Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation on the inner side of the elbow.
Despite its name, this condition affects not only golfers but anyone who engages in activities that put repetitive strain on the forearm muscles and tendons.
In Singapore, where active lifestyles and participation in sports are common, golfer’s elbow can significantly impact daily activities and athletic performance if left untreated.
For many Singaporeans balancing busy professional lives with recreational sports and activities, golfer’s elbow can be particularly disruptive.
Whether you’re an avid weekend golfer at Sentosa Golf Club, a tennis enthusiast playing at public courts across the island, or a construction worker contributing to Singapore’s ever-evolving skyline, understanding this condition and knowing the treatment options available is crucial for maintaining your quality of life and productivity.
You might like: Tennis Elbow Treatment in Singapore: Causes, Symptoms, Recovery
Understanding Golfer’s Elbow
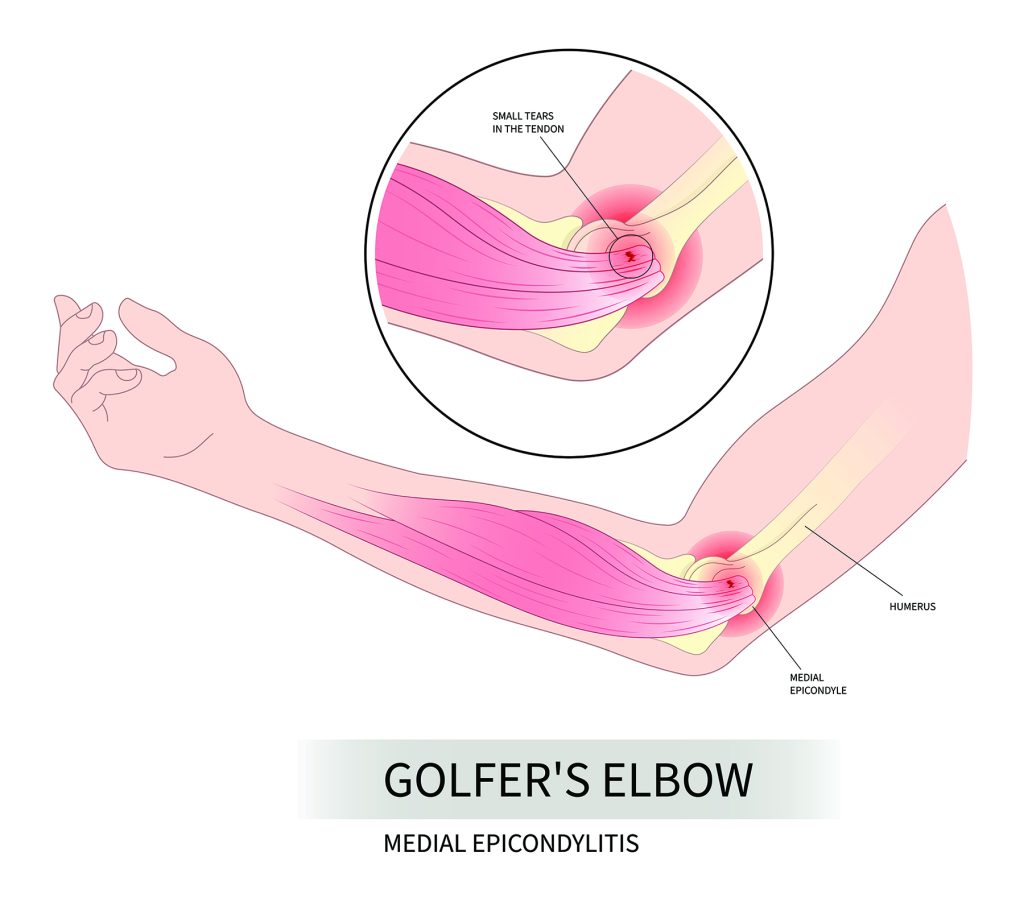
What is Golfer’s Elbow?
Golfer’s elbow occurs due to overuse of the wrist flexor muscles—the muscles that bend the wrist upward with the palm facing up.
The condition develops when the tendons connecting the forearm muscles to the medial epicondyle (the bony bump on the inner side of the elbow) become inflamed or develop small tears due to repetitive stress.
