Receding gums is a common dental condition affecting many Singaporeans, where the margin of gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root.
According to a 2016 survey, 3 out of 10 Singaporeans aged 60 and above have lost all their teeth due to long-term dental neglect and severe dental diseases. The National Adult Oral Health Survey involving 1,196 adult Singaporeans revealed that 90% suffered from some form of gum disease.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide To Seeing A Dentist In Singapore
Maintaining healthy gums is vital for oral health, as untreated gum disease can progress to more serious issues like periodontitis, potentially leading to tooth loss.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies for receding gums in Singapore.
What Are Receding Gums?
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, occur when the gum tissue that surrounds your teeth begins to pull back or wear away. As a result, more of your tooth’s surface becomes exposed, including the sensitive root. This can lead to a range of dental issues, as well as aesthetic concerns.
Read more: Root Canal Treatment in Singapore
When gums recede, they expose the tooth roots which lack the protective enamel layer found on the crown of the tooth. Instead, roots are covered by cementum, a softer tissue that’s more susceptible to erosion and decay caused by bacterial plaque and acids in the mouth. The
absence of the gum’s protective barrier means bacteria can more easily settle and produce acids that cause decay.
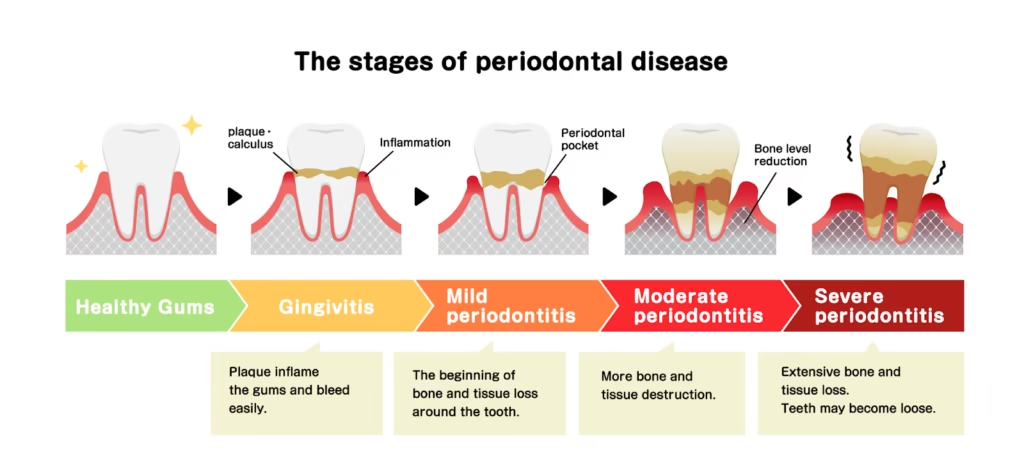
Stages of Gum Recession
Understanding the progression of gum recession can help in early detection and appropriate treatment:
1. Early Stage
- Minor gum line recession
- Slight sensitivity noticed
- Minimal exposure of the tooth root
2. Moderate Stage
- Increased gum recession
- Noticeable tooth root exposure
- Increased sensitivity, especially to temperature changes
3. Advanced Stage
- Significant recession
- Exposing much of the tooth root
4. Severe Stage
- Extensive gum tissue loss
- Very exposed tooth roots
- Potential for tooth loss
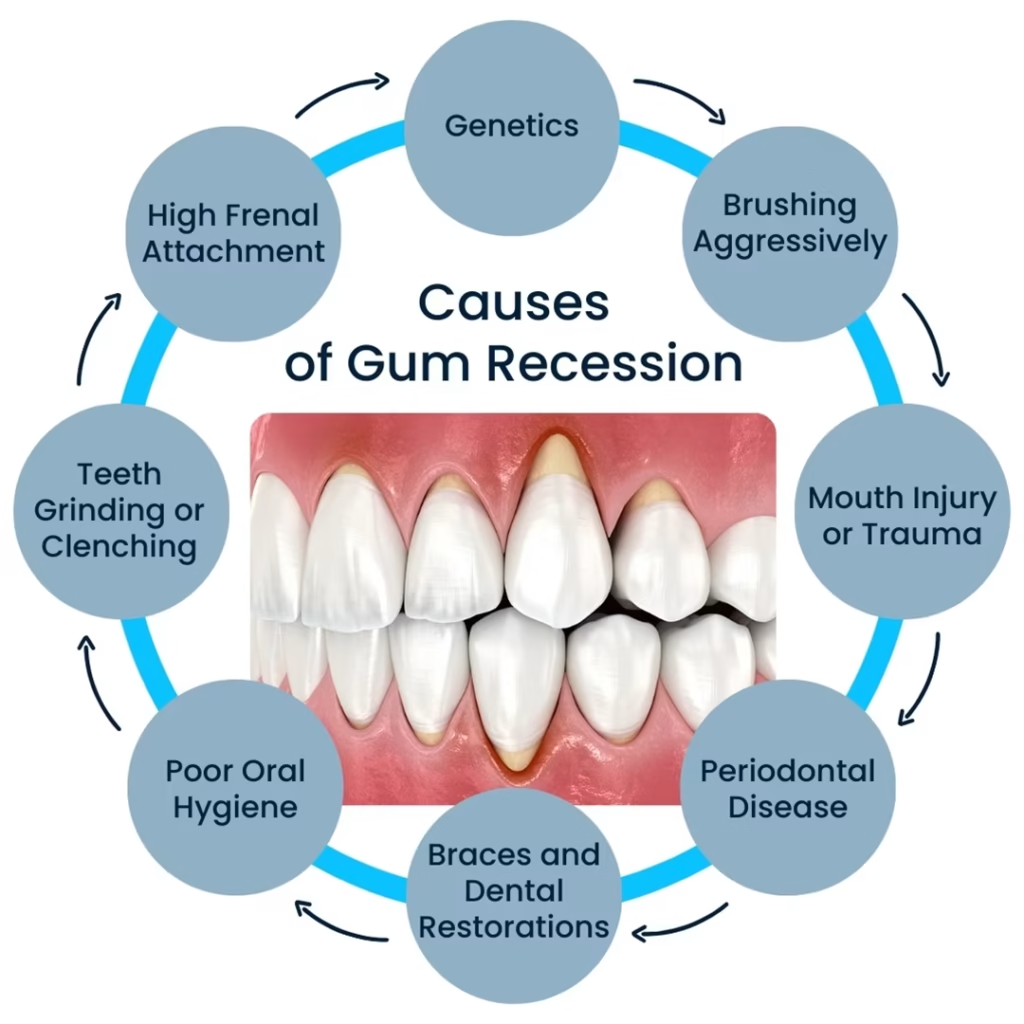
Causes of Receding Gums
Multiple factors can lead to receding gums, each contributing to the deterioration of gum tissue:
1. Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is the primary cause of gum recession, typically progressing from an initial stage known as gingivitis.
Related: Periodontists in Singapore: Everything You Need to Know
As it develops, bacteria produce toxins that irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation and infection. Pockets form between the gums and teeth, allowing more bacteria to thrive, exacerbating tissue loss and leading to recession.
2. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth. If not removed, plaque can harden into tartar, which irritates the gums and begins the process of gum recession.
3. Aggressive Brushing
Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing too vigorously can damage gum tissue, causing inflammation and exposing the roots of the teeth, resulting in gum recession.
4. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Teeth grinding and clenching place significant pressure on the gums, loosening teeth in their sockets and creating deep gingival pockets. Over time, this stress can cause gums to recede.
5. Tobacco Use
Tobacco users tend to have more plaque on their teeth due to chemicals that reduce saliva production. Less saliva encourages bacteria to thrive, resulting in increased plaque buildup. Additionally, tobacco can directly irritate gum tissue.
6. Hormonal Changes
During menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause, hormonal changes can increase blood flow to the gums, leading to inflammation and swelling. This heightened sensitivity can cause gums to react more dramatically to irritants like plaque.
7. Genetic Susceptibility
A significant portion of the population is genetically predisposed to gum disease, affecting gum health despite diligent oral care.
8. Age
While aging itself is not a direct factor, gum tissue tends to recede in older people due to accumulated years of plaque buildup and other untreated oral health issues.
Read more: Common Dental Problems in the Elderly: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
9. Misaligned Teeth / Bite Problems
Irregular force distribution from misaligned teeth can lead to receding gums.
Read more: The Complete Guide to Braces in Singapore
10. Oral Piercings
Jewelry in the lip or tongue can irritate and wear away gum tissue.
