Functional dyspepsia is a chronic digestive condition characterized by persistent or recurrent symptoms of indigestion without a clear identifiable cause.
It’s a very common condition affecting over 20% of the global population, with 8 out of 10 cases of chronic indigestion ultimately being diagnosed as functional dyspepsia.
Understanding Functional Dyspepsia
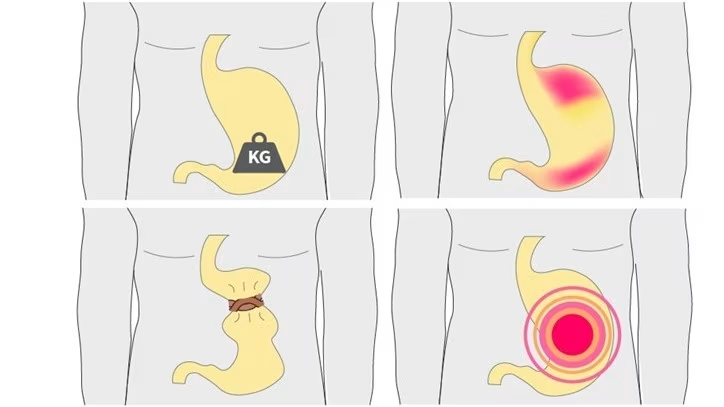
Functional dyspepsia causes pain and discomfort primarily in the upper abdomen, accompanied by a sense of fullness or bloating during or after meals.
Unlike other digestive disorders with clear causes, functional dyspepsia has no known single definitive cause, making it more challenging to diagnose and treat.
Types of Functional Dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia can be classified into two main categories, which often overlap:
- Epigastric Pain Syndrome (EPS) – Characterized by recurrent pain or discomfort in the upper abdomen.
- Postprandial Distress Syndrome (PDS) – Characterized by uncomfortable feelings of fullness that occur following the consumption of a meal, early satiety, and bloating.
Functional Dyspepsia vs. Other Conditions
It’s important to distinguish functional dyspepsia from other similar conditions:
Functional Dyspepsia vs. GERD
While both conditions share similar symptoms, acid reflux and GERD sufferers predominantly present symptoms of heartburn and regurgitation.
Dyspepsia usually involves an intermittent or aching pain that affects the upper abdomen (epigastric pain).
GERD has been on the rise in Singapore in recent years, highlighting the need for accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
Read more: Acid Reflux and GERD in Singapore: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Functional Dyspepsia vs. Gastritis
Gastritis occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed and may have many possible causes, including Helicobacter pylori infection, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
Both conditions share similar symptoms, but they are completely different. It’s possible to experience some relief from gastritis treatment, but specific treatment for functional dyspepsia is still necessary if you have both conditions.
Maybe you are interested: Comprehensive Guide to Colonoscopy in Singapore
Causes of Functional Dyspepsia
While there’s no single definitive cause, several factors may contribute to functional dyspepsia:
- Food allergies and other allergens
- Impaired stomach emptying
- Helicobacter pylori infection
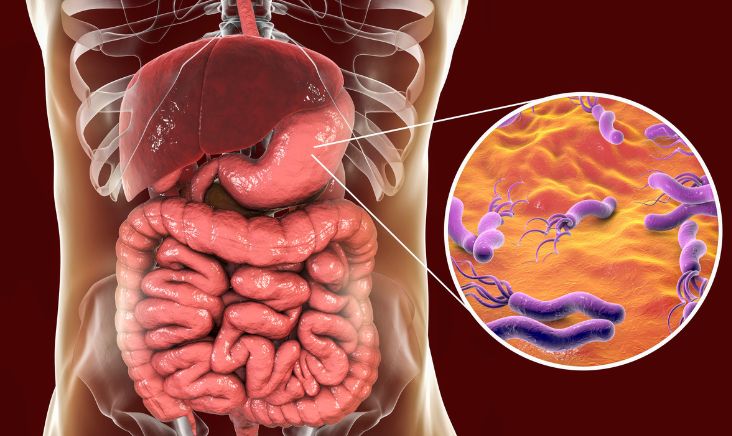
- Intestinal microbiome changes
- Elevated acid secretion
- Diet and lifestyle habits
- Certain medications
- Stress (visceral hypersensitivity)
- Changes in the amount or types of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract
- Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract
You might be interested: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment in Singapore
Symptoms of Functional Dyspepsia
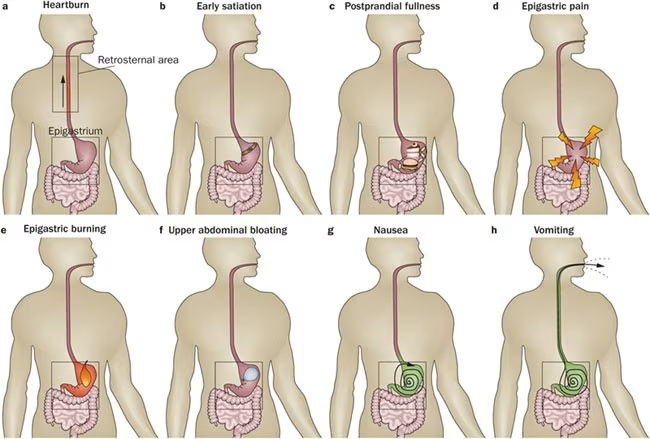
Functional dyspepsia is a chronic condition, and symptoms can come and go over time, depending on certain factors and triggers. Common symptoms include:
- Epigastric (upper abdominal) pain or burning
- Bloated stomach
- Excessive belching
- Sour taste in the mouth
- Early satiety (feeling full quickly after small meals)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Indigestion
- Acid reflux
- Heartburn
These symptoms can significantly impact your quality of life, making everyday activities uncomfortable and sometimes challenging.
