Understanding Hemorrhoids (Piles)
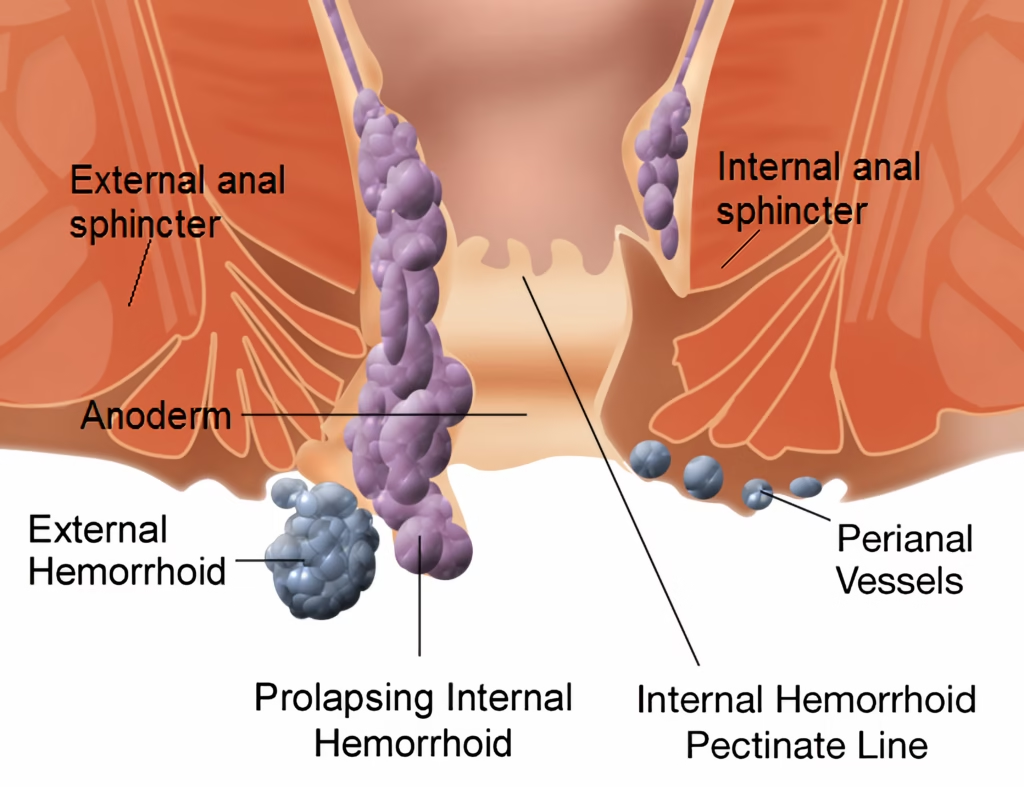
Hemorrhoids, commonly known as piles, are abnormally engorged and swollen blood vessels in the anus and lower rectum. These vessels may rupture and cause bleeding or slip out of place during defecation.
Hemorrhoids cause discomfort and itching, affecting a person’s daily lifestyle, which is when treatment becomes necessary – a condition referred to as hemorrhoidal disease.
Despite its prevalence, many people feel too embarrassed to consult a doctor until the pain becomes unbearable or when bleeding occurs, causing concern that it might be something more serious.
You might be interested: Health Screening in Singapore
Types of Hemorrhoids
There are several types of hemorrhoids that patients should be aware of:
Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids develop within the rectum. They may be present without causing pain or discomfort initially.
However, straining during bowel movements may cause them to bleed and protrude due to prolapse.
Defecation can cause trauma and bleeding, while the presence of stool and constant moisture in the anal canal can lead to anal itchiness, although itchiness is not a common symptom of hemorrhoids.
Internal hemorrhoids are classified according to their degree of prolapse:
- First-degree hemorrhoids: Bleed but do not prolapse (do not protrude from the anus)
- Second-degree hemorrhoids: Prolapse and retract on their own, with or without bleeding
- Third-degree hemorrhoids: Prolapse but must be pushed back in by a finger
- Fourth-degree hemorrhoids: Prolapse and cannot be pushed back in
Less commonly, the hemorrhoid protrudes from the anus and cannot be pushed back inside, a condition referred to as incarceration of the hemorrhoid.
External Hemorrhoids
External hemorrhoids develop around the anus and can be felt as bulges at the anal opening.
They usually cause fewer symptoms typical of internal hemorrhoids but can be irritated, leading to itching or bleeding.