To understand golfer’s elbow better, it helps to know the anatomy involved. The medial epicondyle serves as an attachment point for several muscles that control wrist and finger movements.
The primary muscles involved are the pronator teres (which rotates the forearm) and the flexor carpi radialis (which bends the wrist).
When these muscles contract repeatedly during activities like swinging a golf club or gripping tools, they create tension at their attachment point, leading to micro-tears and inflammation.
Unlike tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) which affects the outer part of the elbow, golfer’s elbow impacts the inner aspect.
Both conditions share similar causes—overuse and repetitive motion—but affect different muscle groups. This distinction is important when determining the appropriate treatment approach.
This might like: Sports Doctors in Singapore: Guide to Finding a Suitable Specialist
What Causes Golfer’s Elbow?
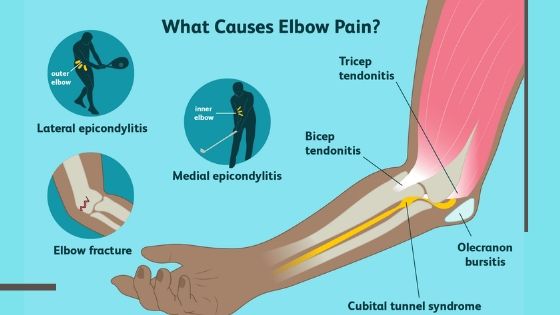
Several factors can contribute to the development of golfer’s elbow.
The primary cause is repetitive movements involving frequent wrist flexion or gripping motions, such as those used in golf, tennis, squash, or occupational tasks like carpentry and construction work.
Improper technique during these activities can place additional stress on the tendons, as can inadequate warm-up before exercise.
Overexertion—performing activities beyond your muscular capacity—and acute trauma to the elbow are also potential causes.
Related article: Neck Pain in Singapore: Causes, Treatments, Prevention
Who is at Risk?
While golfer’s elbow can affect anyone, certain groups face higher risks.
Athletes who participate in racket sports, golf, martial arts, or weightlifting are commonly affected, as are manual workers in professions that involve repetitive wrist movements.
Adults between the ages of 35-55 face increased risk as muscle strength naturally begins to decline during this period, making tendons more vulnerable to injury.
You might like: Low Back Pain in Singapore: Causes, Prevention and Treatment
Symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to faster treatment and recovery.
Common signs of golfer’s elbow include gradual onset of burning or sharp pain on the inner part of the elbow, tenderness when touching the inner bony prominence, and pain that may radiate down the forearm.
You might also experience discomfort when gripping objects, pain when bending the wrist downward, stiffness (especially in the morning), weakness in grip strength, and occasionally numbness or tingling in the ring and little fingers.
If you experience pain after trauma or a fall, or if you notice bruising and swelling, these may indicate conditions other than golfer’s elbow, such as a fracture.
Additionally, pain that doesn’t improve despite rest or wearing an appropriate elbow brace might suggest a tendon tear, while burning pain could indicate a nerve problem.
Related article: Scoliosis Treatment in Singapore: Causes and Symptoms
Diagnosis of Golfer’s Elbow in Singapore
In Singapore, healthcare professionals use several methods to diagnose golfer’s elbow:
Physical Examination
- Pain and tenderness over the medial epicondyle
- Pain when resisting wrist flexion
- Range of motion limitations
- Grip strength
Imaging Tests
If the diagnosis remains unclear or if other conditions need to be ruled out, your healthcare provider might recommend:
- X-rays: While X-rays don’t show soft tissue damage, they can help rule out fractures or arthritis.
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique can reveal inflammation in the tendons.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): For chronic cases (lasting 6-24 months), an MRI might be ordered to assess the extent of tendon damage.
Read more: Which Orthopedic Doctor in Singapore Should You Consider?
Treatment Options for Golfer’s Elbow in Singapore
Singapore offers a comprehensive range of treatment options for golfer’s elbow, from conservative approaches to advanced therapies and surgical interventions.
