Introduction
Colorectal cancer is the most common cancer in Singapore, ranking as the number one cancer affecting men and the second most common cancer affecting women.
With five Singaporeans diagnosed daily and two succumbing to the disease, early detection through colonoscopy screening is vital.
Colonoscopy is the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening and prevention.
Unlike other screening methods, it not only detects abnormalities but also allows for immediate intervention, such as polyp removal, potentially preventing cancer development before it begins.
What is a Colonoscopy?

A colonoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that examines the lining of your colon (large intestine) and rectum.
The procedure uses a colonoscope—a long, thin, flexible tube with a small camera and light attached at the end—which is gently inserted through the anus into the rectum and colon.
The camera transmits real-time images to a monitor, allowing the doctor to examine the entire colon lining. The colonoscope is equipped with tools that enable doctors to:
- Take tissue samples (biopsies) for further examination
- Remove abnormal growths such as polyps
- Treat bleeding or other abnormalities
A typical colonoscopy takes about 20-40 minutes to complete and is usually performed as a day surgery procedure under sedation.
Read more: Health Screening in Singapore
Advancements in Colonoscopy Technology in Singapore
Singapore has been at the forefront of adopting advanced colonoscopy technologies. Since 2021, Raffles Hospital became the first private hospital in Singapore to implement AI in colonoscopy with the GI Genius module.
The GI Genius uses machine learning technology to enhance the accuracy of colonoscopy procedures.
During the examination, it processes each frame to highlight potential polyps and tumors, particularly those that might be missed by the human eye.
This technology is especially valuable for identifying small polyps (a few millimeters in size) that, although typically benign initially, could potentially become cancerous if left untreated for years.
This AI-assisted colonoscopy supports doctors in:
- Screening colonoscopy
- Surveillance colonoscopy
- Diagnostic colonoscopy (to evaluate symptoms like bowel habit changes and rectal bleeding)
The technology facilitates doctors’ decision-making without adding any additional risk to the procedure.
Who Should Get a Colonoscopy?
You should consider getting a colonoscopy if:
You show symptoms of colorectal cancer such as:
- A positive result for your Faecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) or Faecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
- Abdominal pain or bloating
- Change in bowel habits
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation
- Blood in stool
- Unexplained weight loss
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation after passing motion
- Pencil-thin stools
- Persistent ulcers or infection around the anus
- Mucus-like discharge from the anus
- Iron deficiency anemia
You might be interested: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment in Singapore
You have risk factors for colorectal cancer:
- Age 50 years or above
- Family history of colorectal cancer or polyps
- Personal history of colorectal diseases or polyps
- Low-fiber and high-fat diet
- Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking
- Previous radiation therapy in the abdomen or pelvis
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Frequency Recommendations for Colonoscopy
The recommended frequency for colonoscopy depends on your risk profile:
Low-risk individuals:
- First colonoscopy at age 50
- Repeat every 10 years if results are normal
High-risk individuals:
- Those with a family history of colorectal cancer or polyps
- Those with previous polyps or colorectal cancer
- Those with inflammatory bowel disease
- Begin screening earlier (typically 10 years before the age when a family member was diagnosed)
- Repeat every 5 years
For example, if your father was diagnosed with colon cancer at age 55, you should have your first colonoscopy at age 45.
Related article: Functional Dyspepsia Treatment in Singapore
Preparing for a Colonoscopy
Proper preparation is crucial for a successful colonoscopy. The colon must be completely clear of solid waste to allow the doctor to see the entire lining clearly.
Bowel Preparation
- Dietary Adjustments:
- A few days before: Avoid high-fiber foods, seeds, nuts, and whole grains
- The day before: Clear liquid diet (water, clear broth, apple juice, clear sodas, tea without milk)
- Avoid red or purple liquids as they can be confused with blood during the examination
- Laxative Regimen:
- You will be prescribed strong laxatives to clean out your colon
- This typically involves drinking a special solution that induces diarrhea
- Complete all the prescribed preparation as instructed
- If your colon is not completely clear, the procedure may need to be rescheduled
- Fasting:
- No food or drink for at least 6 hours before the procedure
- You may drink clear fluids up to 2 hours before (check with your doctor)
You might be interested: The Ultimate Guide to Losing Weight in Singapore
Medication Considerations
Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, especially:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Blood thinners like aspirin, warfarin (Coumadin), or heparin
- Diabetes medications
- Any prescription or over-the-counter medications
Your doctor may advise you to adjust or temporarily stop certain medications before the procedure.
Read more: Cryotherapy Treatment Singapore: Is It Good For Me?
Special Considerations
Pregnant women or patients with kidney, heart, or liver problems may require special monitoring during bowel preparation due to the risk of electrolyte imbalance and dehydration.
