Heart disease remains one of the leading health concerns globally, and Singapore has positioned itself as a premier destination for comprehensive cardiac care.
With advanced medical technology, world-class facilities, and experienced cardiologists, Singapore offers patients cutting-edge treatment options for various heart conditions.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about heart disease treatment in Singapore, from early detection to advanced surgical interventions.
Understanding Heart Disease: Signs and Symptoms
Heart disease encompasses a range of cardiovascular conditions that affect the heart’s ability to function properly.
Recognizing the warning signs early can be life-saving, as many people in the high-risk category remain unaware of their condition until it’s too late.
Read more: Which Cardiologist in Singapore Should You Consider? (Sort by Reviews)
Common Warning Signs to Watch For
The cardiovascular system can send several warning signals when blood vessels become clogged with fatty deposits, similar to how a sink becomes blocked and needs professional attention. These symptoms should never be ignored:
- Chest discomfort (angina): Often described as pressure, squeezing, or pain in the chest area
- Breathing difficulties: Shortness of breath during normal activities or at rest
- Chest heaviness: A feeling of weight or pressure in the chest region
- Radiating pain: Discomfort that spreads to the jaw, arms, or shoulder areas
- Digestive symptoms: Heartburn-like sensations, nausea, or vomiting
- Excessive perspiration: Unexplained heavy sweating, especially when combined with other symptoms
If these symptoms occur outside of obvious triggers like work stress or family visits, they warrant immediate medical attention and evaluation.
Related article: Comprehensive Guide to Coronary Angioplasty in Singapore
Comprehensive Diagnostic Procedures
Singapore’s healthcare system employs a multi-faceted approach to diagnosing heart disease, utilizing both non-invasive and invasive testing methods to provide accurate assessments.
Standard Diagnostic Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
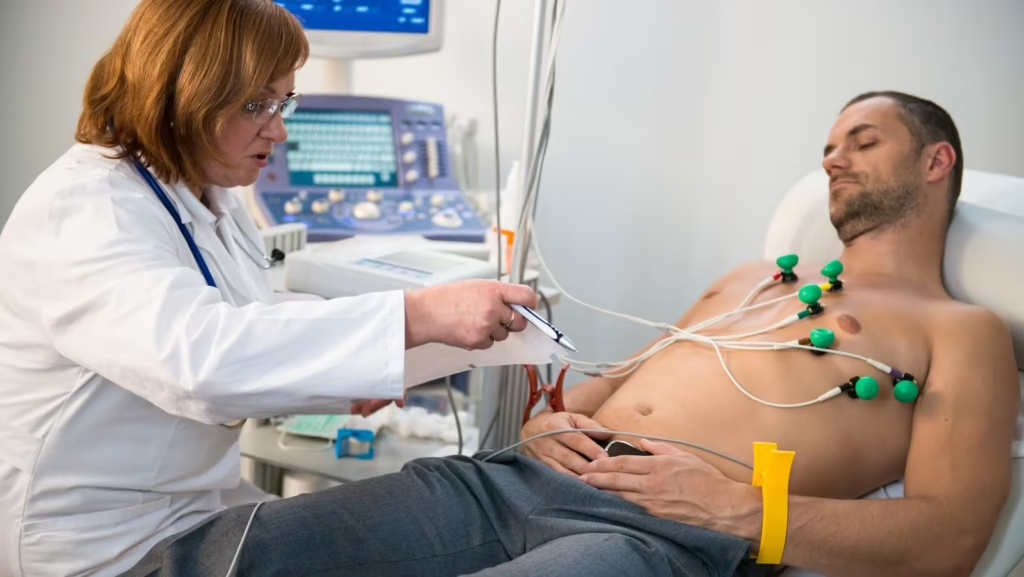
This fundamental test records the heart’s electrical activity over approximately 10 minutes. Small electrodes placed on the arms, legs, and chest capture the heart’s rhythm and electrical patterns, helping identify irregular heartbeats, previous heart attacks, and muscle damage.
Exercise Stress Testing
Patients perform physical activity on a treadmill while connected to monitoring equipment.
This test evaluates how the heart responds to increased demands and can reveal problems that might not appear during rest periods.