External hemorrhoids can cause a very painful anal lump when blood clots inside them, a condition known as thrombosed hemorrhoid.
Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
This occurs when blood clots form in an external hemorrhoid. A thrombosed hemorrhoid often feels like a hard and painful lump due to inflammation and swelling.
Severe pain, itching, and bleeding are also common symptoms of this condition.
This might help: Best JB Health Screening Clinics for Singaporeans
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
The symptoms of hemorrhoids can mimic and mask symptoms of more serious conditions like cancer. It is important for any patient experiencing symptoms that might be attributed to hemorrhoids to consult a specialist surgeon for a full examination.
Signs and symptoms to watch for include bleeding during defecation, bleeding at times other than defecation (which is a warning sign that requires investigation), and a sensation of incomplete emptying that persists despite defecation.
Additional concerning symptoms include changes in the caliber and character of stools, changes in bowel habits, and the presence of an obvious hard mass at the anus.
Patients may also experience unexplained loss of appetite and weight, anal discomfort and pain, swelling around the anal area, discharge or mucus from the anal area, and itching in the anal region.
You might like: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment in Singapore
Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids
Multiple factors can contribute to developing symptomatic hemorrhoids. These are generally associated with conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure.
Common risk factors include persistent straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, and prolonged sitting on the toilet.
Lifestyle factors such as inadequate fiber intake, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle also contribute to hemorrhoid development.
Additional risk factors include genetics, as family history may increase susceptibility to the condition.
Pregnancy can cause hemorrhoids due to the growing fetus and labor exertion creating pressure on blood vessels. Less commonly, the existence of an intra-abdominal or pelvic tumor may contribute to hemorrhoid formation.
Poor toilet habits, such as reading newspapers or using mobile phones while on the toilet, can also increase risk.
You might like: The Ultimate Guide to Losing Weight in Singapore
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids
Diagnosis of hemorrhoids typically involves taking a medical history and conducting a symptom assessment. Healthcare providers perform a physical examination, including a rectal examination, and may use visual inspection with a proctoscope for internal hemorrhoids.
Additional tests like flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy may be necessary if there has been bleeding, to exclude other important causes such as colorectal cancer, polyps, or inflammatory bowel disease.
It’s crucial not to assume that rectal bleeding is simply due to hemorrhoids. Other serious conditions must be ruled out, especially since some rare cancers of the perianal area may masquerade as external hemorrhoids.
This might help: Homeopathy in Singapore
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids in Singapore
The treatment of hemorrhoids depends on the severity and type of symptoms affecting the patient. Here are the various treatment approaches available in Singapore:
Preventive Measures and Conservative Management
Simple preventive measures include:
- Having a balanced diet with adequate fiber intake
- Ensuring sufficient water intake to allow regular bowel movements without straining
- Avoiding prolonged sitting on the toilet
- Regular exercise to promote healthy bowel function
- Maintaining a healthy weight
These conservative measures are often sufficient for first-degree hemorrhoids and can provide relief even for more severe cases.
Medications and Topical Treatments
- Oral medications (such as Daflon, a micronized purified flavonoid fraction)
- Topical suppositories and creams to reduce swelling, pain, and itching
- Fiber supplements to soften stools
- Vasoconstrictors applied to the perianal area, which can reduce swelling and provide mild anesthetic effect
- Cold packs to soothe pain and reduce swelling
Related article: Comprehensive Guide to Colonoscopy in Singapore
Nonsurgical Procedures
For hemorrhoids that don’t respond to conservative treatments, several office-based procedures are available:
Rubber Band Ligation
This treatment works effectively on internal hemorrhoids that protrude with bowel movements.
A small rubber band is placed over the hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid and the band fall off in a few days, and the wound usually heals in a week or two.
This procedure sometimes produces mild discomfort and bleeding but is relatively simple and can be performed in an outpatient setting.
Injection (Sclerotherapy)
For this procedure, the doctor injects a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrivel and subsequently fall off.
This method is relatively painless and can be used on bleeding hemorrhoids that don’t protrude.
These nonsurgical procedures may not be extremely effective in all cases and might require more than one treatment session.
You might like: Acid Reflux and GERD in Singapore: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Surgical Treatments
More definitive measures are needed for severe cases, such as when clots repeatedly form in external hemorrhoids, when ligation fails to treat internal hemorrhoids, when a protruding hemorrhoid cannot be reduced, or when there is persistent bleeding.
