Hip replacement surgery, considered one of the most successful orthopedic procedures of the century, has transformed countless lives by restoring mobility and eliminating chronic pain.
If you’re considering this procedure in Singapore, this comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know—from understanding what the surgery entails to recovery and beyond.
Read more: Which Orthopedic Doctor in Singapore Should You Consider?
Understanding Hip Replacement Surgery
What is Total Hip Replacement?
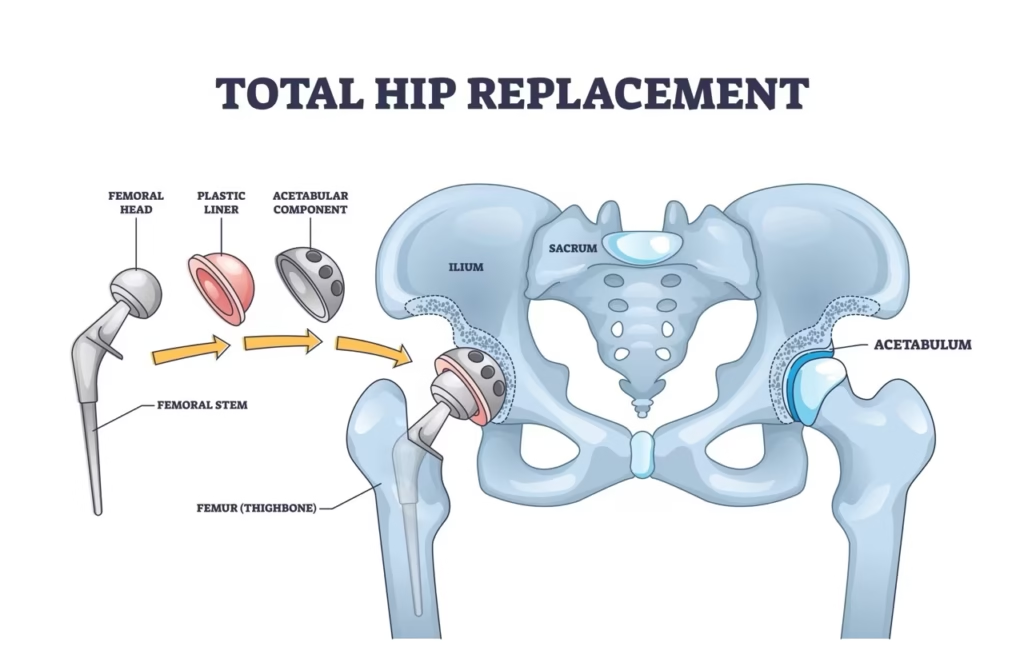
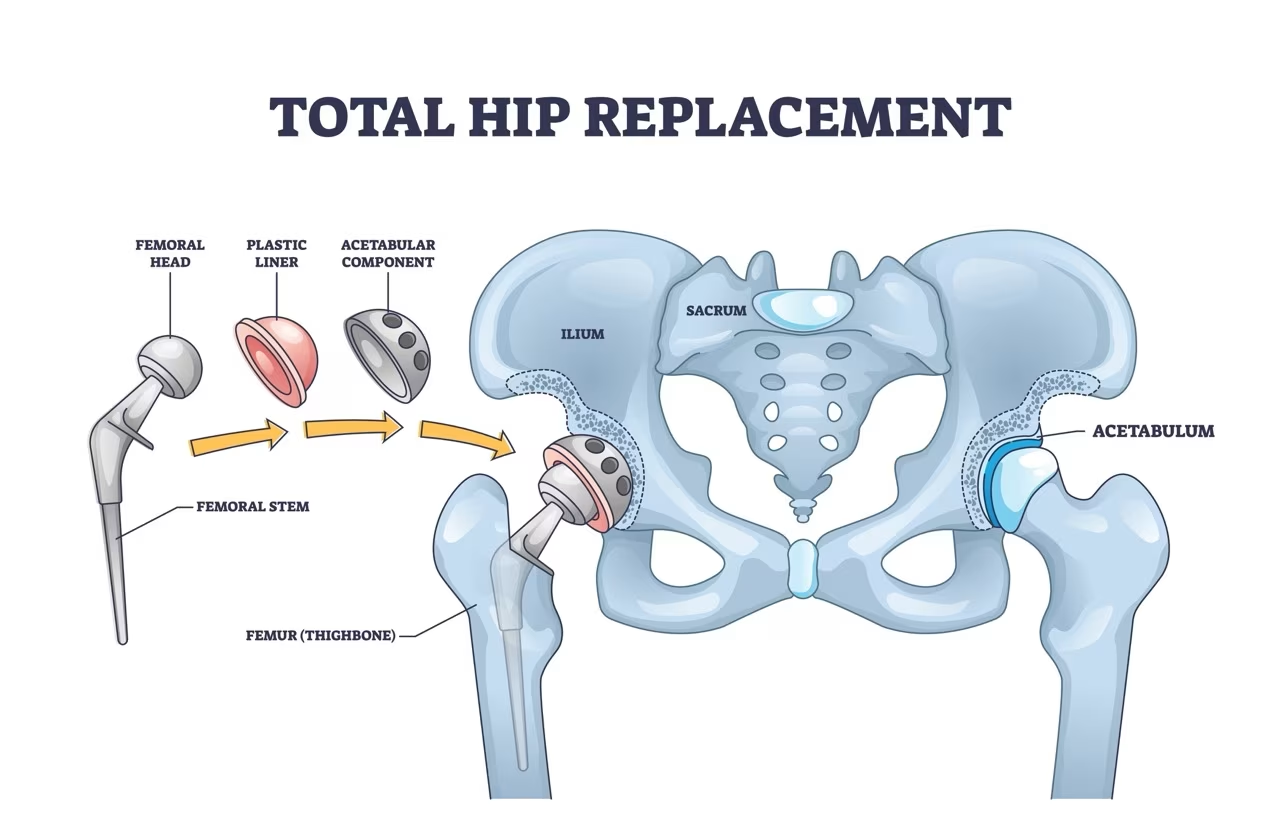
Total hip replacement, also known as total hip arthroplasty (THA), is a surgical procedure that replaces both the femoral head (the ball) and the acetabulum (the socket) of a damaged hip joint with artificial components.