Related article: Celiac Disease Treatment in Singapore
Risk Factors for Functional Dyspepsia
Certain factors can increase your risk of developing functional dyspepsia:
- Female gender
- Overuse of over-the-counter pain relief medication, like aspirin
- Smoking or using tobacco products
- Anxiety or depression
- A history of childhood physical or sexual abuse
- Helicobacter pylori infection
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Food allergies
- Psychosocial dysfunction
- Recent antibiotic use
- Long-term use of NSAIDs
- Being overweight
- Stress
This might help: The Ultimate Guide to Losing Weight in Singapore
When to See a Doctor
While functional dyspepsia is generally not associated with severe complications, it’s important to seek medical attention if:
- Your symptoms persist, causing concern and worry
- You experience severe symptoms like unexplained weight loss
- You have black tarry stools
- You experience bloody vomit
- You have shortness of breath
- You feel pain in your jaw, neck, or arm
- Your symptoms are not resolved by medication
- Your symptoms have persisted for more than 2 weeks
- You’re over the age of 40 with recurring symptoms
You might be interested: Health Screening in Singapore
Diagnosis of Functional Dyspepsia
Diagnosis of functional dyspepsia involves several steps:
- Medical History Review – Your gastroenterologist will assess your condition by reviewing your medical history and current signs and symptoms.
- Physical Examination – A thorough physical examination helps to rule out other conditions.
- Diagnostic Tests – Various tests may be conducted to exclude other disorders that may mimic dyspepsia:
- Gastroscopy (OGD) – To detect any structural abnormalities in the upper GI tract, such as ulcers, inflammation, or tumors.
- Blood Tests – To rule out infections and diseases that may be causing your symptoms.
- Urea Breath Test – To detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori in your stomach.
- Hydrogen Breath Test – Some gastroenterologists may utilize this to detect small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
- Gastric Emptying Studies – To examine how quickly your stomach empties food into your small intestine.
Treatment Options for Functional Dyspepsia in Singapore
The treatment prescribed depends on your symptoms and the suspected probable cause of your functional dyspepsia.
Medications
Several medications can help manage functional dyspepsia symptoms:
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) – These medications help reduce stomach acid production and can be helpful in alleviating the symptoms of acid reflux, making it easier for your stomach lining to heal.
- Histamine Receptor Blockers (H2 blockers) – These prevent the stomach from producing too much acid, which helps you heal.
- Prokinetic Drugs – More effective with PDS than EPS, these medications help your stomach empty its contents quickly into the small intestine without holding onto food for too long.
- Antiemetics – Beneficial in relieving nausea.
- Low-dose Antidepressants – Known to be helpful in treating functional dyspepsia, especially for patients whose symptoms appear to be related to the nervous system. They help reduce the patient’s perception of pain and discomfort and help the stomach to relax.
- Antibiotics – If H. pylori infection is detected, antibiotics will be prescribed to eradicate the bacteria.
You might be interested: Homeopathy in Singapore
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy can be useful in easing symptoms that cannot be managed by medication alone. Working with a therapist or counselor allows you to:
- Learn relaxation techniques that will benefit you in coping with symptoms
- Reduce stress that flares up due to the condition
- Learn cognitive behavioral therapy techniques to manage your symptoms better
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle modifications are often recommended, especially in the initial phase of treatment:
- Dietary Changes
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of large meals
- Avoid trigger foods that worsen your symptoms (often fatty, spicy, or greasy foods)
- Maintain regular mealtimes
- Consider keeping a food diary to identify specific triggers
- Stress Management
- Practice deep breathing exercises
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Try yoga or meditation
- Ensure adequate sleep
- Avoid Irritants
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Quit smoking
- Reduce caffeine intake
- Avoid NSAIDs if possible (consult with your doctor for alternatives)
Living with Functional Dyspepsia in Singapore
Functional dyspepsia is a chronic condition, which means it may come and go, depending on many factors.
Although it is not a severe condition, it can significantly affect your quality of life. With proper management, most people can control their symptoms effectively.