Surgical techniques performed under general anesthesia include:
Hemorrhoidectomy
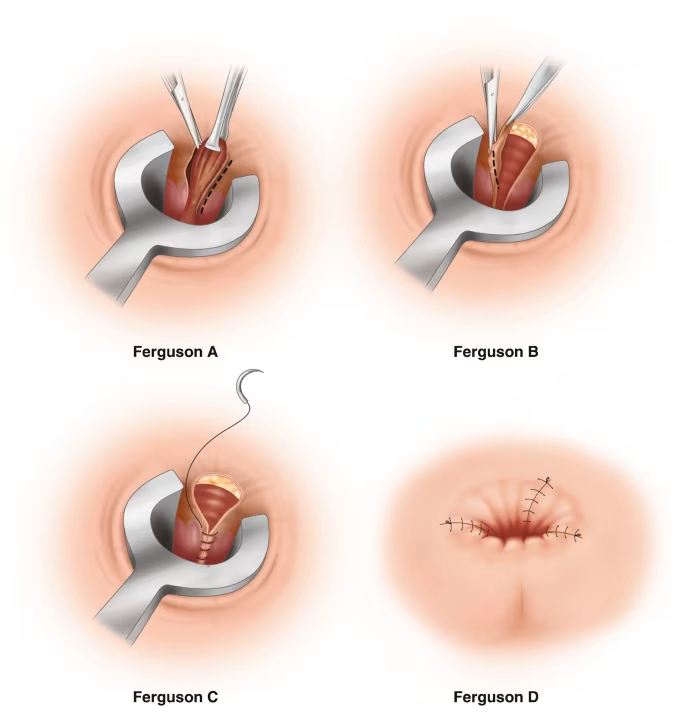
This is surgery to remove excessive tissue causing the bleeding and protrusion. It is the best method for the permanent removal of large, prolapsed hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoidectomy can be performed in two ways:
- Conventional (Open) Hemorrhoidectomy: During this procedure, the internal and external hemorrhoids are excised using diathermy. The wounds left by the removal are left open. This is typically performed as a day case procedure.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy: This technique doesn’t actually remove the hemorrhoids but rather the abnormally lax and expanded hemorrhoidal supporting tissue. A device is used to excise the hemorrhoids internally, and the internal wound is closed via a row of “staples.” Compared to the conventional method, stapled hemorrhoidectomy causes less discomfort and shorter duration of pain in the immediate postoperative period. It’s effective for treating large hemorrhoids that protrude during defecation, particularly for circumferential third or fourth hemorrhoids with minimal external components.
Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization (THD)
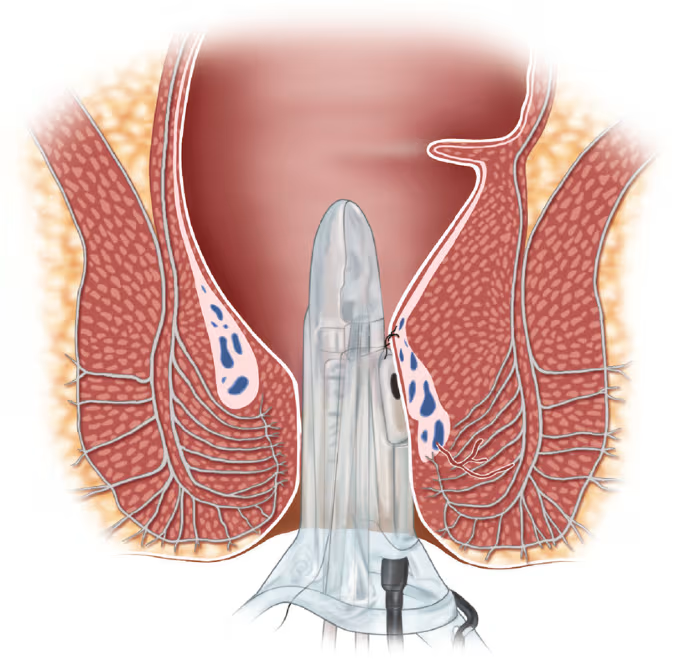
This procedure involves using ultrasound to locate the problematic blood vessels and stitching the hemorrhoids.
As methods may vary slightly from person to person, patients are advised to consult their surgeons to determine the right treatment for their specific condition.