Conservative Treatments
Rest and Activity Modification
The first step in treating golfer’s elbow involves:
- Resting the affected arm
- Avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain
- Modifying techniques or postures during sports or work activities
Ice Therapy
Applying ice to the painful area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
Compression
Wearing an elbow brace or forearm strap below the elbow joint can help reduce the force on the flexor muscles and provide relief during daily activities.
Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Related article: Arthritis Treatment in Singapore: Causes, Risks, Symptoms
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation of golfer’s elbow. In Singapore, physiotherapists offer:
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Physical therapy typically includes wrist flexor stretches performed by extending the arm with the palm facing up, then gently pulling the fingers and hand down toward the floor.
Research has shown that eccentric muscle training (where the muscle lengthens during contraction) is particularly effective for degenerative tendon conditions, improving durability and strength.
A tailored exercise program usually progresses through several stages:
- Isometric exercises: Gentle muscle contractions without joint movement, which help maintain strength while minimizing pain during the acute phase
- Concentric exercises: Gradually introducing movements where muscles shorten while generating force
- Eccentric exercises: Focus on controlled lengthening of muscles under tension, which is particularly beneficial for tendon healing
- Functional exercises: Activities that mimic daily movements or sport-specific actions to prepare for return to normal activities
These exercises are typically performed both during supervised therapy sessions and as part of a home exercise program, with adjustments made based on progress and symptom response.
Manual Therapy Techniques
- Soft Tissue Massage: Targeted manipulation to release tension in the forearm muscles
- Joint Mobilization: Techniques to improve elbow joint mobility
Sports Taping
Physiotherapists can apply specialized taping techniques to reduce stress on the affected region and provide support during activities.
Technique Correction
For sports-related injuries, physiotherapists can help assess and correct your technique to prevent recurrence.
Advanced Treatment Options in Singapore
Singapore’s robust healthcare system offers several advanced treatment options for golfer’s elbow:
Corticosteroid Injections
A localized injection of corticosteroids into the affected area can provide short-term relief by reducing inflammation. However, these are typically used when other conservative treatments have failed.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
This regenerative treatment involves injecting a concentrated solution of the patient’s own platelets into the injured tendon to stimulate healing and tissue repair. PRP therapy has shown promising results for certain cases of golfer’s elbow.
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
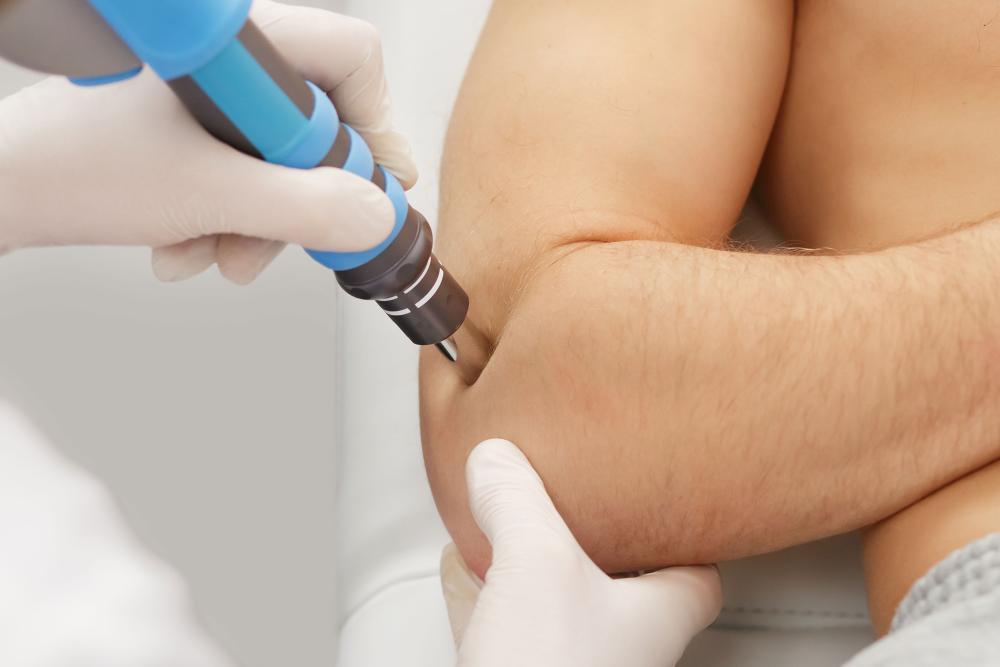
This non-invasive procedure uses shock waves to stimulate healing in the affected area. ESWT comes in two forms:
- Focal Shockwave Therapy: Targets deeper issues within the tendon
- Radial Shockwave Therapy: Better for addressing surface-level inflammation
INDIBA® Radiofrequency Therapy
INDIBA therapy uses radiofrequency energy to:
- Increase blood flow to the affected area
- Accelerate the removal of inflammatory mediators
- Deliver essential nutrients for tissue repair
- Alleviate pain by influencing nerve endings
- Increase tissue elasticity before manual therapy
- Stimulate cellular activity and natural tissue repair
Dry Needling
This technique involves inserting thin needles into trigger points or knots in the forearm muscles to:
- Interrupt the pain-spasm cycle
- Increase blood flow to targeted areas
