Heartburn affects millions of people worldwide, and Singapore is no exception.
With changing dietary habits and lifestyle patterns, understanding this common digestive condition has become increasingly important for residents seeking effective management and relief.
Understanding Heartburn and GERD
Heartburn represents a symptom rather than a standalone medical condition.
It manifests as the primary indicator of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), a digestive disorder affecting the muscular valve separating your esophagus from your stomach.
GERD develops when stomach contents flow backward into the esophagus due to improper functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
This muscular ring normally acts as a one-way valve, allowing food to enter the stomach while preventing acidic stomach contents from traveling upward.
When this valve becomes weakened or relaxed inappropriately, stomach acid and digestive enzymes can escape into the esophagus, causing the burning sensation characteristic of heartburn.
The condition affects people of all ages and has been increasing in prevalence across Southeast Asia, including Singapore.
Read more: Acid Reflux and GERD in Singapore: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Primary Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what triggers heartburn episodes can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and dietary choices.
Physiological Factors
The fundamental cause involves dysfunction of the gastroesophageal junction.
When the muscular valve becomes too weak, it fails to maintain proper closure, allowing stomach acid to reflux into the esophagus.
This often leads to inflammation of the esophageal lining, particularly in individuals with heightened sensitivity.
Weight-Related Factors
Obesity significantly increases heartburn risk through multiple mechanisms.
Excess abdominal fat creates additional pressure around the stomach and other organs, forcing stomach contents upward.
The increased pressure on the lower esophageal sphincter compromises its ability to maintain proper closure.
Read more: Which Gastroenterologist in Singapore Should You Consider?
Pregnancy-Related Changes
Pregnant women experience heightened heartburn susceptibility due to two primary factors.
The growing baby creates physical pressure against the stomach, making acid reflux more likely.
Additionally, elevated progesterone levels during pregnancy cause widespread smooth muscle relaxation throughout the body, including the esophageal sphincter.
Lifestyle Contributors
Several lifestyle factors contribute to heartburn development:
- Dietary choices: Consuming large meals, spicy foods, acidic foods, high-fat content meals, and caffeinated beverages
- Timing of meals: Eating close to bedtime or lying down shortly after meals
- Substance use: Tobacco smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Physical positioning: Bending over or lying flat after eating
Medical Conditions
Hiatal hernia represents a common underlying condition where part of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
This anatomical change facilitates easier passage of stomach contents into the esophagus.
Recognizing Heartburn Symptoms
Heartburn symptoms can vary significantly between individuals, making recognition sometimes challenging.
Classic Manifestations
The most recognizable symptom involves a burning sensation rising from the stomach area through the chest, often extending toward the throat.
This discomfort typically occurs after meals and may persist for several hours.
Additional Symptoms
GERD can produce various other symptoms that may not immediately suggest digestive involvement:
- Chronic throat irritation or persistent cough
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or painful swallowing (odynophagia)
- Excessive saliva production mixed with refluxed acid (water brash)
- Voice changes or hoarseness
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Gum inflammation (gingivitis)
- Dental enamel erosion
- Regurgitation of sour or bitter fluid into the mouth
Related article: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment in Singapore
Symptom Variations
Some individuals describe their discomfort differently than the typical “burning” sensation.
Alternative descriptions include chest pressure, heaviness, or general discomfort.
These variations can sometimes complicate diagnosis, particularly when symptoms overlap with other conditions.
Distinguishing Heartburn from Heart Attack
Given the location of heartburn discomfort, distinguishing it from cardiac events becomes crucial, especially for individuals with risk factors for heart disease.
Heartburn Characteristics
Heartburn typically produces a burning sensation in a vertical line behind the breastbone, sometimes extending into the throat.
The discomfort often correlates with eating patterns and may improve with antacids or position changes.
You might like: Functional Dyspepsia Treatment in Singapore
Heart Attack Warning Signs
Cardiac events typically produce different symptom patterns.
The discomfort often feels like significant pressure across a wider chest area, commonly described as a heavy weight pressing down.
Pain frequently radiates up the left side of the neck and down the left arm.
Heart attacks may also produce accompanying symptoms including nausea, dizziness, perspiration, shortness of breath, and feelings of impending doom.
Unlike heartburn, cardiac symptoms typically don’t correlate with meal timing and don’t improve with antacids.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Any chest discomfort should be taken seriously, particularly in individuals over 40, those with family history of heart disease, or people with risk factors such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
When in doubt, seeking immediate medical evaluation is always the safer choice.
Related article: Celiac Disease Treatment in Singapore
Potential Complications of Untreated Heartburn
While many people experience occasional heartburn without serious consequences, chronic untreated GERD can lead to significant complications.
