Understanding Total Knee Replacement
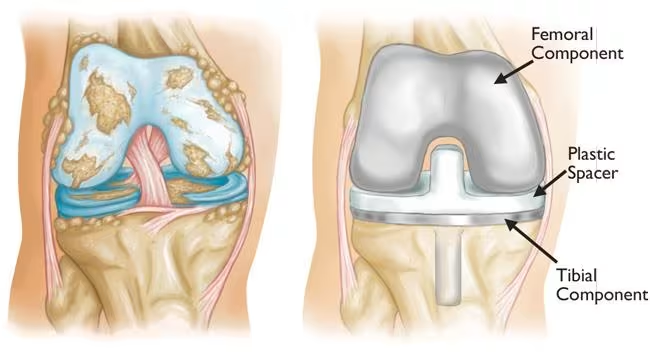
Total knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to replace damaged knee joints with artificial components. This orthopedic procedure aims to restore normal knee function and alleviate pain that typically results from various forms of arthritis affecting the knee joint.
During the procedure, the surgeon removes damaged cartilage and bone from the knee and replaces them with metal and high-grade plastic components that mimic the function of a healthy knee. The artificial joint serves to recreate the smooth, gliding surface that allows for painless movement.
Read more: Which Orthopedic Doctor in Singapore Should You Consider?
Who Needs Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery is typically recommended for individuals who suffer from severe knee pain that interferes with daily activities. Candidates also experience persistent knee pain even while resting or sleeping.
They have chronic knee inflammation and swelling that doesn’t improve with rest or medication. Many show signs of knee deformity, such as bowing in or out of the knee.
These individuals have stiffness that limits mobility and makes walking difficult. Additionally, they have not responded to conservative treatments such as medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle modifications.
The primary conditions that lead to knee replacement surgery include several key diagnoses.
Read more: Arthritis Treatment in Singapore: Causes, Risks, Symptoms
Osteoarthritis is the most common reason for knee replacement, characterized by degeneration of cartilage that cushions the ends of bones.
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory condition where the synovial membrane surrounding the joint becomes inflamed.
Post-traumatic arthritis develops after a severe knee injury.
Other conditions that may require knee replacement include osteonecrosis, gout, or knee deformities.
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief and knee pain significantly impacts quality of life, knee replacement surgery becomes a viable treatment option.
Read more: Best Orthopedic Doctor in JB for Singaporeans
Benefits of Total Knee Replacement Surgery
Patients who undergo successful knee replacement surgery in Singapore typically experience:
- Significant reduction or elimination of knee pain
- Improved mobility and knee function
- Correction of knee deformities
- Enhanced quality of life
- Ability to return to daily activities with greater ease
- Improved sleep quality due to reduced pain
- Independence in movement and activities
- Potential return to low-impact sports and recreational activities
For working individuals, successful surgery allows continued employment without knee pain concerns. For retirees, it enables enjoyment of retirement activities including travel and participation in low-impact sports.