During the procedure, your surgeon removes the damaged or diseased parts of your hip joint and replaces them with an artificial femoral component (ball) typically made of strong metal or ceramic and an artificial acetabular component (socket) usually made of durable, wear-resistant polyethylene, which may be backed with metal.
This artificial joint is designed to glide smoothly, replicating the natural movement of your hip.
With proper care and modern materials, hip implants can last around 15-20 years or even longer.
You might like: Total Knee Replacement Surgery in Singapore
The Hip Joint Anatomy
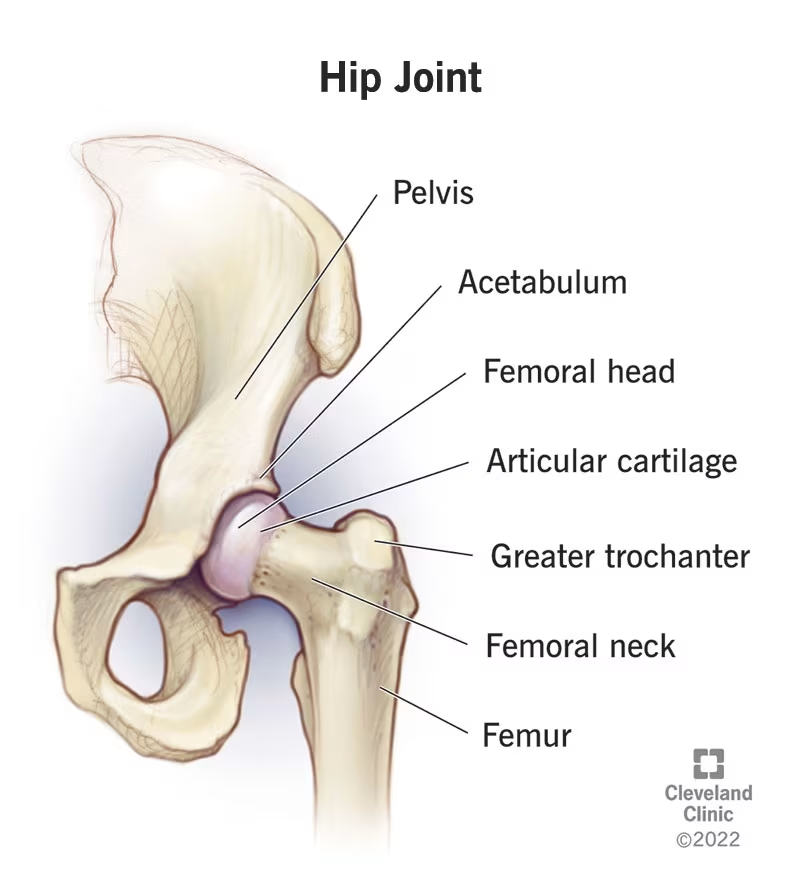
The hip is a classic ball-and-socket joint where the rounded head of the femur (thigh bone) fits into the acetabulum (a cup-shaped socket in the pelvis).
