What is Indirect Pulp Therapy?
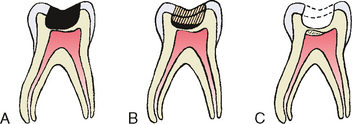
Indirect Pulp Therapy (IPT), also referred to as indirect pulp capping, is a minimally invasive dental procedure performed on teeth with deep cavities where the outer dentin layers are infected but the inner pulp remains healthy and unaffected.
The procedure is designed to protect and restore the tooth by reducing the risk of exposure to the tooth’s pulp tissue.
In this conservative treatment approach, the dental pulp tissue is left untouched and is covered with a biocompatible material to prevent microleakage.
Unlike more invasive procedures such as pulpotomy, indirect pulp therapy doesn’t require reopening the cavity for treating deep caries lesions.
This treatment is particularly valuable for primary teeth and young permanent teeth that may be developing incorrectly, as it helps maintain the tooth’s vitality while allowing for natural development.
You might want this: Pulpotomy Treatment in Singapore
When is Indirect Pulp Therapy Necessary?
Deep cavities requiring indirect pulp therapy may result from various factors, including:
- Tooth decay (dental caries)
- Chipped or fractured teeth
- Moderate to severe tooth wear
- Tooth abnormalities
The ideal candidates for indirect pulp therapy are patients with deep carious lesions that approach the pulp but show no signs or symptoms of pulpal degeneration. The tooth must be free from spontaneous pain, which is a crucial diagnostic factor indicating healthy pulp status.
For primary teeth and young permanent molars, the long-term retention requires a root with a favorable crown-to-root ratio and dentinal walls thick enough for proper function. IPT helps preserve these structures while treating the infection.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide To Seeing A Dentist In Singapore
Benefits of Indirect Pulp Therapy
Minimally Invasive Approach
Indirect pulp therapy is a conservative, less invasive treatment option compared to alternatives like pulpotomy or pulpectomy.
This approach helps preserve the vitality of the dental pulp, which is essential for continued tooth development in children.
Preventive Measure
IPT serves as an effective preventive measure against diseases of the pulp that could otherwise lead to toothache, dental infection, or gum disease.
By addressing deep caries before they reach the pulp, this treatment prevents more serious complications.
High Success Rates
Studies have consistently shown that indirect pulp therapy has high success rates compared to other similar methods.
Normal Exfoliation Pattern
For primary teeth, IPT has been shown to maintain a normal exfoliation pattern. Studies comparing IPT to formocresol pulpotomy found that 38% of pulpotomy-treated teeth demonstrated early exfoliation, while teeth treated with IPT maintained their natural exfoliation timeline.
You might be interested: Which Dental Clinic in Singapore Should You Consider? (Sort by Reviews)
The Indirect Pulp Therapy Procedure in Singapore
The indirect pulp therapy procedure typically involves two main stages:
Stage 1: Pre-Treatment Preparation
The first stage focuses on removing infected dentin while preparing the tooth for treatment:
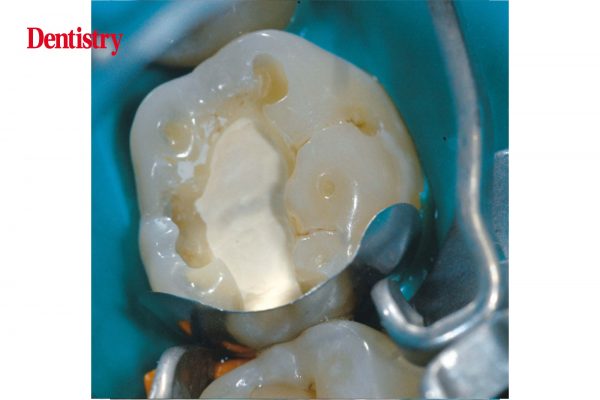
- The dentist removes the bulk of the carious tissue using hand instruments (excavators) rather than rotating burrs to avoid unnecessary pulp exposure.
- A bactericidal liner, such as calcium hydroxide, is applied over the remaining carious dentin.
- This application aims to induce tertiary dentin (reparative dentin) formation, protect the dental pulp tissue, and stimulate healing and repair.
- The liner also enhances the restorative material and tooth structure interfacial seal, providing adequate control of microleakage.
Related article: Receding Gums in Singapore: Causes, Treatments & Prevention
Stage 2: The Main Procedure
The second stage involves the application of medication and restoration of the tooth:
- Indirect pulp therapy is performed as a supplementary procedure to placing a dental filling (typically composite resins).
- Just before the filling is placed, a layer of medication is used to line the base of the cavity overlying the pulp.
- This medication has antibacterial and soothing effects that help protect and heal the pulp, preserving its health and vitality.
- The tooth is then restored with a material that seals it from microleakage, usually a dental composite or glass ionomer cement.
- In some cases, a temporary filling might be placed for 2-3 weeks before the final restoration to ensure the pulp remains healthy.