Related article: ACL Reconstruction Surgery in Singapore: Causes, Costs
Advanced Surgical Techniques in Singapore
Singapore has established itself as a leader in knee replacement surgery by adopting cutting-edge technologies that enhance precision and outcomes:
Computer Navigation
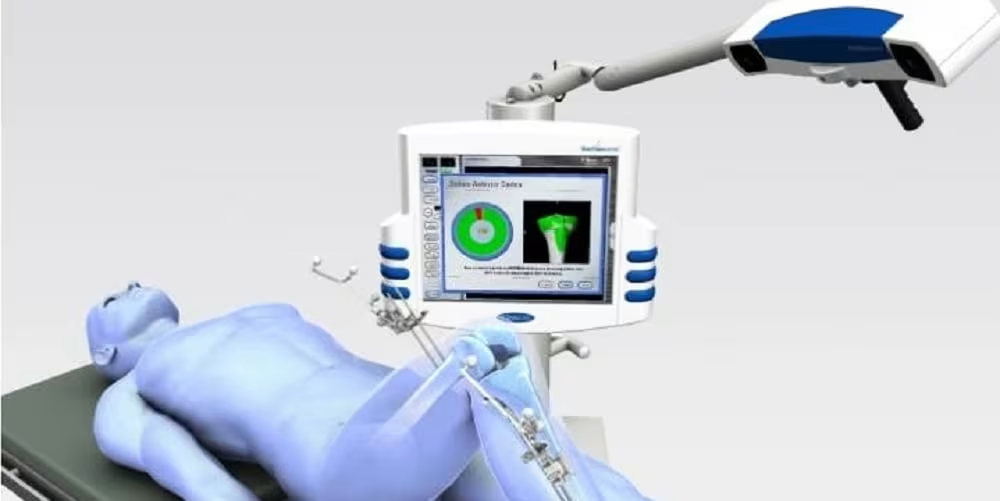
This technology has revolutionized knee replacement procedures by improving accuracy and reducing human error.
The system works by mapping the “coordinates” of the patient’s knee, including anatomical landmarks of the hip, knee, and ankle joints.
It provides real-time guidance for precise placement of cutting instruments. The system verifies cuts to ensure proper alignment.
Additionally, it enables fine-tuning of soft tissue balance by studying knee joint kinematics.
Read more: Knee Pain in Singapore: Causes, Treatment & Prevention
3D Printing Technology
Patients opting for this technique undergo several specific steps.
They receive preoperative MRI scanning of the lower limb. Data collection determines optimal implant size and alignment.
The process includes creation of Patient Specific Instruments (PSI) via 3D printing. These instruments achieve precise fitting to the patient’s unique knee anatomy. This approach results in a quick and accurate replacement procedure.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery (MAKOplasty)
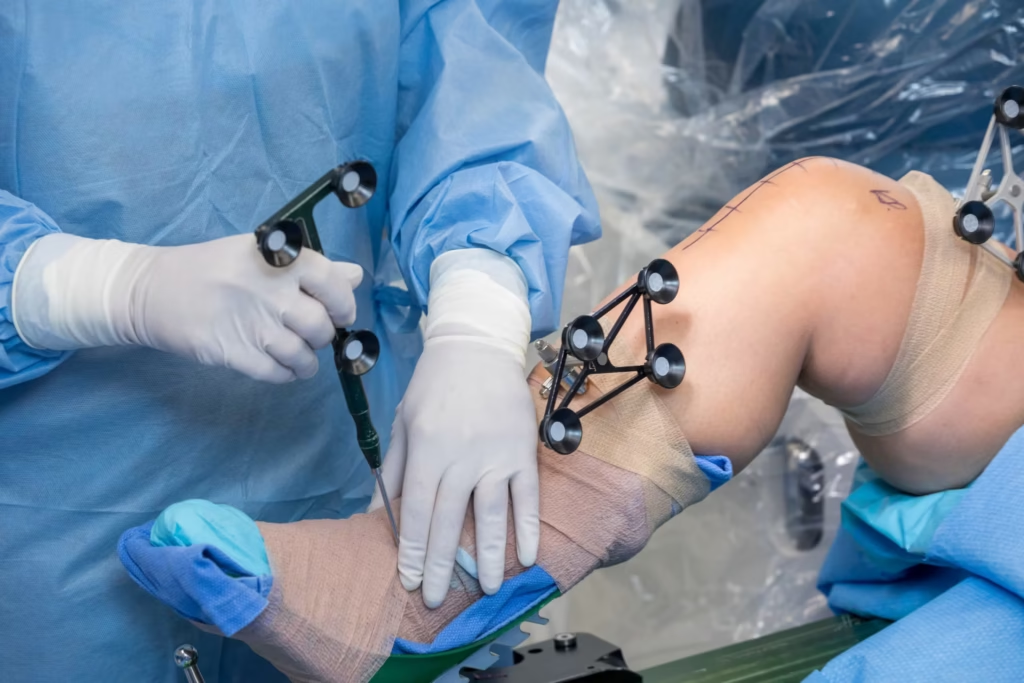
This semi-automated robotic arm assists surgeons in executing total knee replacement with exceptional precision.