Esophageal Inflammation and Damage
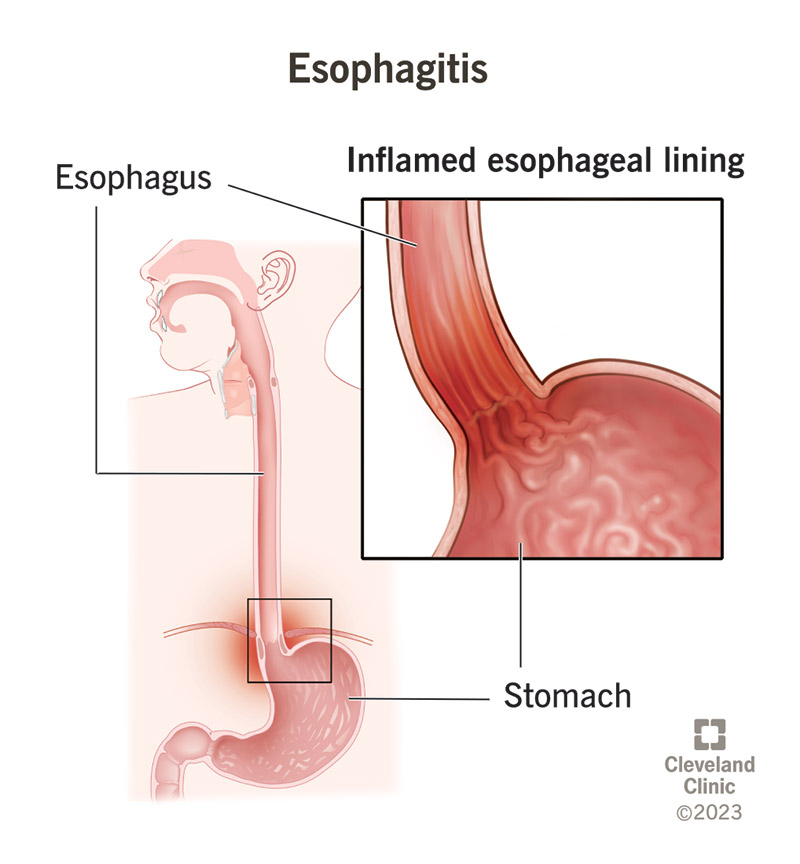
Repeated acid exposure can cause inflammatory damage to the esophageal lining, leading to erosions or ulcers. In severe cases, these ulcers may cause bleeding when blood vessels rupture.
Esophageal Stricture
Chronic inflammation can result in scarring that narrows the esophagus, creating swallowing difficulties.
This condition, called stricture, may require medical intervention to restore normal swallowing function.
This might help: Health Screening in Singapore
Barrett’s Esophagus
Long-term acid exposure can cause changes in the esophageal lining, where stomach-type cells replace normal esophageal cells.
This condition, known as Barrett’s esophagus, increases the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
While Barrett’s esophagus occurs less frequently in Asian populations compared to Western countries, it remains a concern requiring surveillance through regular endoscopic examinations with tissue sampling.
Cancer Risk
In rare cases, chronic GERD can contribute to the development of esophageal cancer, particularly when Barrett’s esophagus is present.
This represents one of the most serious potential complications, emphasizing the importance of proper management.
Related article: Best JB Health Screening Clinics for Singaporeans
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Determining when to seek professional medical advice depends on symptom severity, frequency, and impact on daily life.
Immediate Medical Attention
Certain situations warrant urgent medical evaluation:
- Severe chest pain that lasts many hours or throughout the night
- Symptoms accompanied by significant difficulty swallowing
- Vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds
- Severe weight loss without explanation
- Symptoms that interfere with sleep or daily activities
Routine Medical Consultation
Less urgent but still important reasons to consult a healthcare provider include:
- Heartburn occurring more than twice weekly
- Symptoms that don’t respond to over-the-counter medications
- Progressive worsening of symptoms over time
- Chronic cough or throat irritation
- Recurring symptoms lasting more than two weeks
Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare providers use various methods to diagnose GERD and rule out other conditions.
Initial Assessment
The diagnostic process typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination.
Doctors assess symptom patterns, timing, triggers, and associated factors to determine the likelihood of GERD.
