Dental cysts are a common oral health issue that many Singaporeans face, often discovered during routine dental examinations.
These fluid-filled sacs develop within the jawbone and, while typically asymptomatic initially, can lead to significant complications if left untreated.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about dental cysts, their removal, and the enucleation procedure as practiced in Singapore’s dental clinics.
Understanding Dental Cysts
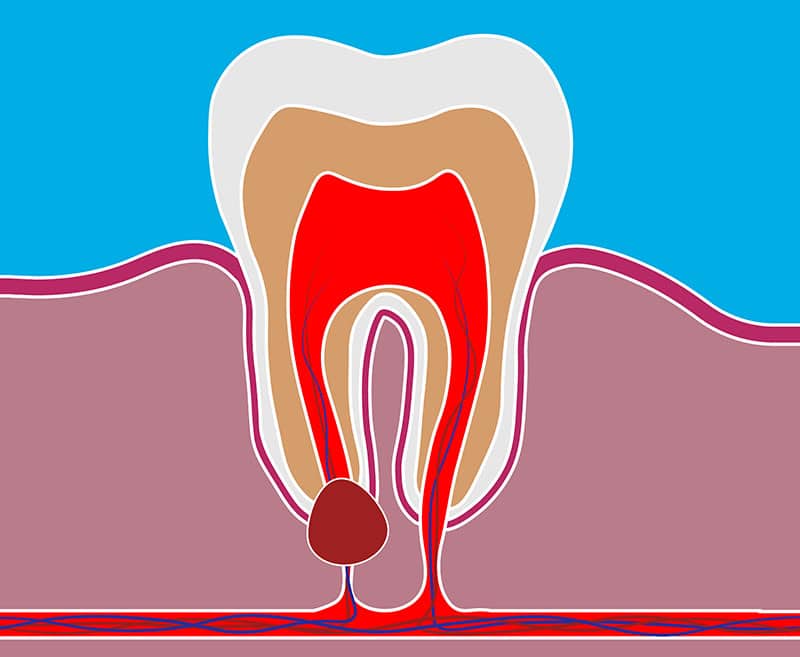
A dental cyst is an abnormal sac of tissue containing fluid or soft materials that develops within the jawbone. Interestingly, cysts occur more frequently in the jaw than in any other bone in the human body. These formations can develop for various reasons, including:
- Infections from damaged or decayed teeth
- Inflammation at the root of a tooth with non-vital pulp
- Gum inflammation over erupting teeth (particularly wisdom teeth)
- From cells and fibers surrounding a developing tooth
- Certain inherited conditions such as Gorlin-Goltz syndrome
Most dental cysts grow slowly and silently, often without causing noticeable symptoms until they reach a considerable size.
This silent progression makes regular dental check-ups particularly important for early detection.
Read more: Which Dental Clinic in Singapore Should You Consider? (Sort by Reviews)
Types of Dental Cysts
Dental cysts are broadly categorized into two main groups: odontogenic cysts (related to tooth development) and non-odontogenic cysts (unrelated to tooth development).
Understanding these different types can help patients comprehend their diagnosis better.
Odontogenic Cysts
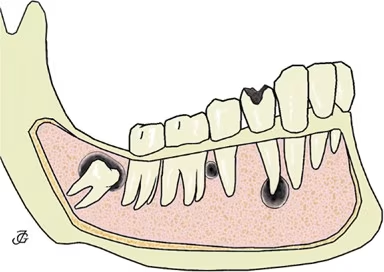
These cysts originate from dental tissue and are the most common type found in the jawbone. They include:
Dentigerous Cysts: These develop around the crown of an unerupted tooth, commonly affecting wisdom teeth or other teeth that haven’t emerged properly. They form from the accumulation of fluid between the tooth crown and surrounding follicle.
Periapical Cysts (Radicular Cysts): These form at the root tip of a tooth with infected or dead pulp. They’re often a consequence of untreated dental decay that has progressed to pulp infection. A periapical cyst may potentially develop into an abscess if not addressed.
Keratocystic Odontogenic Cysts: These aggressive cysts are typically found in the lower jaw (mandible) and have a higher recurrence rate than other types, making thorough treatment essential.