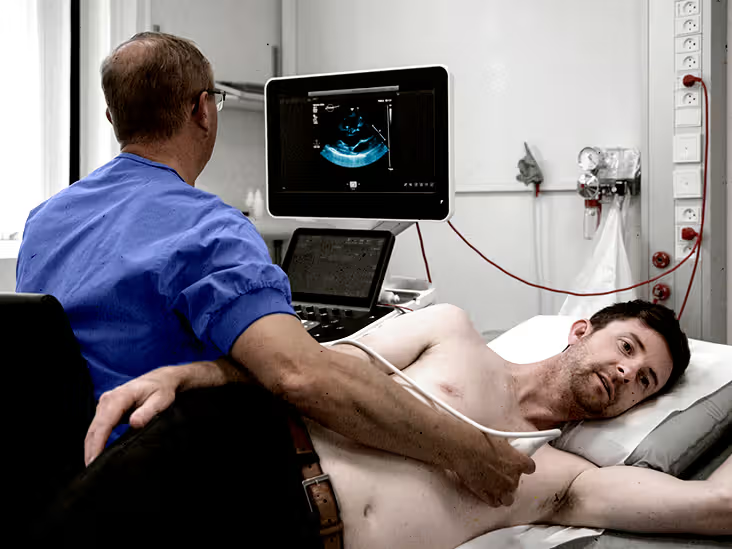
Using ultrasound technology, this procedure creates detailed images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and major blood vessels.
It provides crucial information about heart function and can detect structural abnormalities.
This specialized procedure involves injecting contrast dye through a catheter to visualize the coronary arteries on X-ray images.
It precisely identifies blocked vessels and determines the extent of narrowing in the arteries.
This might help: Health Screening in Singapore
Advanced Imaging Technologies
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
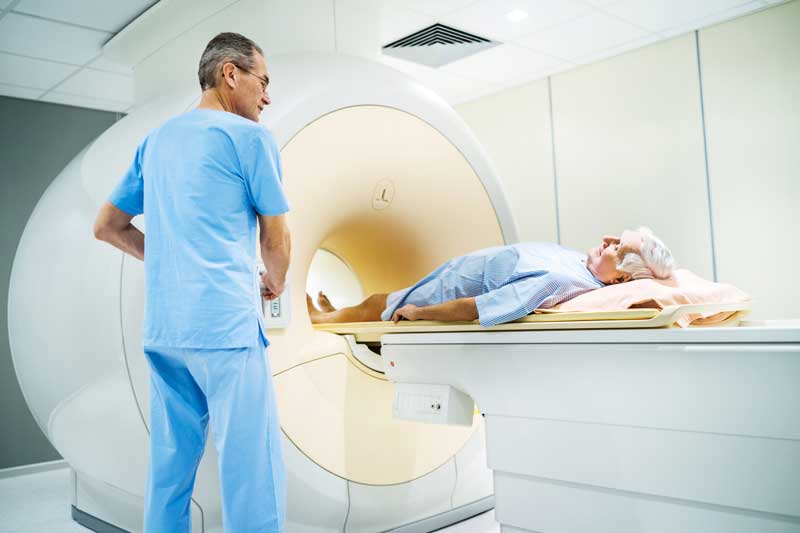
MRI technology produces high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the heart muscle, providing detailed information about tissue damage, coronary artery disease, and other cardiovascular defects.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans create cross-sectional images of the chest, including the heart and surrounding blood vessels.
They’re particularly useful for diagnosing cardiac tumors, aortic disease, and pericardial conditions.
Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
This procedure involves injecting small amounts of radioactive substances to track blood flow through the heart.
It helps assess chamber function, blood supply adequacy, and identify areas damaged by heart attacks.
Non-Invasive Treatment Approaches
Medication Management
Singapore’s cardiologists employ various medications to manage different aspects of heart disease:
These medications treat hypertension and congestive heart failure by reducing the narrowing effect on blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood efficiently.
Beta-Blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers
These drugs work by relaxing heart and blood vessel muscles, reducing the crushing chest pain associated with angina attacks.
Beta-blockers slow down hormone actions like adrenaline, while calcium channel blockers reduce calcium entry into coronary artery muscle cells.
Anticoagulants and Antiplatelet Medications
These blood-thinning medications prevent dangerous clot formation.
Anticoagulants target fibrin proteins, while antiplatelet drugs reduce the stickiness of blood platelets.
Aspirin is commonly prescribed for patients with coronary heart disease.
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Medications like amiodarone and flecainide help control irregular heart rhythms, ensuring the heart maintains a steady, effective beating pattern.