Finding the Right Specialist
In Singapore, gastroenterologists specialize in treating functional dyspepsia and other digestive disorders.
When seeking treatment, look for a specialist with experience in treating functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Support and Resources
Living with functional dyspepsia can be challenging, but you’re not alone. Consider:
- Joining support groups for people with digestive disorders
- Using relaxation techniques and stress management strategies
- Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider about symptom changes
- Educating yourself about the condition through reliable resources
Prevention Strategies
While it may not always be possible to prevent functional dyspepsia entirely, these strategies may help reduce your risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat balanced, nutritious meals
- Manage stress effectively
- Avoid overuse of NSAIDs
- Quit smoking
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Stay hydrated
- Exercise regularly
FAQ on Functional Dyspepsia
What is the difference between functional dyspepsia and common indigestion?
The main difference is that we know the causes of common indigestion, which include overeating, consuming fatty, greasy, or spicy food.
However, the cause of functional dyspepsia is currently unknown, and symptoms persist for longer periods (at least three months).
Functional dyspepsia is a chronic condition requiring proper medical management.
Can functional dyspepsia be cured completely?
Functional dyspepsia is a chronic condition that can’t be completely cured in most cases.
However, with proper treatment and management, symptoms can be effectively controlled, allowing for a good quality of life. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms rather than providing a permanent cure.
Is functional dyspepsia the same as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)?
No, although they may coexist as medical conditions and are often misdiagnosed as each other. A thorough examination by a gastroenterologist will help identify which condition you have.
While both are functional gastrointestinal disorders, they affect different parts of the digestive system.
Functional dyspepsia affects the upper digestive tract, particularly the stomach and duodenum, while IBS affects the lower intestines.
Do I need to follow a special diet if I have functional dyspepsia?
There’s no one-size-fits-all diet for functional dyspepsia, but many patients benefit from eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding trigger foods such as spicy, fatty, or greasy items.
Some patients also find that reducing caffeine and alcohol intake helps. It’s advisable to keep a food diary to identify your specific triggers and work with a healthcare provider or dietitian to develop a personalized eating plan.
How common is functional dyspepsia in Singapore?
Functional dyspepsia is a very common disorder in Singapore, affecting a significant portion of the population.
It’s estimated that globally, 7 in every 100 people have the condition, and in Singapore, the prevalence is similarly high.
With the changing dietary habits and increased stress levels in urban settings like Singapore, the incidence of functional dyspepsia continues to be significant.
Can stress cause functional dyspepsia?
Stress doesn’t directly cause functional dyspepsia, but it can trigger or worsen symptoms in people who already have the condition.
The gut-brain connection plays a significant role in functional gastrointestinal disorders, and stress can increase sensitivity to pain and discomfort.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and other stress-reduction strategies can be an important part of controlling functional dyspepsia symptoms.
Is it safe to take over-the-counter medications for functional dyspepsia?
While over-the-counter medications like antacids can provide temporary relief for occasional symptoms, they’re not recommended as a long-term solution for functional dyspepsia without medical supervision.
Some medications may mask symptoms without addressing underlying issues, and some, like NSAIDs, can actually worsen the condition.
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any medication regimen for functional dyspepsia.
Will probiotics help with functional dyspepsia?
Changes in gut microbiota may play a role in functional dyspepsia, and probiotics might help restore a healthier bacterial balance.
However, not all probiotics are the same, and their effectiveness can vary based on strains and individuals. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting probiotic supplements.
How is functional dyspepsia different in elderly patients?
Elderly patients with functional dyspepsia may present with less typical symptoms, sometimes reporting more vague complaints like decreased appetite or unexplained weight loss rather than specific pain patterns.
Additionally, older patients often have more comorbidities and take multiple medications that can complicate diagnosis and treatment. It’s especially important for elderly patients to seek proper medical evaluation for digestive symptoms to rule out more serious conditions.
Can children get functional dyspepsia?
Yes, children can develop functional dyspepsia, although it’s less commonly diagnosed than in adults. In children, the symptoms may present differently, and diagnosis requires careful evaluation to rule out other conditions.
Treatment approaches are similar to those for adults but must be adjusted for age and developmental considerations. If your child is experiencing persistent digestive discomfort, consult with a pediatric gastroenterologist.
Conclusion
Functional dyspepsia is a common and often frustrating condition that affects many Singaporeans. While it’s not life-threatening, it can significantly impact your quality of life.
The good news is that with proper diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment approach combining medications, behavioral therapy, and lifestyle changes, most people can effectively manage their symptoms.
If you’re experiencing persistent digestive symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult with a gastroenterologist.
Early diagnosis and targeted treatment can help you regain control of your digestive health and improve your overall well-being.
Remember that functional dyspepsia is a chronic condition that may require ongoing management, but with the right approach, you can minimize its impact on your daily life.