Read more: The Complete Guide to Orthodontists in Singapore
Non-Odontogenic Cysts
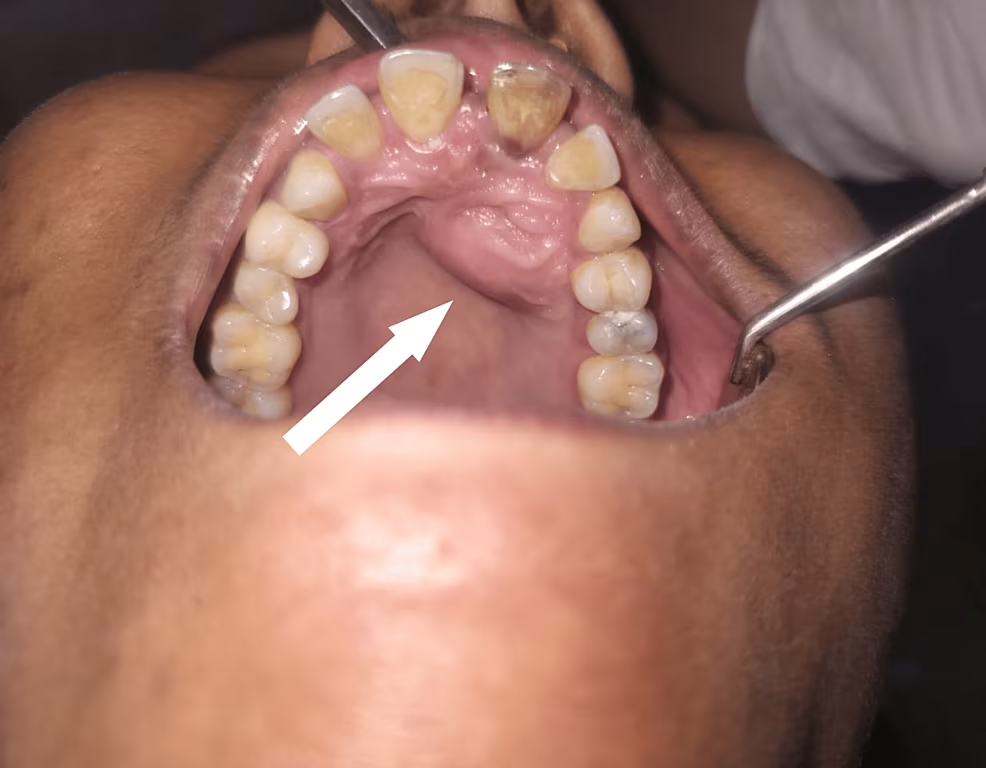
These cysts develop in tissues surrounding teeth but aren’t directly related to tooth development. They are less common than odontogenic cysts and can be found in:
- Bone marrow spaces
- Nasal canals
- Soft tissues of the mouth
While rarer, these cysts still require prompt attention when discovered.
Why Dental Cyst Removal is Necessary
Many patients wonder why asymptomatic cysts require treatment. The answer lies in their potential for growth and complications:
- Progressive Growth: Dental cysts tend to enlarge over time, potentially reaching sizes that can significantly compromise jaw structure.
- Damage to Adjacent Structures: As cysts expand, they can damage neighboring teeth, nerves, and jawbone, potentially leading to:
- Tooth displacement or loosening
- Nerve damage and sensory disturbances
- Weakening of the jawbone, increasing fracture risk
- Interference with dental function
- Infection Risk: Large cysts are more prone to infection, which can lead to abscess formation and systemic health issues.
- Treatment Complexity: Smaller cysts are easier to treat with fewer complications. Waiting until a cyst becomes problematic typically results in more complex surgery and potentially less favorable outcomes.
Early intervention is therefore the preferred approach in Singapore’s dental practices, where preventive care is emphasized.
Read more: Which Orthodontist in Singapore Should You Consider? (Sort by Reviews)
The Cyst Removal Procedure in Singapore
In Singapore, dental cyst removal is typically performed by oral surgeons or specialists in oral and maxillofacial surgery. The procedure follows several well-defined stages:
Stage 1: Diagnosis and Consultation
Dental cysts are usually discovered during routine dental examinations through:
- Regular dental X-rays
- Cone Beam CT (CBCT) scans for more detailed imaging
Once identified, your dentist will discuss the findings with you and recommend removal of both the cyst and any involved teeth if necessary. This consultation stage is crucial for understanding your specific condition and treatment options.
Stage 2: Pre-Operative Planning
Before surgery, your dental surgeon will:
- Evaluate the size, location, and type of cyst
- Assess proximity to vital structures like nerves
- Determine the appropriate anesthetic approach
- Discuss your medical history to identify any risk factors
- Create a personalized treatment plan
Related article: Pulpotomy Treatment in Singapore
Stage 3: The Cyst Removal Surgery
The actual procedure typically takes between 45 to 90 minutes, depending on the cyst’s complexity. Here’s what to expect:
- Anesthesia: The area will be completely numbed with local anesthesia. Depending on your needs and agreed treatment plan, you may also receive:
- IV sedation for increased comfort
- General anesthesia for more complex cases
- Surgical Access: The surgeon will:
- Create a flap by lifting the soft gum tissue over the cyst
- If necessary, create an access window through the jawbone to reach the cyst
- Tooth Extraction: Any teeth involved with the cyst will be extracted if required.