Patients undergo a preoperative CT scan of the lower limb. Important parameters are gathered and entered into the computer system.
The data merges with real-life anatomical landmarks during surgery. The robotic arm helps perform the procedure with high precision. Built-in safety mechanisms minimize risk of nerve or blood vessel injury.
These advanced technologies are particularly beneficial for patients with previous injuries resulting in deformed anatomy. They also help patients with variant anatomy such as severe bowing of femurs.
Additional benefits include reduced blood loss and minimal risk of embolic events, as these techniques avoid instrumentation near the bone’s medullary cavity.
You might like: Shoulder Pain in Singapore: Causes, Treatments, Recovery
The Knee Replacement Procedure
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Before surgery, patients typically undergo:
- Assessment: A comprehensive evaluation including:
- Financial counseling for estimated costs
- Blood tests and other diagnostic tests
- ECG (if indicated)
- Chest and/or knee X-rays
- Anesthesia assessment
- Patient education session
- Physiotherapy consultation
- Knee measurement at the Orthopedic Diagnostic Centre
- Pre-Operative Care:
- Antiseptic body wash usage to reduce germ presence (1 day before and on surgery day)
- Fasting as instructed (typically no food or drinks except plain water after midnight)
- Discontinuation of certain medications as advised by the doctor
- Home Preparation:
- Installing safety bars in the shower
- Arranging for a stable chair and footstool to elevate the leg
- Installing a toilet seat riser
- Ensuring daily necessities are accessible without climbing stairs
You might like: Hip Replacement Surgery in Singapore: Cost, Risks
During Surgery
The actual surgical procedure involves several steps:
- The patient receives either general or regional (spinal) anesthesia.
- The surgeon makes an incision of 10-15 cm at the front of the affected knee.
- The knee is flexed at approximately 90 degrees, and the lower leg is secured in place.
- A tourniquet may be applied to the upper leg to minimize blood flow.
- The damaged bone surfaces and cartilage are removed using precision instruments.
- Small portions of bone from the femur, tibia, and patella (kneecap) are removed.
- The implants are attached to each bone:
- A metal implant covers the end of the femur
- A metal baseplate with a durable plastic surface is placed on the tibia
- The back of the patella may be covered with a durable plastic implant
- The ligaments are adjusted to achieve optimal knee function.
- The wound is closed with sutures, and a drain may be inserted to remove fluids.
- The knee is wrapped in a sterile bandage.
The entire procedure typically takes between 1-3 hours.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Immediately after surgery:
Patients are monitored in a recovery room where vital signs are checked. Pain medication is administered to manage discomfort.
Physical therapy begins as early as the day after surgery. A continuous passive motion machine may be used to move the affected leg. Patients are encouraged to bear weight on the new knee as tolerated.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Hospital Stay (3-5 days)
During this period, patients receive:
Patients receive care from a multidisciplinary team including surgeons, nurses, physiotherapists, and other healthcare professionals. They receive pain management through various methods including oral medication, intravenous access, or injections.
Patients get assistance with mobility and daily activities. Deep breathing and coughing exercises are provided. Instruction on leg exercises promotes circulation. Anti-embolic stockings and pneumatic pumps are used to prevent deep vein thrombosis.
The First Three Months
This critical recovery period involves:
Critical recovery period involves building strength in muscles surrounding the knee. Patients learn to move with walking aids until the knee can bear weight.
They gradually reduce dependence on mobility aids. Prescribed strengthening exercises are performed regularly.
Pain is managed with medication and ice. Any abnormal swelling or pain is monitored carefully. Patients work to regain full range of motion.
