In Singapore, ESWT is often integrated into comprehensive treatment plans, either as a primary treatment or as an adjunct to enhance post-surgical recovery.
Can I claim Medisave for rotator cuff surgery in Singapore?
Yes, rotator cuff repair surgery is generally claimable under Medisave in Singapore.
The exact amount covered depends on the surgical procedure’s complexity and the approach used (arthroscopic versus open).
As of 2023, patients can typically claim between S$5,000 to S$7,550 from their Medisave Account for such procedures.
For more specific information regarding your coverage, it’s advisable to consult with your healthcare provider’s financial counseling service or the Central Provident Fund Board directly.
What is the difference between arthroscopic and open rotator cuff repair?
Arthroscopic repair uses small incisions (typically 5-10mm) through which a camera and specialized instruments are inserted to repair the tear, resulting in less pain, reduced risk of infection, minimal scarring, and faster initial recovery.
Open repair involves a larger incision (approximately 8-10cm) that allows direct visualization and access to the rotator cuff, which may be necessary for complex or large tears. Mini-open repair combines elements of both techniques.
The choice between these approaches depends on tear characteristics, surgeon expertise, and patient factors, with the goal of achieving the most durable repair with the least invasive approach possible.
What lifestyle modifications should I make after recovering from rotator cuff surgery?
After recovery, consider adopting these long-term lifestyle adjustments: maintain regular shoulder strengthening exercises focusing on rotator cuff and scapular stabilizers; practice proper lifting techniques (using legs rather than arms for heavy items); avoid prolonged overhead activities when possible; take frequent breaks during activities that stress the shoulders; maintain good posture to reduce abnormal shoulder stress; consider ergonomic modifications at work and home; stay physically active with shoulder-friendly exercises like walking, stationary cycling, or swimming (once fully healed); and address any new shoulder symptoms promptly before they worsen.
Conclusion
Rotator cuff tears represent a significant challenge for many Singaporeans, particularly those engaged in physically demanding occupations or sports.
Through a combination of advanced diagnostic techniques, comprehensive non-surgical approaches, cutting-edge surgical interventions, and dedicated rehabilitation programs, patients in Singapore have access to excellent care pathways for this common shoulder condition.
The key to successful outcomes lies in early diagnosis, appropriate treatment selection, and committed participation in the rehabilitation process.
Whether through conservative management or surgical repair, the goal remains consistent: to restore shoulder function, alleviate pain, and enable patients to return to their desired activities with confidence and comfort.
For those facing rotator cuff challenges, Singapore’s healthcare system offers world-class expertise and a range of treatment options tailored to individual needs, ensuring the best possible path to recovery.