Muscles, cartilage, and ligaments surround this joint, allowing for smooth, pain-free movement.
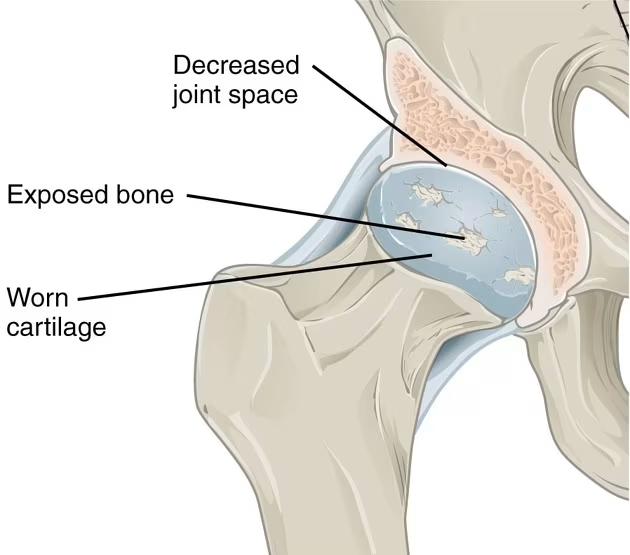
In conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, the protective cartilage becomes worn out and can no longer serve as an effective cushion.
When these bones rub against each other, the result is often excruciating pain and stiffness.
You might be interested: ACL Reconstruction Surgery in Singapore: Causes, Costs
When Is Hip Replacement Surgery Needed?
Hip replacement is typically considered when hip pain and stiffness significantly affect daily activities such as walking, standing, or sitting; when pain persists despite conservative treatments like physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and injections; when X-rays or MRI scans show severe joint damage; or when quality of life is significantly reduced due to hip problems.
Read more: Osteoarthritis Treatment in Singapore: Symptoms, Prevention
Common Conditions Leading to Hip Replacement
Several conditions may contribute to the need for hip replacement surgery.
Osteoarthritis is the most common reason for hip replacement, where cartilage breaks down, leading to bone-on-bone contact, pain, swelling, and deformity.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes severe pain, stiffness, and swelling affecting mobility.
This autoimmune disease can affect many joints and body organs and sometimes occurs in younger patients.
Osteonecrosis (avascular necrosis) is a condition where blood supply to the femoral head is disrupted, resulting in bone death and potential joint collapse or deformity.
Severe hip fractures affecting the hip joint that do not heal properly may require replacement.
Post-traumatic arthritis develops after an injury such as a fracture or dislocation.
Related article: Neck Pain in Singapore: Causes, Treatments, Prevention
Types of Hip Replacement Surgeries
There are several types of hip replacement procedures, each tailored to the patient’s specific condition and needs:
Total Hip Replacement (THR)
This is the most common type, where the entire hip joint—both the ball and socket—is replaced with artificial components. THR can significantly improve quality of life for patients with severe hip damage.
Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty)
Only the femoral head (ball) is replaced while preserving the natural socket.
This is typically performed for certain hip fractures rather than for arthritis.
Hip Resurfacing
A less invasive alternative where the femoral head is reshaped and capped with a metal covering instead of being completely replaced.
This approach is generally considered for younger, more active patients with strong, healthy bones.
This might help: Low Back Pain in Singapore: Causes, Prevention and Treatment
Revision Hip Replacement
This procedure is performed when a previous hip replacement has failed due to infection, implant wear, or dislocation, or when artificial implants have worn out over time.
Robotic Hip Replacement
Similar to traditional hip replacement but performed with the assistance of a robotic arm for greater precision. This method often allows for a shorter recovery time.