Materials Used in Indirect Pulp Therapy
Several materials are commonly used in indirect pulp therapy in Singapore:
Calcium Hydroxide
For decades, calcium hydroxide has been considered the gold standard for indirect pulp therapy. When applied to affected dentin, it:
- Creates conditions conducive to healing of the pulp tissue
- Induces the formation of tertiary dentin through its high pH
- Provides antibacterial properties to eliminate remaining bacteria
- Stimulates the production of reparative dentin
Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA)
MTA has gained popularity as an alternative to calcium hydroxide in recent years:
- Contains primarily tricalcium and dicalcium silicate, similar to Portland cement
- Includes bismuth oxide for radiopacity
- Exhibits calcified tissue-conductive activity
- Facilitates the differentiation of pulp cells into odontoblast-like cells
- Forms a superior long-term seal and demonstrates enhanced biocompatibility
- Has higher success rates in clinical studies
Glass Ionomer Cements
Glass ionomer cements are often used as liners in indirect pulp therapy because they:
- Bond chemically to tooth structure
- Release fluoride, providing antibacterial properties
- Create a good seal against microleakage
- Are biocompatible with pulp tissue
You might be interested: Teeth Whitening in Singapore
Biodentine
Biodentine is a newer bioactive material used in indirect pulp therapy:
- Contains primarily tricalcium and dicalcium silicate
- Uses zirconium dioxide as a contrast medium
- Forms calcium hydroxide during the setting process
- Stimulates tertiary dentin formation more rapidly than traditional materials
- Offers better physical properties with high compressive strength
- Provides excellent sealing ability
Related article: Common Dental Problems in the Elderly: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Indirect Pulp Therapy vs. Direct Pulp Capping

It’s important to understand the difference between indirect pulp therapy and direct pulp capping:
Indirect Pulp Therapy:
- Used when the pulp is not exposed
- Preserves a layer of demineralized dentin over the pulp
- Lower risk of pulp complications
- Preferred for primary teeth with deep caries
- Higher success rates in primary dentition
Direct Pulp Capping:
- Used when there is a small pulp exposure
- Medication is applied directly to the exposed pulp
- Higher risk of pulp inflammation and necrosis
- Less predictable results in primary teeth
- Better outcomes in young permanent teeth
In Singapore dental practices, indirect pulp therapy is generally preferred over direct pulp capping for primary teeth with deep caries, as it has demonstrated superior clinical and radiographic success rates.
Risks and Considerations
While indirect pulp therapy is generally considered safe and effective, there are some potential risks and considerations:
Residual Pulp Deterioration
As much as IPT aims to heal and soothe the pulp, there remains a slight chance that the pulp condition may deteriorate in the future, potentially requiring root canal treatment or extraction.
However, in deep cavities with a healthy pulp, attempting indirect pulp therapy followed by a simple filling is often worthwhile as a first-line approach.
Complete Caries Removal
The success of indirect pulp therapy depends significantly on the complete removal of decay from the walls of the cavity while preserving a thin layer over the pulp. Inadequate caries removal can lead to treatment failure.
Allergic Reactions
Patients with known allergies to any of the materials used (e.g., plasters) should inform their dentist beforehand so that alternative materials can be selected to avoid allergic reactions.
Follow-up Requirements
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the success of the treatment and ensure that the pulp remains healthy.
Radiographic evaluations may be necessary to confirm the formation of tertiary dentin.
You might be interested: Root Canal Treatment in Singapore
Indirect Pulp Therapy in Singapore: Current Practices
In Singapore, indirect pulp therapy is widely practiced in pediatric dentistry for managing deep caries in primary teeth.
The procedure aligns with the current emphasis on minimally invasive dentistry and preserving natural tooth structure whenever possible.
Singapore dental practitioners typically follow a stepwise excavation approach when performing indirect pulp therapy:
- Removal of the bulk carious tissue without disturbing the tissue closest to the pulp
- Application of a biocompatible liner or medication
- Placement of a temporary or permanent restoration
- Follow-up evaluations to monitor treatment success
The high success rates of indirect pulp therapy in Singapore make it a preferred treatment option for children with deep caries, helping to maintain primary teeth until their natural exfoliation.
Long-term Outcomes and Success Rates
Research on indirect pulp therapy in primary teeth has shown favorable long-term outcomes:
- Studies report 3-year survival rates of approximately 96% in primary molars
- Comparative studies have shown IPT to be significantly more successful than formocresol pulpotomy (96.2% vs. 65.8%)
- At 4-year follow-up, IPT demonstrated a 93% success rate compared to approximately 63% for ferric sulphate pulpotomy
- IPT-treated teeth typically maintain normal exfoliation patterns
These high success rates make indirect pulp therapy an excellent choice for preserving and maintaining primary teeth until their natural replacement by permanent teeth.