You might want to read: Celiac Disease Treatment in Singapore
The Colonoscopy Procedure: What to Expect

Before the Procedure
- Arrival and Registration:
- Arrive at the endoscopy center as instructed
- Complete necessary paperwork
- Change into a hospital gown
- Pre-Procedure Assessment:
- Medical staff will check your vital signs
- Review your medical history and medications
- Insert an intravenous line in your hand or arm for sedation
You might be interested: The Comprehensive Guide to Liposuction in Singapore
During the Procedure
- Sedation:
- You will receive sedation intravenously to help you relax and minimize discomfort
- Most patients doze off and have little to no recollection of the procedure
- Positioning:
- You will lie on your left side with your knees bent
- This position facilitates the insertion of the colonoscope
- Colonoscope Insertion:
- The doctor gently inserts the colonoscope through the anus
- Air or carbon dioxide is introduced to inflate the colon for better visibility
- You may feel some pressure, bloating, or cramping, but the sedation helps minimize discomfort
- Examination:
- The colonoscope is slowly advanced through the entire colon
- The camera transmits images to a monitor for the doctor to examine
- If polyps or suspicious tissues are found, they can be removed or biopsied using tools passed through the colonoscope
After the Procedure
- Recovery:
- You will be monitored in a recovery area until the sedation effects begin to wear off
- This typically takes about 30-60 minutes
- Light refreshments may be provided once you’re fully awake
- Results Discussion:
- Your doctor will discuss the preliminary findings with you
- If biopsies were taken, you’ll be informed when to expect results
- Follow-up appointments will be scheduled if necessary
- Discharge:
- You must have someone accompany you home
- You should not drive, operate machinery, or make important decisions for 24 hours after sedation
- A medical certificate can be provided if needed
Recovery and Post-Procedure Care
Immediate Effects
- Some bloating or gas pain is normal and should subside within 24 hours
- Walking can help relieve this discomfort
- You may pass gas frequently as your body expels the air introduced during the procedure
- You can resume your normal diet unless instructed otherwise
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Fever
- Rectal bleeding that continues or increases
- Vomiting
- Dizziness or weakness
Understanding Your Colonoscopy Results
Normal Results
If no abnormalities are found, your colon is considered normal. However, this doesn’t guarantee you’ll never develop colorectal cancer, which is why regular screening is important according to the recommended intervals.
Abnormal Results
If polyps or other abnormalities are detected:
- Most polyps can be removed during the colonoscopy
- Tissue samples (biopsies) will be sent to a laboratory for analysis
- Your doctor will discuss the findings and recommend appropriate follow-up care or treatment
- More frequent colonoscopies may be recommended for monitoring
Risks and Complications of Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is generally very safe, especially when performed by experienced specialists. However, as with any medical procedure, there are some risks:
- Bleeding: Occurs in less than 1% of cases, especially after polyp removal
- Perforation (tear in the colon wall): Extremely rare, occurring in about 1 in 1,000 cases
- Adverse reaction to sedation
- Infection: Very rare
If you experience severe abdominal pain, fever, rectal bleeding, or other concerning symptoms after the procedure, seek immediate medical attention.
Alternatives to Colonoscopy
While colonoscopy remains the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening, alternatives exist:
CT Colonography (Virtual Colonoscopy)
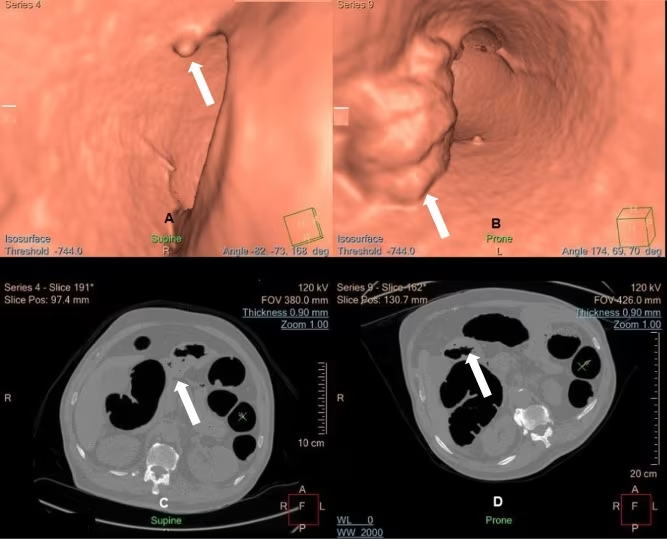
- Uses CT scanning to create detailed images of the colon
- Less invasive but still requires bowel preparation
- Cannot remove polyps if found
Barium Enema
- X-ray examination using barium to highlight the colon
- Less accurate in detecting small polyps
- Cannot remove polyps if found
Stool-Based Tests
- Faecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT)
- Faecal Immunochemical Test (FIT)
- Stool DNA test
- Less invasive but if positive, colonoscopy is still needed
It’s important to note that if these alternative tests detect abnormalities, a colonoscopy will still be necessary for further examination and potential treatment.