11. Trauma to Gums
Physical injuries or trauma to the gum tissue can also contribute to recession.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Recognizing the signs of gum recession is essential for early intervention:
- Visual Indicators: Gums visibly receding, creating gaps between teeth and altering gum tissue’s appearance
- Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet stimuli
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing
- Inflammation: Red and swollen gums
- Bad Breath: Persistent halitosis
- Gum Pain: Discomfort or pain localized at the gum line
- Tooth Root Exposure: Visible roots due to receded gums
- Loose Teeth: Teeth becoming mobile in advanced cases
Diagnosing Gum Recession
Dental professionals use various techniques to diagnose and assess gum recession:
- Visual Examination: Inspection of the gums for signs of recession
- Dental Probes: Measurement of pocket depths around teeth
- Gingival Probing: Assessment of the gap between the gum line and where the gum tissue firmly attaches to the tooth
- Digital X-rays: Evaluation of bone structure beneath the gums
- Intraoral Cameras: Detailed view of teeth and gums
- Periodontal Charting: Documentation of oral health status over time
- Patient History Review: Assessment of contributing factors like brushing technique and tobacco use
Treatments for Receding Gums
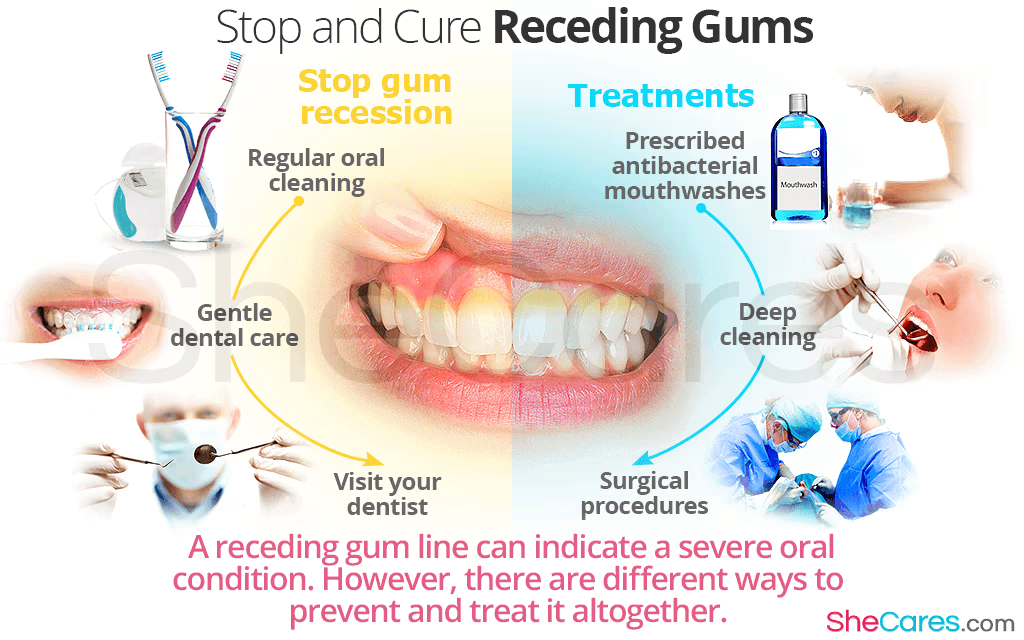
Treatment options range from non-invasive methods to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition:
Non-Surgical Treatments
1. Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
This non-surgical procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line (scaling) and smoothing rough spots on the tooth root (root planing).
This helps remove bacteria and provides a clean surface for the gums to reattach to the teeth.
2. Orthodontics
Braces or clear aligners can realign teeth, distributing forces evenly to mitigate gum recession. While not a direct treatment, it aids in oral hygiene management and can prevent worsening of gum recession.
Read more: Invisalign vs Clear Aligners: What are the Differences?
3. Desensitizing Agents and Varnishes
These treatments minimize sensitivity of exposed roots by creating a protective barrier, making daily oral hygiene less painful.
4. Dental Bonding and Restoration
Composite resin can be applied to cover exposed tooth roots, lessening sensitivity and enhancing appearance with minimal preparation.
5. Medications
Various treatments include antiseptic chips post-deep cleaning, antimicrobial mouthwash for reducing bacteria levels, and enzyme suppressants to block gum tissue breakdown.
6. Laser Periodontal Therapy (LANAP)
LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure) is a minimally invasive laser treatment that removes diseased tissue while preserving healthy gums.
The Fotona Twin Light Therapy uses two different wavelengths of lasers (Nd and Er) to optimize healing and restoration of periodontal tissues through three steps:
- Nd laser application to target and remove diseased tissue
- Er laser cleaning to remove harmful biofilm and tartar
- Nd laser coagulation to promote tissue healing
This approach avoids incisions, ensuring less postoperative discomfort.