You might be interested: Scoliosis Treatment in Singapore: Causes and Symptoms
Surgical Approaches to Hip Replacement
There are three main surgical approaches your surgeon may use to access your hip joint:
Direct Anterior Approach (DAA)
This minimally invasive technique allows the surgeon to reach the hip joint from the front by going between muscles rather than cutting through them. The patient lies on their back during the procedure.
Benefits of DAA include:
- Potentially faster recovery time
- Less post-operative pain
- Reduced muscle damage
- Smaller incision and less scarring
- Improved hip stability
- Better facilitation of imaging for accurate component positioning
Posterior Approach
This traditional approach accesses the hip joint from the back of the hip.
The posterior approach provides excellent visibility of the hip joint and easier placement of artificial components. It’s also more familiar to many surgeons. Potential drawbacks include greater muscle disruption, potentially longer recovery time, and a slightly higher risk of post-surgery dislocation.
Lateral Approach
Accesses the hip joint from the side.
Comparison: Anterior vs. Posterior Approach
| Feature | Anterior Approach | Posterior Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Access Point | From the front | From the back |
| Muscle Impact | Less muscle disruption | Greater muscle disruption |
| Recovery Time | Potentially faster | May be longer |
| Dislocation Risk | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Technical Difficulty | More technically demanding | Less technically demanding |
| Visibility | May be more challenging | Excellent visibility |
| Ideal For | Patients seeking faster recovery | Complex hip conditions requiring direct joint view |
The Hip Replacement Procedure
Before Surgery: Preparation
Proper preparation for hip replacement surgery includes a thorough medical evaluation with blood tests and imaging to ensure you’re fit for surgery. If you’re overweight, losing weight may be recommended to reduce strain on your new joint. Pre-operative physiotherapy to build muscle strength around the hip is often beneficial.
Your doctor will review your medications, as some (particularly blood thinners and certain supplements) may need to be stopped around two weeks before surgery. You should also prepare your home by setting up a recovery-friendly environment with mobility aids like walkers and handrails, and arrange for someone to help during the initial recovery period.
Hospital Admission
You may be admitted either a day before surgery or on the day of the procedure. If you have additional medical issues, earlier admission might be necessary.
Important pre-surgery preparations include:
- Bowel preparation (if advised)
- No smoking (especially the week before surgery)
- Pre-operative exercises as taught by your physiotherapist
- No food or drink after midnight before surgery
- Showering with antibacterial soap
During Surgery
The surgical procedure begins with anesthesia – either general anesthesia (you’ll be asleep) or spinal anesthesia (you’ll be numb from the waist down). The surgeon makes an incision over the hip, removes damaged bone and cartilage, then attaches artificial components to the thigh bone and hip socket. Depending on your condition, components may be secured with or without bone cement. Finally, the prosthetics are aligned properly, and the incision is closed.
After Surgery: Recovery Room
After the operation, you’ll be taken to a recovery room where:
- Your blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate will be monitored
- Pain management will begin (possibly using Patient-Controlled Analgesia or epidural catheter)
- When stable, you’ll be transferred to a High Dependency Room or ward
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
Hospital Care
- Nurses will regularly check your vital signs, bandages, and leg circulation
- An abduction pillow may be used to keep your hip in neutral position
- Pain medication will be administered as needed
- You’ll gradually progress from liquid to solid food
Wound Care
- Your wound will be covered with a dressing, which will be changed to a lighter one within 48 hours
- One or two drainage tubes may be inserted near the wound to drain excess fluid
- Stitches or clips are typically removed 10-14 days after surgery
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation starts almost immediately after surgery:
- Your physiotherapist will develop a hip exercise program
- You’ll begin walking with assistance (usually a walking frame) within a few days
- Exercise will include gym sessions and progressing from frame to crutches
- Before discharge, you’ll practice walking up and down stairs
- An occupational therapist may help with daily living modifications
Length of Hospital Stay
The average length of stay is 10-14 days, though this varies by individual and surgical approach.
With the Direct Anterior Approach, hospital stays may be shorter.
Life After Hip Replacement
Recovery Timeline
Most patients can expect to use walking aids for several weeks, to drive after about six weeks, to avoid flying long-haul for at least six weeks (due to blood clot risk), to return to sedentary jobs within 6-8 weeks, and to return to more physically demanding jobs after 3-6 months.