Cost of Hemorrhoid Surgery in Singapore
The cost of hemorrhoid surgery in Singapore can vary depending on factors such as the medical facility, the complexity of the procedure, and individual insurance coverage:
- The fee for hemorrhoid surgery at a private hospital in Singapore typically costs between $3,000 – $3,800 (before GST). This is just the surgeon’s fee and does not include hospital or consumable fees.
- Hemorrhoid surgery is typically covered by insurance for those who have purchased an Integrated Shield Plan in Singapore, which enhances the basic MediShield Life coverage.
- The amount covered by insurance depends on your specific plan and coverage details. Typically, the plan can cover a significant portion of the surgery cost, including hospital fees and surgeon’s fees.
- Out-of-pocket expenses may include any deductible, co-payment, or costs not covered by your plan. The remaining amount can often be paid using a combination of Medisave and cash.
Additional Costs to Consider
There may be additional costs before and after hemorrhoid surgery that patients should factor into their budget.
Pre-surgical expenses include consultations with the surgeon and diagnostic tests such as imaging scans, blood tests, and other necessary assessments.
Post-surgical costs encompass follow-up appointments with the healthcare team, medications for pain management or other post-surgical needs, and physical therapy if recommended for recovery.
These costs are typically claimable under an Integrated Shield Plan, but patients may need to pay upfront and seek reimbursement later.
Complications and Risks
While hemorrhoid surgery is generally safe and effective, patients should be aware of potential complications that may arise.
Post-surgical pain represents the major concern with conventional hemorrhoidectomy procedures. Delayed hemorrhage can occur seven to fourteen days after surgery, affecting one to two percent of patients.
Infection is uncommon, with abscess formation occurring in less than one percent of cases.
Discharge is common and expected as wounds heal during the recovery process. Other possible complications include stricture, which involves narrowing of the anus due to scar tissue formation, and urinary retention.
For stapled hemorrhoidectomy specifically, additional risks may include damage to the rectal wall, sphincter dysfunction, pelvic sepsis, or persistent pain and fecal urgency. Patients should discuss these potential complications thoroughly with their surgeon before proceeding with any hemorrhoid surgery.
Preventing Hemorrhoids
One of the simplest ways to prevent hemorrhoids is to keep stools soft to reduce straining the blood vessels around the anal and rectal area. Here are some prevention tips:
- Increase fiber intake: The Singapore Health Promotion Board (HPB) recommends a daily intake of 26g of fiber for men and 20g for women – equivalent to two servings of fruit and two servings of vegetables per day. Adding more fiber to your diet can help reduce gas and bloating. Fiber supplements can be considered for those prone to constipation.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Stay hydrated to help soften stools. The Singapore Health Promotion Board recommends at least 6-8 glasses of water (approximately 1.5-2 liters) daily.
- Reduce straining during bowel movements: Avoid holding your breath when trying to pass stool, as this puts more pressure on the veins in the anal and rectal area.
- Respond promptly to the urge to defecate: Delaying can make stools dry and hard, making them more difficult to pass.
- Improve toilet habits: Avoid spending excessive time on the toilet while engaging in activities like reading, playing games, or using your phone. Long periods of sitting and poor posture can increase pressure on the veins.
- Exercise regularly: Moderate, consistent exercise helps promote regular bowel movements and maintains a healthy weight, reducing pressure on veins.
FAQ Section
What are hemorrhoids exactly?
Hemorrhoids are enlarged and swollen blood vessels in the anus and lower rectum. They are actually present in everyone and serve a normal function of helping with liquid and gas continence.
However, they become a problem when they enlarge, bleed, or protrude from the anus, causing symptoms that require treatment.
How common are hemorrhoids in Singapore?
One in three people in Singapore suffers from hemorrhoids, making it an extremely common condition. In particular, about half of the people over the age of 50 exhibit hemorrhoid symptoms.
Singapore has sometimes been jokingly referred to as the “piles capital of the world” due to the high prevalence of this condition.
At what age do people typically develop hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are more common after the age of 30. In particular, about half the people over the age of 50 experience hemorrhoid symptoms.
However, they can affect people of any age, including younger adults and even children in some cases.
Are hemorrhoids dangerous?
Hemorrhoids are rarely dangerous but can cause significant discomfort and affect quality of life. It is essential to see a doctor if symptoms are prolonged (especially for more than a week) to prevent further infection and to rule out more serious conditions.
The symptoms of hemorrhoids can sometimes mimic those of colorectal cancer, so proper diagnosis is important.
Why are pregnant women more likely to get hemorrhoids?