Cost and Insurance Coverage in Singapore
Colonoscopy costs in Singapore vary depending on the hospital, doctor’s expertise, and whether additional procedures like polyp removal or biopsies are performed.
- You can claim up to $1,250 from MediSave for colonoscopy procedures
- Most insurance plans cover colonoscopy, especially when medically necessary
- Screening colonoscopies may be subsidized under certain health screening programs
Always check with your healthcare provider or insurance company for specific coverage details.
Common Misconceptions about Colonoscopy
“Colonoscopy is extremely painful”
Fact: Most patients receive sedation and experience little to no discomfort. Many don’t even remember the procedure.
“I only need a colonoscopy when I have symptoms”
Fact: Colorectal cancer often develops without symptoms until advanced stages. Screening colonoscopies can detect and remove precancerous polyps before symptoms appear.
“The bowel preparation is unbearable”
Fact: While not pleasant, modern bowel preparations have improved significantly. Clear instructions and proper hydration can make the process more manageable.
“The procedure might damage my colon”
Fact: Serious complications are extremely rare (less than 0.1%) when performed by trained specialists.
“Men are more at risk for colorectal cancer than women”
Fact: While it’s the #1 cancer for men in Singapore, it’s the #2 cancer for women, making screening equally important for both genders.
Choosing a Colonoscopy Provider in Singapore
When selecting a colonoscopy provider, consider:
- The experience and qualifications of the specialist
- Hospital or clinic accreditation and facilities
- Technology and equipment used (such as AI-assisted colonoscopy)
- Cost and insurance coverage
- Location and accessibility
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a colonoscopy take?
A typical colonoscopy procedure takes about 20-40 minutes, though you should plan to be at the facility for 2-3 hours total for preparation, the procedure, and recovery.
Will I be awake during the colonoscopy?
Most colonoscopies are performed under sedation, so you’ll be in a twilight sleep state and unlikely to remember the procedure.
How long is the recovery after a colonoscopy?
Most people can resume normal activities the day after the procedure. However, you should not drive or make important decisions for 24 hours after sedation.
Can I eat normally after a colonoscopy?
Yes, most people can return to their normal diet immediately after the procedure unless instructed otherwise by their doctor.
How effective is colonoscopy at preventing colorectal cancer?
Studies show that colonoscopy can reduce colorectal cancer deaths by up to 60% through early detection and polyp removal.
What if I have hemorrhoids? Will that affect the colonoscopy?
Hemorrhoids should not interfere with a colonoscopy. The doctor will be able to perform the procedure and can even evaluate the hemorrhoids during the examination.
How do I know if my bowel preparation is adequate?
Your stool should be liquid, clear, and yellowish (like urine) by the time you’re finished with your preparation.
Is colonoscopy the only method to screen for colorectal cancer?
No, although it’s the most comprehensive method. Alternative screening methods include FIT, FOBT, stool DNA tests, and CT colonography.
What’s the difference between a screening and a diagnostic colonoscopy?
A screening colonoscopy is performed on individuals with no symptoms to detect potential issues early, while a diagnostic colonoscopy is performed to investigate specific symptoms or abnormal results from other tests.
Can I take my regular medications before a colonoscopy?
Some medications may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before the procedure. Always discuss all medications with your doctor in advance.
How much does a colonoscopy cost in Singapore?
The cost varies widely depending on the facility, ranging from approximately $1,200 to $3,000 or more, depending on whether you choose a public or private hospital and if additional procedures are performed.
Will colonoscopy detect all forms of colorectal cancer?
While colonoscopy is the most accurate method for detecting colorectal cancer, it’s not 100% perfect. However, it has a very high detection rate, especially when performed with modern equipment by experienced specialists.
Can I get a colonoscopy without sedation?
Yes, it’s possible to have a colonoscopy without sedation, but most doctors recommend it for patient comfort. Discuss your preferences with your doctor.
How do I prepare mentally for a colonoscopy?
Understanding the procedure, asking questions in advance, practicing relaxation techniques, and remembering the health benefits can help reduce anxiety.
What’s the youngest age someone should consider a colonoscopy?
While regular screening typically begins at age 50, individuals with a family history of colorectal cancer or other risk factors may need to start screenings at a younger age, sometimes as early as age 40 or 10 years before the age at which a first-degree relative was diagnosed.
Conclusion
Colonoscopy remains the most effective tool for colorectal cancer prevention and early detection.
In Singapore, where colorectal cancer is the most common cancer, regular screening is crucial, especially for those over 50 or with additional risk factors.
Modern advances, including AI-assisted technologies, have made colonoscopies more accurate and effective than ever before.
The minor discomfort of preparation and the brief procedure are small prices to pay for the potential life-saving benefits of early detection and prevention.
If you’re due for a colonoscopy or have symptoms that warrant investigation, consult with a healthcare provider to schedule this important screening procedure. Remember, early detection saves lives.