You might like: The Ultimate Guide to Losing Weight in Singapore
Lifestyle Modification Programs
Singapore’s healthcare system emphasizes comprehensive lifestyle changes as a cornerstone of heart disease treatment:
Nutritional Counseling
Patients receive guidance on adopting heart-healthy diets that emphasize vegetables, fruits, and lean proteins while reducing saturated fats, sodium, and sugar intake.
Exercise Rehabilitation
Structured physical activity programs help patients safely increase their cardiovascular fitness.
The National Heart Centre Singapore offers supervised exercise programs for patients with multiple heart disease risk factors.
Smoking Cessation Support
Comprehensive programs help patients quit smoking, as tobacco use significantly increases plaque formation in arteries and elevates blood pressure.
Advanced Invasive Procedures
Angioplasty and Stent Placement
This procedure involves inserting a catheter with a deflated balloon through an artery in the patient’s leg, then maneuvering it to the blocked coronary artery.
The balloon is inflated multiple times to compress cholesterol deposits against the artery wall, widening the opening and improving blood flow.
Stent Implantation
Following angioplasty, expandable metal mesh devices called stents are often placed to keep arteries open. These devices significantly reduce the likelihood of re-narrowing and maintain improved blood flow to the heart muscle.
Success Rates and Recovery
Both procedures boast success rates of approximately 90%, with relatively low risks of major complications.
Minor complications like bruising or bleeding at the insertion site may occur but typically heal without intervention.
Read more: Diabetes Treatment in Singapore: Types, Risks
Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
For patients with multiple blockages or those unsuitable for angioplasty, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) offers an alternative solution.
This procedure creates new pathways for blood to flow around blocked portions of coronary arteries.
Surgical Technique
Surgeons harvest healthy blood vessels from other parts of the patient’s body, typically from the leg veins or internal mammary arteries.
These grafts are then connected to create alternative routes for blood flow, bypassing the obstructed areas.
Recovery and Outcomes
Patients typically require three to four bypass grafts on average. Following recovery, most patients experience dramatic improvements in their cardiac function and quality of life.
This might help: Diabetes Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Heart Failure Management
Heart failure occurs when the heart becomes too weak or stiff to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in tissues and insufficient oxygen delivery to organs.
Classification System
Singapore’s healthcare providers use a standardized staging system to assess heart failure severity:
| Stage | Description | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| A | At risk for heart failure | No symptoms present |
| B | Structural heart disease present | No symptoms yet apparent |
| C | Overt heart failure | Symptoms present with structural disease |
| D | Advanced heart failure | Severe symptoms despite maximum treatment |
Heart Failure Treatment Options
Medication Therapy Multiple drug categories help manage heart failure by lowering blood pressure, slowing heart rate, strengthening heart contractions, and relieving symptoms.
Device Therapy Advanced cases may require specialized devices:
- Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): Helps coordinate ventricular contractions
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD): Monitor heart rhythm and deliver shocks when dangerous arrhythmias occur
- Ventricular Assist Devices (VAD): Mechanical pumps that support heart function
Heart Transplantation For end-stage heart failure patients who meet strict criteria, heart transplantation offers the possibility of dramatically improved quality of life.
Singapore’s transplant programs achieve survival rates of 80% at one year and 70% at five years.
You might like: TCM Weight Management Singapore
Specialized Cardiac Procedures
Valve Repair and Replacement
When heart valves become damaged, they compromise the heart’s efficiency. Singapore offers both surgical and minimally invasive options:
Traditional Valve Surgery
Damaged valves can be repaired through cutting, stretching, or sewing techniques. When repair isn’t possible, artificial valves (either tissue-based or mechanical) provide replacement options.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI)
This innovative procedure allows valve replacement without removing the damaged valve.
A catheter delivers the new valve through the heart from the thigh, where it expands and takes over the regulation of blood flow.
Electrical Device Implantation
Pacemaker Installation
These devices regulate heartbeat in patients with severe arrhythmias.
The pacemaker consists of leads inserted into the heart through veins, connected to a control unit with electrical circuits that stimulate the heart when needed.
Defibrillator Implantation
These devices restore normal heart rhythms by delivering carefully regulated electrical currents when the heart stops beating effectively.
Heart Disease Prevention Strategies
Risk Factor Management
Maintaining Healthy Weight
Singapore healthcare providers recommend maintaining a BMI between 18.3 and 22.9 kg/m² through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
Blood Pressure Control
Regular monitoring and management of blood pressure help prevent the heart from working too hard to circulate blood throughout the body.