- Enucleation: The surgeon will carefully remove (enucleate) the entire cyst. This involves separating the cyst lining from surrounding bone while keeping the cyst intact when possible.
- Cavity Cleaning: The remaining cavity is thoroughly cleaned to remove any remnants of cyst tissue.
- Closure: A watertight closure of the surgical site is performed to promote proper healing.
- Dressing Application: For larger cyst cavities, an external dressing might be placed over the area and removed after 24-48 hours. This helps reduce swelling and controls blood clot formation for enhanced healing.
- Pathological Examination: In most cases, the removed cyst is sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination to confirm its nature and ensure complete removal.
In Singapore, many dental clinics use advanced surgical techniques and equipment to minimize trauma and enhance recovery.
You might be interested: Orthognathic (Jaw) Surgery in Singapore: Costs, Risks, Recovery
Stage 4: Post-Operative Care
After surgery, your body requires time to heal. Your dentist will:
- Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor healing
- Provide instructions for home care
- Recommend appropriate pain management
- Advise on diet modifications during recovery
While complete bone healing and regeneration can take 6-12 months, most patients find that once their gums have healed within a few weeks, they’re no longer bothered by the cyst cavity.
Related article: Wisdom Tooth Removal Surgery: Risks, Benefits, Recovery
Recovery and Aftercare
Following dental cyst removal in Singapore, patients can expect:
First 24-48 Hours:
- Some bleeding from the surgical site (controllable with pressure using gauze)
- Swelling of the face, particularly around the surgical area
- Discomfort or pain manageable with prescribed medications
First Week:
- Gradual reduction in swelling and discomfort
- Soft diet recommended to avoid disturbing the surgical site
- Regular gentle rinsing with prescribed antimicrobial solutions
- Avoidance of strenuous physical activity
Long-Term Recovery:
- Gradual bone regeneration in the cyst cavity
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor healing
- Complete bone healing within 6-12 months
Your Singapore dental professional will provide specific aftercare instructions tailored to your individual case.
You might like: Root Canal Treatment in Singapore
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, dental cyst removal carries certain risks:
- Pain, swelling, and bruising (common and temporary)
- Infection (preventable with proper antibiotics and hygiene)
- Bleeding (typically minor and controllable)
- Damage to adjacent teeth or structures (rare with experienced surgeons)
- Temporary or permanent numbness if the cyst was near major nerves
- Incomplete removal and cyst recurrence (more common with certain cyst types)
Singapore’s dental professionals are trained to minimize these risks through careful planning and precise surgical techniques.
Choosing a Dental Clinic for Cyst Removal in Singapore
When seeking treatment for a dental cyst in Singapore, consider these factors:
- Specialist Qualifications: Look for clinics with oral surgeons or specialists in oral and maxillofacial surgery who have specific experience with cyst removal.
- Advanced Imaging Technology: Clinics with CBCT scanning capabilities can provide more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Comprehensive Approach: Choose providers who offer complete care from diagnosis through to post-operative follow-up.
- Treatment Options: Some clinics offer various anesthesia options, including sedation for anxious patients.
- Facilities: Modern, well-equipped surgical facilities indicate a clinic’s commitment to quality care.
Many Singapore dental clinics publish their success rates and patient testimonials, which can help in your decision-making process.
Prevention and Early Detection
While not all dental cysts are preventable, these practices can help with early detection and management:
- Maintain regular dental check-ups (at least twice yearly)
- Complete recommended dental X-rays
- Address tooth decay or infections promptly
- Follow through with recommended extractions, particularly for problematic wisdom teeth
- Seek immediate consultation for any unusual symptoms like swelling, pain, or numbness
Early detection typically results in simpler treatment and better outcomes.
FAQ
What is the cost of dental cyst removal in Singapore?
The cost of dental cyst removal in Singapore varies widely depending on several factors, including the size and complexity of the cyst, the type of anesthesia used, the credentials of the surgeon, and the clinic’s location. Generally, prices range from SGD 800 to SGD 3,000 for standard cyst removal procedures. More complex cases involving larger cysts or those near vital structures may cost more. Many Singapore dental clinics offer payment plans, and some procedures may be partially covered by Medisave for Singapore citizens and permanent residents.
How long does recovery take after dental cyst removal?