- Stimulate the body’s natural pain-relieving chemicals
- Break down adhesions in the muscle tissue
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
This gentle massage technique focuses on the lymphatic system to:
- Reduce inflammation at its root
- Remove waste products and inflammatory mediators
- Promote overall healing of the affected tissues
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is typically considered only when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief after several months. Surgical options in Singapore include:
- Removal of damaged tissue
- Repair of torn tendons
- Removal of built-up scar tissue
- Addressing bone spurs that may be pressing on the tendon
Recovery time after surgery can range from 4 weeks to 6 months or more, depending on the severity of the condition and the specific procedure performed.
Recovery Timeline and Prevention
How Long Does Golfer’s Elbow Take to Heal?
The healing timeline varies based on severity:
- Mild cases often resolve in 3-6 weeks with proper rest and conservative treatment
- Moderate to severe cases may take several months to heal
- Chronic cases might require 6 months to 2 years for complete recovery
The recovery process typically progresses through several stages. During the acute phase (first 1-2 weeks), the focus is on reducing pain and inflammation through rest, ice, compression, and anti-inflammatory medications.
As symptoms begin to improve, gentle stretching exercises are introduced to maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness.
The rehabilitation phase (weeks 3-8 for mild cases) incorporates progressive strengthening exercises for the forearm muscles. Initially, these exercises are performed without resistance, gradually advancing to include light weights or resistance bands as tolerance improves.
Throughout this phase, modifications to daily activities and sports techniques are implemented to reduce strain on the healing tendons.
The final phase focuses on functional rehabilitation and return to normal activities. For athletes, sport-specific exercises and gradual return to play protocols are essential to prevent reinjury.
Most patients with mild to moderate golfer’s elbow can expect to return to their previous level of activity within 2-3 months, though continued attention to proper technique and preventive exercises remains important.
It’s worth noting that recovery isn’t always linear—some patients experience plateaus or occasional flare-ups during the healing process.
Persistence with the prescribed treatment plan and open communication with your healthcare provider are key to navigating these challenges.
Preventing Golfer’s Elbow Recurrence
To prevent golfer’s elbow from recurring or developing in the first place, focus on strengthening your forearm muscles through regular exercises that build strength and flexibility.
Always warm up properly before engaging in activities that strain the forearm, and ensure you’re using correct form during sports or work activities.
Take regular breaks during repetitive tasks, use appropriate equipment that fits your hand size, and gradually increase the intensity of your training. Most importantly, listen to your body and stop activities that cause pain to allow for adequate rest.
Seeking Treatment in Singapore
Singapore boasts a comprehensive healthcare system with numerous specialists and facilities dedicated to sports medicine and orthopedics.
From well-known orthopedic surgeons and physiotherapists to specialty sports clinics, individuals can receive tailored care for their specific needs.
The city-state’s healthcare infrastructure offers several advantages for those seeking treatment for golfer’s elbow.
Singapore’s medical facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic tools and therapeutic technologies, making it a regional hub for sports medicine and rehabilitation.
Many clinics offer integrated care models where orthopedic specialists work alongside physiotherapists, ensuring a coordinated approach to treatment.