Long-term Recovery
Full recovery may take several months, with continued improvement possible for up to a year. Patients should:
Patients should follow a graduated walking program. They resume normal household activities including climbing stairs. Specific exercises are performed several times daily. Regular physiotherapy sessions are attended.
Driving resumes approximately 4-6 weeks after surgery when the knee bends sufficiently. Patients return to low-impact sports and activities as advised by their healthcare team.
Cost of Knee Replacement Surgery in Singapore
The cost of knee replacement surgery in Singapore varies:
- Private hospitals: Between $19,000 to $32,000
- Public hospitals: Between $16,000 to $22,000
These costs typically include hospitalization and use of operating theaters. They also cover implant materials such as ceramic, steel, and titanium.
Medication is included in the cost. Professional fees for the surgeon and anesthesiologist are also covered. Patients are advised to check with their personal or corporate insurance plans for coverage options.
Risks and Complications
While knee replacement surgery is generally safe and effective, potential risks include infection. Stiffness may occur in some patients. Nerve and blood vessel injury are possible complications.
Periprosthetic fractures can develop. Loosening and wear of the prosthesis may happen over time. Deep vein thrombosis is a potential risk. Blood clots can form. Persistent pain may continue after surgery.
Implant failure is another possible complication. These risks are discussed thoroughly with patients before surgery, and informed consent is required.
Sports and Activities After Knee Replacement
Most patients can return to low-impact activities after recovery. Walking is encouraged and generally well-tolerated.
Swimming provides excellent exercise without joint stress.
Cycling is another beneficial low-impact activity. Gentle jogging may be possible for some patients. Low-impact aerobic exercises are recommended.
However, high-impact activities that may shorten the lifespan of the implant should be avoided.
Heavy lifting puts excessive stress on the knee joint. High-impact sports can damage the prosthesis.
Activities with excessive twisting motions should be limited to protect the implant.
FAQ Section
What is osteoarthritis and how does it affect the knee?
Osteoarthritis describes the degeneration of cartilage in the knee joint. This smooth cartilage normally covers the ends of bones like the femur and tibia, allowing them to glide painlessly against each other.
When this cartilage wears down due to aging, injury, or other factors, the underlying bones begin to rub together, resulting in narrowing of the joint space and the formation of bone spurs.
This leads to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. Osteoarthritis typically develops gradually, with symptoms worsening over time and most commonly affects middle-aged and older individuals.
What are the signs that I may have arthritis in my knee?
Signs of knee arthritis include persistent pain and swelling in the knee joint, which may be sudden or progressive. You might experience difficulty walking or climbing stairs, and notice clicking, creaking, grinding, or snapping sounds when moving your knee.
Severe joint stiffness is common, especially after periods of inactivity. Some patients experience their knee suddenly buckling or giving out, while others find their knee becomes locked and cannot be bent or straightened.
If you notice these symptoms, especially if they interfere with daily activities, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis.
How do I know if I need knee replacement surgery?
Determining if knee replacement surgery is necessary requires careful consideration with your orthopedic surgeon. Generally, surgery becomes an option when conservative treatments like medication and physical therapy no longer provide relief.
You might be a candidate if you experience severe pain that limits daily activities, pain that persists even when resting or sleeping, significant knee stiffness or deformity, or if your knee condition is affecting your quality of life.
Your surgeon will assess your knee pain, examine your joint function, review X-rays to evaluate the degree of arthritis, and consider your overall health before recommending surgery.
What types of knee replacement surgeries are available?
There are several types of knee replacement surgeries available in Singapore. Partial (unicompartmental) knee replacement replaces only one damaged compartment of the knee, preserving healthy parts.
This option typically has a smaller incision, faster recovery, and more natural feeling. Total knee replacement (TKR) replaces all three compartments of the knee with metal and plastic components.
This is the most common procedure for widespread arthritis. Bicompartmental knee replacement addresses two compartments but is less common.