Long-term Activity Guidelines
To protect your new hip, avoid sitting on low chairs and keep your knees apart without crossing your legs when seated. Use a pillow between your legs when sleeping on your side (for at least 3 months) and avoid long baths and squatting toilets.
Consider installing handrails in the bathroom, use helping hands or tongs to pick up items from the floor, and avoid high-impact activities for at least 6-12 weeks.
Risks and Complications
While hip replacement is generally safe, potential risks include blood clots (particularly in leg veins due to limited mobility after surgery), infection at the incision site or in deeper tissue near the new hip, nerve or blood vessel injury from swelling or pressure around the implant, dislocation (the ball of the new joint may dislocate from its socket if positioned incorrectly), implant issues (the prosthetic may loosen, wear out, or cause instability over time), and leg length discrepancy (the operated leg may be slightly longer or shorter than the other).
Patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus, diabetes, or hemophilia may face a higher risk of complications.
Cost of Hip Replacement in Singapore
The cost of hip replacement surgery in Singapore varies widely:
- In public hospitals, costs start from approximately S$14,000 for a single hip
- In private hospitals, costs typically range from S$35,000 to S$45,000, inclusive of doctors’ fees
Final costs depend on several factors:
- Type of replacement (total or partial)
- Hospital choice and ward type
- Surgeon’s expertise
- Type of implant used
- Pre-operative tests
- Post-operative care and rehabilitation services
Advanced Technology in Hip Replacement
Modern Implant Materials
Today’s hip implants benefit from advanced materials including ceramic components (like Biolox®), highly cross-linked polyethylene, and advanced surface technologies for increased longevity.
Robotic Surgery (Makoplasty®)
This technology enhances surgical precision:
- Patients undergo a pre-operative CT scan
- Data is merged with real-time anatomical landmarks
- A robotic arm assists the surgeon in performing the procedure with pinpoint accuracy
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do hip implants last?
Hip implants typically last between 15-20 years, though this varies depending on factors like age, activity level, weight, and overall health.
Modern materials and techniques continue to improve longevity.
Am I too old for hip replacement?
Age is not a limiting factor if you’re medically fit. Many older patients undergo successful hip replacements and experience significant improvements in mobility and quality of life.
Can hip replacement be performed as an outpatient procedure?
For suitable candidates, hip replacement can be done as an outpatient procedure, allowing return home the same day.
This depends on overall health, home support, and the specific surgical technique used.
How painful is hip replacement recovery?
Pain levels vary between individuals, but post-surgical pain is well-managed with medications.
Most patients find that pain improves significantly after the initial healing period and is much less than the arthritic pain they experienced before surgery.
Can I have both hips replaced at the same time?
Bilateral (simultaneous) hip replacement is possible but not commonly recommended due to increased risks and longer recovery time. This option is typically only considered for relatively healthy individuals with severe bilateral hip joint disease.
When can I drive after hip replacement?
Most patients can resume driving about six weeks after surgery, once hip mobility and strength have sufficiently recovered.
When can I fly after hip replacement?
It’s generally advised to avoid long-haul flights for at least six weeks after surgery to reduce the risk of blood clots.
Will I set off airport metal detectors with my new hip?
Modern hip implants may trigger metal detectors. It’s useful to inform security personnel about your hip replacement before screening.
What activities should I avoid after hip replacement?
High-impact activities like running, jumping, and contact sports may need to be limited or avoided. Your surgeon will provide specific guidance based on your individual case and implant type.
Can I postpone hip replacement if recommended by my doctor?
Delaying necessary hip replacement can lead to increased pain, further joint deterioration, and potentially more complex surgery later. Always discuss concerns and alternatives with your surgeon.
What is the success rate of hip replacement surgery?
Hip replacement is considered one of the most successful orthopedic procedures, with success rates exceeding 95%. Most patients experience significant pain relief and improved function.
Conclusion
Hip replacement surgery in Singapore offers excellent outcomes for those suffering from debilitating hip conditions. With advanced techniques like the Direct Anterior Approach and robotic assistance, patients can expect reduced recovery times and improved long-term results.
If you’re considering hip replacement, consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to determine if the procedure is right for you, which approach would be most beneficial, and to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Remember that successful outcomes depend not only on the surgical procedure itself but also on your commitment to the rehabilitation process and following post-operative guidelines.