Pregnant women have a higher incidence of hemorrhoids because of the increased pressure on the pelvic area due to the growing fetus. Hormonal changes during pregnancy also contribute to this condition.
Additionally, straining during labor can exacerbate existing hemorrhoids or cause new ones to form.
How do I know if I have internal or external hemorrhoids?
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum where you typically cannot see or feel them. The most common symptom is bright red blood covering the stools.
External hemorrhoids occur near the anus and are covered by sensitive skin. You can usually feel them as bulges around the anal area, and they may cause itching, pain, and irritation.
When should I see a doctor about hemorrhoid symptoms?
You should see a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist for more than a week
- There is bleeding during bowel movements
- You experience severe pain
- You notice a substantial change in bowel habits
- There is an obvious hard mass at the anus
- You experience unexplained weight loss or appetite changes
Additionally, seek immediate medical attention if you observe non-stop bleeding and/or large blood clots.
What is the difference between rubber band ligation and hemorrhoidectomy?
Rubber band ligation is a quick, office-based procedure effective for treating internal hemorrhoids.
A small rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off blood flow, causing it to shrink and fall off. Hemorrhoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia to remove excessive hemorrhoidal tissue.
It’s typically reserved for more severe cases (third or fourth-degree hemorrhoids) when other treatments have failed.
Is hemorrhoid surgery painful?
Post-surgical pain is the major challenge with conventional hemorrhoidectomy. However, stapled hemorrhoidectomy is associated with less pain than traditional methods, allowing patients to return to work earlier.
Pain management options include NSAIDs and other prescribed pain medications to enhance relief during recovery.
Will my insurance cover hemorrhoid treatment in Singapore?
Hemorrhoid surgery is typically covered by insurance if you have purchased an Integrated Shield Plan in Singapore.
This plan enhances the basic MediShield Life coverage, providing more comprehensive protection for procedures like hemorrhoid surgery.
The amount covered depends on your specific plan details, the type of ward chosen, and other factors. It’s best to consult with your insurer for precise information.
Can hemorrhoids come back after treatment?
Yes, hemorrhoids can recur even after treatment, especially if the underlying causes (such as constipation, straining, or poor toilet habits) are not addressed.
After rubber band ligation, symptoms can recur several years later but usually can be treated with further ligation.
Even after surgery, there is a possibility of recurrence if preventive measures are not followed.
What lifestyle changes can help manage hemorrhoids?
Several effective lifestyle changes can help manage hemorrhoids and prevent their recurrence.
Dietary modifications play a crucial role, including increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as drinking plenty of water with a recommended intake of six to eight glasses daily.
Regular exercise is beneficial for overall digestive health and hemorrhoid prevention. Bathroom habits should also be modified by avoiding prolonged sitting on the toilet and responding promptly to the urge to defecate.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding straining during bowel movements are important preventive measures.
What are the risks of leaving hemorrhoids untreated?
Leaving hemorrhoids untreated can lead to several serious complications. One significant risk is anemia resulting from excessive blood loss, especially if bleeding persists for a prolonged period. Infection may also occur due to bacterial exposure in the affected area.
More severe complications include thrombosed hemorrhoids rupturing, which can lead to severe pain and bleeding. Strangulated hemorrhoids represent another serious condition where the blood supply gets cut off, causing extreme pain.
Finally, untreated hemorrhoids may lead to the development of skin tags that can make maintaining proper hygiene difficult.
What is a thrombosed hemorrhoid and how is it treated?
A thrombosed hemorrhoid occurs when a blood clot forms inside an external hemorrhoid. It causes an anal lump that is very painful and may require incision and drainage for immediate symptom relief.
This small procedure can provide quick pain relief. In some cases, the thrombosed hemorrhoid heals with scarring and leaves a skin tag protruding from the anus.
How effective is stapled hemorrhoidectomy compared to conventional surgery?
Stapled hemorrhoidectomy causes less discomfort and shorter duration of pain in the immediate postoperative period compared to conventional hemorrhoidectomy.
It’s particularly effective for circumferential third or fourth-degree hemorrhoids with minimal external components.
However, it’s not suitable for all patients, and the best results are obtained in only a selected group of patients. The procedure also carries specific risks, including damage to the rectal wall, sphincter dysfunction, and potential persistent pain.
The comprehensive approach to hemorrhoid treatment in Singapore ensures that patients have access to various options based on their specific condition, from conservative management to advanced surgical techniques.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can make informed decisions about managing this common but often embarrassing condition.