Gastroscopy (Upper Endoscopy)
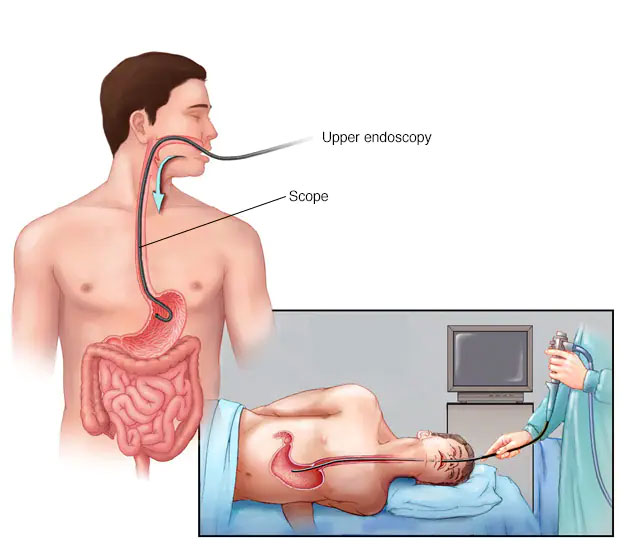
For patients with significant symptoms, gastroscopy represents the most common diagnostic procedure.
This examination involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera through the mouth to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and upper small intestine.
Modern gastroscopy procedures are designed for patient comfort, utilizing local anesthetics and mild sedatives to minimize discomfort.
Many patients report little to no memory of the procedure due to the sedation.
Advanced Testing
When symptoms are atypical or don’t respond to standard treatment, more sophisticated tests may be necessary:
- 24-hour pH monitoring: Measures acid levels in the esophagus over a full day
- Manometry: Evaluates esophageal muscle function and coordination
- pH-impedance monitoring: Detects both acidic and non-acidic reflux episodes
Cardiac Evaluation
When symptoms suggest possible cardiac involvement, additional testing may include electrocardiograms, blood tests, echocardiography, or cardiac catheterization, typically performed by cardiologists.
Treatment Options
GERD treatment approaches range from simple lifestyle modifications to surgical interventions, depending on symptom severity and response to initial treatments.
Medications
Antacids
Simple over-the-counter antacids provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid. These work best for mild, occasional symptoms but aren’t suitable for frequent use.
H2 Receptor Blockers
These medications reduce acid production by blocking histamine receptors in the stomach. They provide longer-lasting relief than antacids and can be used preventively.
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs represent the most powerful acid-suppressing medications available. They work by blocking the enzyme system responsible for acid production, providing comprehensive symptom relief and allowing esophageal healing.
Potassium Channel Blockers
For the most severe cases, these newer medications provide even stronger acid suppression than PPIs, reserved for situations where maximum acid control is necessary.
Prokinetic Agents
These medications help accelerate stomach emptying, reducing the likelihood of reflux by clearing stomach contents more quickly into the small intestine.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery becomes necessary only in rare circumstances when maximum medical treatment fails to control symptoms or complications develop.
Laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication
This minimally invasive procedure involves wrapping the upper portion of the stomach around the lower esophagus to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter. Most patients experience significant symptom improvement and can resume normal activities within days.
Recovery typically involves a liquid diet for the first two weeks, progressing to soft foods, then regular diet over the following month. The procedure often provides symptom relief lasting five to seven years.
Effective Home Remedies
Several natural approaches can provide symptomatic relief for heartburn sufferers.
Herbal Remedies
Chamomile Tea:
Known for its soothing properties, chamomile can help calm irritated digestive tissues. Avoid peppermint or spearmint teas, which may worsen reflux symptoms.
Ginger:
This anti-inflammatory root has been used traditionally for digestive issues. Fresh ginger tea can help reduce heartburn symptoms naturally.
Dietary Approaches
Honey and Lemon Water:
Despite lemon’s acidic nature, when combined with water and honey, it can create an alkaline mixture that may help neutralize stomach acid.
Low-Fat Milk:
Milk can act as a temporary buffer between stomach acid and the esophageal lining. Choose low-fat options, as high-fat content may worsen symptoms.
Important Considerations
While home remedies can provide relief, they shouldn’t replace professional medical treatment for chronic symptoms.
Always consult healthcare providers for persistent or severe heartburn.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing heartburn episodes involves strategic lifestyle modifications that address common triggers and risk factors.
Dietary Modifications
Foods to Limit or Avoid
- Spicy foods (chili, hot peppers, curry)
- Acidic foods (citrus fruits, tomatoes, vinegar)
- High-fat foods (fried foods, fatty meats, full-fat dairy)
- Caffeinated beverages (coffee, tea, cola)
- Alcoholic beverages
- Chocolate and mint
- Carbonated beverages
Beneficial Foods
- High-fiber foods (oatmeal, brown rice, vegetables)
- Alkaline foods (bananas, melons, cauliflower)
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, tofu)
- Non-citrus fruits
- Vegetables (except tomatoes and onions)
- Probiotics (yogurt, kefir)
Eating Habits
Meal timing and portion control play crucial roles in preventing heartburn episodes.
| Strategy | Recommendation | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Meal Size | Eat smaller, more frequent meals | Reduces stomach pressure and acid production |
| Timing | Stop eating 2-3 hours before bedtime | Prevents nighttime reflux |
| Eating Speed | Chew thoroughly and eat slowly | Improves digestion and reduces air swallowing |
| Position | Stay upright after meals | Uses gravity to prevent reflux |
Lifestyle Modifications
Weight Management
Maintaining healthy body weight significantly reduces heartburn risk. Even a 10% weight reduction can improve symptoms substantially.