Surgical Treatments
1. Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation (PST)
A minimally invasive procedure where a small pinhole is made to adjust the gum line. It offers quick recovery and immediate aesthetic improvements without sutures or scalpels, ideal for patients without active gum disease.
2. Gum Graft Surgery
For severe gum recession, this procedure involves tissue transplantation to cover exposed roots. It provides a durable solution and is ideal for significant recession, with a high success rate for root coverage and aesthetic improvement.
3. Gum Contouring
A cosmetic procedure to reshape the gums after recession. Using advanced techniques like Fotona’s LightWalker® Laser System allows for precision and minimally invasive treatment.
Treatment Selection Based on Severity
| Gum Recession Stage | Surgical Treatments | Non-Surgical Treatments |
| Early | Not typically required | Improved oral hygiene, Desensitizing agents, Orthodontics |
| Moderate | Not typically required | Deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), Orthodontics, Dental Bonding |
| Advanced | Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation | LANAP, Orthodontics, Desensitizing agents |
| Severe | Gum grafting, Pinhole Gum Rejuvenation | Not applicable |
Note: Topical antibiotics and various medications may be used across different stages to manage bacterial infection and inflammation.
Risks of Receding Gums
Untreated gum recession can lead to several complications:
- Increased Tooth Sensitivity: Exposed dentin leads to sensitivity to temperature and pressure
- Higher Cavity Risk: Exposed roots are more vulnerable to decay
- Aesthetic Concerns: Receded gums alter the appearance of your smile
- Teeth Loosening: Recession weakens tooth support, potentially leading to tooth loss
- Infection: Exposed roots are susceptible to bacterial infection
- Bone Loss: Advanced recession can lead to deterioration of jawbone
Read more: Complete Guide to Fixing a Gummy Smile: Causes and Treatment Options
Preventing Receding Gums
Preventing gum recession is achievable through consistent oral care and healthy habits:
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush using gentle circular motions; floss daily
- Choose the right toothpaste: Look for ingredients like fluoride, hydroxyapatite for enamel repair, potassium nitrate for sensitivity, xylitol to combat decay, and calcium phosphate for remineralization
- Schedule regular dental check-ups: Professional cleanings prevent plaque and tartar buildup
- Quit smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk of gum disease
- Address teeth grinding: Use a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night
- Maintain a balanced diet: Limit sugary foods and acidic drinks to reduce tooth and gum issues
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration promotes saliva production, which protects gums
- Use therapeutic mouthwash: Helps reduce plaque and removes food particles
- Manage stress: High stress can weaken the immune system, making it harder to fight off infections including gum disease
Cost of Receding Gums Treatment in Singapore
The cost of treatment varies based on severity and specific procedures needed:
- Deep cleaning (e.g., root planing): Typically ranges from $185.30 to $327.00
- Periodontal surgery (e.g., gum grafting): Approximately $327.00 to $436.00
- Regenerative procedures (e.g., pinhole gum rejuvenation): Available starting from $970
Subsidies and Financial Assistance
- CHAS (Community Health Assistance Scheme) provides subsidies for medical and dental care
- CHAS Orange and CHAS Blue cardholders can enjoy dental subsidies, including for gum treatment
- Pioneer Generation and Merdeka Generation status also offer subsidies for selected dental procedures
- Dental insurance policies can cover treatments for receding gums, depending on the plan’s coverage
Recovery After Gum Treatment
The journey to optimal healing and long-term gum health depends on diligent post-treatment care:
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine using a soft-bristle toothbrush, daily flossing, and non-alcoholic mouthwash
- Diet: Consume soft, nutritious foods and ensure adequate hydration; avoid hard, sticky, or spicy foods during healing
- Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-ups to monitor healing progress
- Lifestyle Changes: Quit smoking and manage underlying health conditions like diabetes that can compromise gum health
Frequently Asked Questions About Receding Gums
Are receding gums reversible?
Receding gums cannot be completely reversed once gum tissue has been lost, as it cannot regenerate naturally. However, treatment can stop further recession and improve the appearance and health of gums.
For mild cases caused by factors like aggressive brushing or poor oral hygiene, improved dental care can halt progression.
Moderate to severe cases may require professional interventions such as gum grafting or the pinhole surgical technique to cover exposed roots.
How many treatments will I need for receding gums?
The number of treatments depends on the severity of your condition. For mild receding gums, one to two deep cleaning treatments (scaling and root planing) might suffice.
Moderate to severe cases could require multiple appointments and possibly surgical intervention, with one or two surgeries depending on the extent of the issue and healing outcomes.