Cholesterol Management
Keeping LDL (bad cholesterol) levels below 100 mg/dL through diet, exercise, and medication when necessary helps prevent arterial plaque buildup.
Diabetes Management
Proper blood sugar control reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications, particularly important given Singapore’s high diabetes prevalence.
Insurance Coverage and Cost Considerations
Medisave Benefits
Singapore’s Medisave system provides coverage for heart disease treatment through two main categories:
Chronic Disease Coverage ($500 annual limit)
Covers approved conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cholesterol disorders, stroke, and ischemic heart disease.
Diagnostic Procedures ($600 annual limit)
Includes outpatient MRI scans, CT scans, and ultrasound examinations.
Healthcare Financing Options
Patients can access various financing schemes to manage treatment costs, including insurance plans and government subsidies for citizens and permanent residents.
Leading Heart Treatment Centers
Singapore houses world-class cardiac facilities, with the National Heart Centre Singapore (NHCS) serving as the premier specialized institution. These centers offer:
- Comprehensive cardiovascular therapeutics
- Emergency coronary intervention services
- Specialized clinics for hypertension, heart failure, and arrhythmia management
- Personalized cardiovascular medicine including genetic risk profiling
- Advanced research and clinical trials
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early warning signs of heart disease?
Early warning signs include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest, pain radiating to the jaw or arms, unexplained nausea or heartburn, and excessive sweating.
These symptoms require immediate medical evaluation, especially when they occur without obvious triggers.
How is heart disease diagnosed in Singapore?
Singapore uses a comprehensive diagnostic approach including electrocardiograms, stress tests, echocardiography, and coronary angiograms. Advanced imaging techniques like cardiac MRI and CT scans provide detailed heart structure analysis, while nuclear imaging assesses blood flow and heart function.
What is the difference between angiogram and angioplasty?
An angiogram is a diagnostic procedure that uses contrast dye and X-rays to visualize blocked arteries, essentially a “search” function.
Angioplasty is a treatment procedure that uses balloons and stents to open blocked arteries, functioning as the “destroy” component of blockage removal.
Is angioplasty a permanent cure for heart disease?
Angioplasty is not a cure but rather a treatment that helps control symptoms and improve blood flow.
Long-term success requires significant lifestyle changes including dietary modifications, regular exercise, weight management, and ongoing medical monitoring to address the underlying causes of heart disease.
What lifestyle changes are essential after heart treatment?
Essential changes include creating a smoking cessation plan, maintaining healthy weight through diet and exercise, monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels, taking prescribed medications consistently, limiting sodium intake, and attending regular medical check-ups for ongoing monitoring.
How safe are modern heart procedures in Singapore?
Modern heart procedures in Singapore are very safe, with angioplasty and stent placement achieving approximately 90% success rates.
Minor complications like bruising or bleeding at insertion sites may occur, but serious complications including arterial damage or severe bleeding are uncommon.
Can heart disease be inherited?
Yes, heart disease can have genetic components. Family history of cardiovascular disease increases your risk even with healthy lifestyle choices.
Individuals with family history should undergo regular screening for risk factors and maintain preventive care measures.
What role does cholesterol play in heart disease?
High cholesterol, particularly LDL (bad cholesterol), contributes significantly to arterial plaque formation.
Some individuals have genetic predispositions to high cholesterol that cannot be controlled through lifestyle changes alone, requiring medication management alongside dietary modifications.
When should someone seek emergency cardiac care?
Seek immediate emergency care for sudden, severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness, severe sweating combined with chest discomfort, or any combination of heart attack symptoms. Quick medical intervention can be life-saving in cardiac emergencies.
What heart failure symptoms require medical attention?
Contact your healthcare provider for worsening shortness of breath unrelated to exercise, increased swelling in ankles or abdomen, unexplained weight gain over short periods, persistent coughing, trouble sleeping, or increased fatigue that interferes with daily activities.
How does Singapore’s healthcare system support heart patients?
Singapore provides comprehensive cardiac care through specialized centers, government subsidies through Medisave, structured rehabilitation programs, and integrated care teams including cardiologists, nurses, and rehabilitation specialists to support patients throughout their treatment journey.
What preventive measures can reduce heart disease risk?
Preventive measures include maintaining healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity (minimum 150 minutes weekly), eating balanced diets rich in vegetables and fruits, avoiding tobacco use, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress levels, and maintaining regular medical check-ups for early detection.