Initial recovery from dental cyst removal typically takes about 7-14 days, during which most swelling and discomfort subsides. During this period, patients can usually return to normal activities within 2-3 days, though strenuous physical activity should be avoided for at least a week. Complete healing of the surgical site takes approximately 2-4 weeks. However, full bone regeneration in the cyst cavity can take 6-12 months, though this doesn’t typically affect daily life once the initial healing is complete.
Is dental cyst removal painful?
The dental cyst removal procedure itself is not painful as it’s performed under local anesthesia, which completely numbs the area.
For anxious patients or complex cases, additional options like IV sedation or general anesthesia are available in many Singapore dental clinics.
After surgery, patients typically experience mild to moderate discomfort for several days, which can be managed with prescribed pain medications.
The level of post-operative discomfort depends on the size and location of the cyst and individual pain tolerance.
Can dental cysts come back after removal?
Most dental cysts, when properly removed through enucleation (complete removal of the cyst lining), do not recur. However, certain types, particularly keratocystic odontogenic tumors, have higher recurrence rates of up to 30%.
Following proper surgical protocol and complete removal of the cyst lining significantly reduces recurrence risk.
In Singapore, dental surgeons typically send removed cyst tissue for pathological examination to confirm complete removal and determine the cyst type, which helps assess recurrence risk and plan appropriate follow-up.
How are dental cysts diagnosed in Singapore?
Dental cysts are typically diagnosed through a combination of clinical examination and imaging studies. In Singapore, dentists routinely use panoramic X-rays during regular check-ups, which can reveal cysts as radiolucent (dark) areas in the jawbone.
For more detailed assessment, Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is widely available in Singapore dental clinics, providing three-dimensional images that show the cyst’s exact size, location, and relationship to surrounding structures.
In some cases, aspiration (fluid removal with a needle) might be performed to analyze the cyst contents and confirm diagnosis.
What causes dental cysts to form?
Dental cysts form due to various factors. Periapical (radicular) cysts develop from inflammation at the root tip of a tooth with infected or dead pulp, often resulting from untreated decay.
Dentigerous cysts form around the crown of an unerupted tooth, commonly wisdom teeth, due to fluid accumulation in the follicle. Some cysts develop from epithelial remnants left over from tooth development.
Certain genetic conditions, such as Gorlin-Goltz syndrome, can predispose individuals to multiple cysts. Trauma to teeth can also lead to cyst formation in some cases due to pulp damage and subsequent inflammation.
What are the signs that I might have a dental cyst?
Many dental cysts remain asymptomatic and are discovered during routine dental examinations.
However, as cysts enlarge, you might experience symptoms such as facial swelling or asymmetry, a noticeable lump in the gum tissue, pain or tenderness in the jaw, loosening of nearby teeth, delayed or prevented eruption of teeth, drainage of fluid with a salty taste, and numbness or tingling of the lips or gums if the cyst presses on nerves.
Any of these symptoms warrant prompt dental evaluation, as they may indicate a growing cyst or other oral health issues.
Are there alternatives to surgical removal of dental cysts?
For certain types of small cysts, particularly those associated with non-vital teeth, endodontic (root canal) treatment of the involved tooth might be sufficient to resolve the cyst without surgical intervention.
Another alternative for large cysts is marsupialization, where the cyst is surgically opened, sutured, and drained rather than completely removed. This technique reduces the size of the cyst gradually before complete removal.
Decompression, using a drain to gradually reduce cyst size, is another conservative approach. However, complete enucleation remains the gold standard in Singapore for most cysts to ensure total removal and prevent recurrence.
What should I eat after dental cyst removal surgery?
After dental cyst removal surgery, it’s advisable to follow a soft food diet for at least the first week. Suitable foods include yogurt, smoothies, mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, oatmeal, soft-cooked pasta, and soups (not too hot).
As healing progresses, you can gradually reintroduce firmer foods. Avoid spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods that might irritate the surgical site. Also avoid using straws, as the suction can dislodge blood clots and delay healing.
Stay well-hydrated but avoid alcohol and caffeine, which can interfere with healing and medication effectiveness.
How common are dental cysts in Singapore?
Dental cysts are relatively common in Singapore, with radicular (periapical) cysts being the most frequently encountered type.
Studies from the region indicate that approximately 7-12% of routine dental radiographs reveal cystic lesions, though many are small and asymptomatic.
The prevalence increases in adults over 30 years of age and is slightly higher in males than females. Dentigerous cysts associated with impacted wisdom teeth are particularly common in the Singaporean population due to the high rate of wisdom tooth impaction.
Regular dental check-ups are essential for early detection and treatment of these common oral conditions.