Your dentist will create a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs.
Can retainers cause receding gums?
Retainers themselves do not directly cause gum recession, but improper cleaning and maintenance can lead to bacterial buildup. This can contribute to gum disease, which may ultimately result in gum recession.
Additionally, if retainers fit poorly or create excessive pressure on certain teeth, this could potentially affect gum health over time. It’s important to maintain good oral hygiene and have regular check-ups with your dentist if you wear retainers.
Can I get braces if my gums are receding?
Yes, you can get braces if you have receding gums, but it’s essential to address the underlying cause of the recession first.
Your orthodontist and periodontist should work together to develop a treatment plan that considers your gum health. In some cases, treating the gum recession
before starting orthodontic treatment may be recommended. During orthodontic treatment, maintaining excellent oral hygiene becomes even more crucial to prevent further gum problems.
What foods should I avoid if I have receding gums?
If you have receding gums, it’s advisable to avoid:
- Sugary foods and beverages that promote bacterial growth
- Acidic foods and drinks that can erode enamel and irritate gums
- Hard foods like nuts, hard candies, and ice that can traumatize gums
- Sticky foods that can get trapped between teeth and promote plaque buildup
- Very hot or very cold foods that may trigger sensitivity in exposed roots
- Spicy foods that might irritate already inflamed gum tissue
Do receding gums cause bad breath?
Receding gums themselves don’t directly cause bad breath, but they create conditions that can lead to halitosis. When gums recede, they form pockets where bacteria can accumulate and thrive. These bacteria produce sulfur compounds that contribute to bad breath.
Additionally, gum recession is often associated with periodontal disease, which is a known cause of persistent bad breath. Maintaining good oral hygiene and addressing the underlying gum recession can help alleviate bad breath issues.
How does smoking affect receding gums?
Smoking significantly impacts gum health and contributes to receding gums in several ways:
- It reduces blood flow to the gums, limiting oxygen and nutrients needed for healing
- Nicotine and other chemicals degrade gum tissue directly
- Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder to fight off gum infections
- It promotes bacterial plaque formation and tartar buildup
- Smokers have reduced saliva production, which normally helps cleanse the mouth
- The healing process after any gum treatment is compromised in smokers
What role does genetics play in receding gums?
Genetics plays a significant role in gum recession. Some people inherit traits that make them more susceptible to gum disease and recession, including:
- Thin or weak gingival tissue structure
- Predisposition to aggressive immune responses to oral bacteria
- Tooth positioning and jaw structure that affect how forces are distributed when chewing
- Tendency toward certain inflammatory responses
While genetic factors create predispositions, environmental factors and oral hygiene practices still heavily influence whether someone will develop receding gums.
Can natural remedies cure receding gums?
Natural remedies cannot cure or reverse receding gums, but some may help reduce inflammation and support gum health as complementary approaches:
- Oil pulling with coconut or sesame oil may help reduce bacteria
- Green tea contains antioxidants that may benefit gum health
- Aloe vera gel has anti-inflammatory properties that might soothe gum tissue
- Saltwater rinses can help reduce bacteria and soothe inflammation
These should be used alongside, not instead of, professional dental care and good oral hygiene practices.
Is an electric toothbrush better for receding gums?
Electric toothbrushes can be beneficial for people with receding gums because:
- Many models have pressure sensors that alert you if you’re brushing too hard
- Built-in timers ensure adequate brushing duration
- Some have specialized brush heads designed for sensitive gums
- The consistent motion may provide more thorough cleaning with less effort
However, proper technique is still essential—use gentle circular motions and hold the brush at a 45-degree angle to the gum line.
How often should I visit the dentist if I have receding gums?
If you have receding gums, you should visit your dentist more frequently than the standard twice-yearly recommendation. Every three to four months is often advised for monitoring and professional cleaning.
Your dentist might suggest even more frequent visits depending on the severity of your condition and how well you’re managing it at home.
Regular professional cleaning helps remove plaque and tartar that contribute to gum recession and allows your dentist to catch any worsening conditions early.
Conclusion
Receding gums is a common dental condition in Singapore that requires attention and proper care. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can take proactive steps to maintain your gum health and prevent further recession.
Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene practices, and healthy lifestyle choices are essential in managing and preventing gum recession.
Remember that early detection and intervention are key to preventing the progression of gum recession and maintaining optimal oral health.
If you notice any signs of receding gums, consult with a dental professional who can provide a comprehensive assessment and personalized treatment plan to address your specific needs.