Revision knee replacement refers to surgery to replace or repair a previous knee replacement.
Robotic-assisted knee replacement uses technology like MAKOplasty for enhanced precision.
What is the recovery like after knee replacement surgery?
Recovery after knee replacement surgery progresses in phases. Initially, patients stay in the hospital for 3-5 days for pain management, monitoring, and beginning physical therapy.
You’ll be encouraged to stand and walk with assistance as soon as possible. After discharge, you’ll use walking aids like frames or crutches while building strength.
The first three months are crucial for rehabilitation, focusing on regaining range of motion, strengthening muscles, and gradually increasing activity levels.
Most patients can resume normal daily activities within 3-6 weeks, though some pain with activity is normal for several weeks.
Complete recovery may take 6-12 months, with continued improvement in strength and function. Regular physiotherapy is essential throughout this process.
What are the advantages of minimally invasive surgery for knee replacement?
Minimally invasive surgery for knee replacement offers several advantages over traditional approaches. Instead of large 8-10 inch incisions, this technique uses smaller 3-5 inch incisions and spares the quadriceps muscles and tendons at the front of the knee.
The benefits include less tissue trauma, reduced pain, fewer unwanted injuries, lower infection rates, shorter recovery time, and reduced costs. Patients typically require half the time to transition from a walker to a cane.
The procedure employs robotic arms and high-definition magnified imaging, enhancing surgical precision and success rates. However, this approach isn’t suitable for all patients, particularly those with knee deformities or who require revision surgery.
How long do knee replacements last?
Modern knee replacements have impressive longevity. Current ten-year survival rates for fixed and mobile bearing unicompartmental knee replacements range from 90-95%. Total knee replacements can last 15-20 years or more with proper care.
Several factors affect implant longevity, including the patient’s weight, activity level, and implant materials. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding high-impact activities, and following medical advice can extend the lifespan of knee replacements.
Advances in materials and surgical techniques continue to improve durability. However, younger patients should be aware that very active lifestyles might require revision surgery later in life.
What advanced technologies are used for knee replacement in Singapore?
Singapore employs cutting-edge technologies for knee replacement surgery. Computer navigation systems map the patient’s knee anatomy and provide real-time guidance for precise implant placement, reducing human error.
Patient-Specific Instruments (PSI) created through 3D printing technology allow for customized surgical tools that fit the patient’s unique knee anatomy.
Robotic-assisted surgery systems like MAKOplasty use preoperative CT scans to create detailed surgical plans and guide implant placement with exceptional precision.
These technologies particularly benefit patients with complex anatomy or previous injuries and have been shown to improve surgical results with benefits like reduced blood loss and lower risk of complications.
Can I have both knees replaced at the same time?
Bilateral knee replacement (replacing both knees simultaneously) is an option for certain patients. This approach is particularly beneficial for individuals whose rehabilitation would be compromised if only one knee were replaced.
Candidates for bilateral knee replacement should be relatively younger, have minimal medical conditions, and be physically capable of handling the more demanding recovery process.
The recovery timeline might be slightly longer than single knee replacement, with walking typically beginning on day two rather than day one post-surgery.
This approach allows patients to undergo rehabilitation once rather than twice and can be more efficient for those with severe arthritis in both knees.
What preparation is needed before knee replacement surgery?
Preparing for knee replacement surgery involves several important steps. Medical preparation includes a comprehensive assessment with blood tests, imaging, and anesthesia evaluation.
You’ll need to follow fasting instructions and may need to temporarily stop certain medications. Home preparation is crucial – install safety features like shower bars and a toilet seat riser, arrange for a stable chair with footstool, and organize your living space to minimize stair climbing.
Remove tripping hazards and ensure essentials are within easy reach. You should also arrange for someone to help during early recovery and prepare meals in advance.
Meeting with a physiotherapist before surgery to learn about post-operative exercises is also beneficial. Following these preparations helps ensure a smoother recovery process.