Choosing the Right Dental Provider for Indirect Pulp Therapy in Singapore
When seeking indirect pulp therapy in Singapore, consider these factors when selecting a dental provider:
Specialized Training
Look for dentists with specialized training in pediatric dentistry or endodontics, as they have advanced knowledge and experience in pulp therapy procedures.
Modern Technology and Materials
Choose dental clinics that utilize contemporary materials like MTA or Biodentine and have access to modern diagnostic tools such as digital radiography for accurate assessment of caries depth.
Patient-Centered Approach
Select providers who demonstrate a gentle, patient-centered approach, especially when treating children, as this contributes significantly to the overall success of the treatment.
Follow-up Care
Ensure that the dental practice has a structured follow-up protocol to monitor the success of indirect pulp therapy and address any concerns promptly.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Deep Caries
While indirect pulp therapy is an effective treatment for deep caries, preventing the development of extensive cavities remains the best approach. Consider these preventive measures:
- Maintain regular dental check-ups every 6 months
- Practice thorough oral hygiene with proper brushing and flossing
- Use fluoride toothpaste and consider professional fluoride treatments
- Implement dietary modifications to reduce sugar consumption
- Consider dental sealants for susceptible teeth
- Address early signs of dental decay promptly
Frequently Asked Questions
Is indirect pulp therapy painful?
Indirect pulp therapy is generally not painful as it is performed under local anesthesia.
The procedure aims to preserve the vitality of the pulp and actually helps relieve pain associated with deep caries. Most patients, particularly children, tolerate the procedure well with minimal discomfort during and after treatment.
How long does indirect pulp therapy last?
When performed correctly on suitable cases, indirect pulp therapy can be highly successful with studies showing success rates of up to 96% after 3 years. For primary teeth, the treatment typically lasts until the natural exfoliation of the tooth. For permanent teeth, successful indirect pulp therapy can potentially preserve the tooth indefinitely, provided good oral hygiene is maintained.
Can indirect pulp therapy be performed on adults?
Yes, indirect pulp therapy can be performed on adults, particularly for deep caries in permanent teeth where pulp exposure is imminent but has not yet occurred.
However, the procedure is more commonly performed on children with deep caries in primary teeth or young permanent teeth. In adult cases, the dentist will carefully evaluate pulp vitality and the extent of caries before recommending this treatment.
How much does indirect pulp therapy cost in Singapore?
The cost of indirect pulp therapy in Singapore typically ranges from SGD $150 to $300 per tooth, depending on the clinic, the dentist’s expertise, and the materials used. This price usually includes the procedure itself and the final restoration.
Additional costs may apply for diagnostic procedures such as X-rays or follow-up visits. Some dental insurance plans may cover part of this treatment.
How is indirect pulp therapy different from a regular filling?
Indirect pulp therapy differs from a regular filling in that it specifically addresses deep cavities that are close to the pulp.
While a standard filling simply removes all caries and restores the tooth, indirect pulp therapy involves a more conservative approach to caries removal near the pulp, followed by the application of special medicaments to promote healing and repair before the final restoration is placed.
What signs indicate that indirect pulp therapy has failed?
Signs that may indicate failure of indirect pulp therapy include persistent or new pain, swelling or abscess formation, tooth sensitivity to temperature changes that doesn’t resolve, mobility of the treated tooth, or radiographic evidence of periapical pathology.
If any of these symptoms occur, further treatment such as pulpotomy, pulpectomy, or extraction may be necessary.
Is indirect pulp therapy covered by MediSave in Singapore?
Generally, indirect pulp therapy is not covered by MediSave in Singapore as it falls under routine dental treatment.
However, some integrated shield plans or private dental insurance may provide coverage for this procedure.
It’s advisable to check with your specific insurance provider regarding coverage for dental treatments. Public healthcare institutions might offer subsidized rates for eligible patients.
What are the alternatives to indirect pulp therapy?
Alternatives to indirect pulp therapy include direct pulp capping (if there’s minimal pulp exposure), pulpotomy (removal of the coronal pulp tissue), pulpectomy (complete removal of pulp tissue), or extraction followed by space maintenance or eventual replacement. The choice between these options depends on the extent of caries, pulp status, patient’s age, and the strategic importance of the tooth.
How long does the indirect pulp therapy procedure take?
The actual indirect pulp therapy procedure typically takes about 30 to 45 minutes to complete. This includes time for administering local anesthesia, removing caries, applying the medicament, and placing the final restoration.
In some cases where a temporary restoration is used initially, a second appointment of similar duration may be required for the final restoration.
Can indirect pulp therapy be performed on baby teeth?
Yes, indirect pulp therapy is actually most commonly performed on baby teeth (primary dentition). It’s particularly valuable for preserving primary molars with deep caries until their natural exfoliation time.
Maintaining these primary teeth is important for proper speech development, chewing function, and preserving space for the permanent teeth that will eventually replace them.