When seeking treatment in Singapore, patients typically have multiple options:
- Public healthcare institutions offer comprehensive orthopedic services at subsidized rates for citizens and permanent residents.
- Private specialist clinics throughout areas provide more personalized care with shorter waiting times, though at higher cost.
- Sports medicine centers specialize in treating sports-related conditions like golfer’s elbow, with teams experienced in helping both recreational and competitive athletes.
- Rehabilitation centers focus specifically on physical therapy and rehabilitation, offering extensive programs to restore function and prevent recurrence.
Most healthcare providers in Singapore adopt a multidisciplinary approach to treating golfer’s elbow, combining medical interventions with physical therapy, patient education, and preventive strategies.
This holistic approach addresses not only the immediate symptoms but also the underlying causes and potential risk factors for recurrence.
Early intervention is crucial for preventing the condition from worsening and accelerating the healing process. If you suspect you have golfer’s elbow, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional as soon as symptoms appear.
Many clinics in Singapore offer same-day or next-day appointments for acute musculoskeletal conditions, allowing for prompt assessment and treatment initiation.
Conclusion
Golfer’s elbow can significantly impact daily activities and sports performance, but with Singapore’s array of treatment options, individuals can find effective relief and rehabilitation strategies.
Whether through conservative measures like rest and physical therapy or more advanced interventions such as PRP therapy or surgery, comprehensive care is available to help individuals recover and return to their active lifestyles with minimal disruption.
Remember that early intervention and proper guidance from healthcare professionals are key to managing and overcoming this common yet troublesome condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will golfer’s elbow go away on its own?
In many instances, golfer’s elbow can heal fully through self-care and physical therapy alone, often within three to six months.
However, this requires consistent effort and patience during the recovery process. More severe or chronic cases may need medical intervention.
What is the main cause of golfer’s elbow?
Golfer’s elbow typically stems from repetitive strain on the forearm muscles or improper technique in activities such as golf, racquet sports, weightlifting, and throwing sports.
Excessive wrist flexion movements and forceful gripping are common contributors to the condition.
Can I continue exercising with golfer’s elbow?
You should avoid activities that exacerbate your symptoms, especially during the acute phase.
However, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises recommended by a physiotherapist can be beneficial.
When resuming your regular exercise routine, maintain proper form and gradually increase intensity to prevent reinjury.
How is golfer’s elbow different from tennis elbow?
While both conditions result from overuse and repetitive motion, they affect different parts of the elbow. Golfer’s elbow causes pain on the inner side of the elbow and stems from activities requiring wrist flexion and gripping.
Tennis elbow affects the outer side and is associated with activities requiring wrist extension.
What happens if golfer’s elbow goes untreated?
If left untreated, golfer’s elbow may lead to chronic issues such as restricted elbow movement, persistent pain, and weakened grip strength.
The condition may worsen over time and significantly impact your quality of life and ability to perform daily activities.
Are corticosteroid injections effective for golfer’s elbow?
Corticosteroid injections can provide short-term relief by reducing inflammation and pain.
However, they are typically recommended only when other conservative treatments have failed, as repeated injections may weaken the tendon over time.
How long should I wear an elbow brace for golfer’s elbow?
An elbow brace or forearm strap can be worn during activities that might stress the forearm muscles.
Your healthcare provider can give you specific guidance about how long to wear it based on your individual condition and activity level.
Is surgery always necessary for golfer’s elbow?
No, surgery is typically considered only when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief after several months.
Most cases of golfer’s elbow respond well to non-surgical approaches such as rest, physical therapy, and other conservative interventions.
Can PRP therapy accelerate healing for golfer’s elbow?
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has shown promising results for certain cases of golfer’s elbow by stimulating the body’s natural healing processes.
However, results can vary between individuals, and this treatment may not be suitable for everyone.
How can I prevent golfer’s elbow when playing golf?
To prevent golfer’s elbow while playing golf:
- Use proper grip technique (avoid gripping the club too tightly)
- Ensure your clubs are the right size and grip thickness for your hand
- Warm up properly before playing
- Take lessons to improve your swing mechanics
- Take regular breaks and avoid overplaying, especially when you begin to feel discomfort