Sleep Position
Elevating the head of the bed by 6-8 inches helps prevent nighttime reflux by using gravity to keep stomach contents from flowing upward.
Clothing Choices
Avoid tight-fitting clothing around the waist and abdomen, which can increase abdominal pressure and promote reflux.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise supports healthy digestion and weight management. However, avoid vigorous exercise immediately after eating, and choose activities that don’t require frequent bending or lying down.
Smoking Cessation
Tobacco use weakens the lower esophageal sphincter and increases acid production. Quitting smoking provides multiple health benefits beyond reflux improvement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause heartburn symptoms?
Stress doesn’t directly cause GERD, but it can worsen symptoms through several mechanisms.
Stress may increase stomach acid production, slow digestion, and lead to unhealthy eating patterns.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help reduce symptom frequency.
Is it safe to take antacids daily for heartburn relief?
While occasional antacid use is generally safe, daily use may indicate underlying GERD requiring professional evaluation.
Long-term antacid use can interfere with nutrient absorption and mask symptoms of more serious conditions.
Consult a healthcare provider if you need antacids more than twice weekly.
How long does it take for heartburn medications to work?
Response time varies by medication type. Antacids provide relief within minutes but last only 1-2 hours. H2 blockers take 30-60 minutes to work and last 6-12 hours.
Proton pump inhibitors may take 1-4 days for full effect but provide 24-hour acid suppression.
Complete healing of esophageal inflammation may take 8 weeks to 3 months.
Can heartburn medications cause side effects?
Most heartburn medications have excellent safety profiles when used appropriately.
Short-term use rarely causes significant side effects. Long-term PPI use may slightly increase risks of kidney disease, bone fractures, and certain infections, but these risks are generally outweighed by benefits for people with chronic GERD.
Are there any foods that actually help prevent heartburn?
Several foods may help reduce heartburn risk. High-fiber foods help prevent overeating and promote healthy digestion.
Alkaline foods like bananas and melons may help neutralize stomach acid. Probiotics support digestive health.
Lean proteins are less likely to trigger symptoms than high-fat alternatives.
Is heartburn more common during pregnancy and why?
Pregnancy significantly increases heartburn risk due to hormonal changes and physical pressure.
Progesterone levels rise throughout pregnancy, relaxing smooth muscles including the lower esophageal sphincter.
Additionally, the growing baby creates upward pressure on the stomach, promoting reflux. Symptoms often improve after delivery.
When should I consider surgery for heartburn?
Surgery is typically considered only when maximum medical treatment fails to control symptoms or complications develop.
Candidates usually have tried multiple medications without success, experience severe symptoms affecting quality of life, or develop complications like Barrett’s esophagus or strictures.
Surgery should always be discussed thoroughly with qualified specialists.
Can children develop GERD and heartburn?
Children can develop GERD, though symptoms may differ from adults. Infants may experience frequent spitting up, feeding difficulties, or irritability.
Older children may complain of stomach pain, chronic cough, or respiratory symptoms.
Pediatric GERD often improves with dietary modifications and positioning changes.
Does drinking milk really help with heartburn symptoms?
Milk provides temporary relief by coating the esophageal lining and neutralizing acid.
However, this effect is short-lived, and milk’s fat and protein content may actually stimulate increased acid production later.
Low-fat milk is preferable to whole milk, but it’s not a long-term solution for chronic symptoms.
How do I know if my heartburn is actually something more serious?
Warning signs that warrant immediate medical attention include severe chest pain, difficulty swallowing, weight loss, vomiting blood, or symptoms that don’t respond to over-the-counter treatments.
Additionally, heartburn occurring more than twice weekly or symptoms that interfere with sleep or daily activities should be evaluated by healthcare providers.
Can heartburn lead to throat or voice problems?
Acid reflux can definitely affect the throat and voice box, causing symptoms like chronic sore throat, hoarseness, chronic cough, or feeling of a lump in the throat.
This occurs when stomach acid reaches the upper throat area. These symptoms may be the only manifestation of GERD in some patients, making diagnosis more challenging.
Is there a difference between heartburn in Singapore compared to other countries?
While the basic mechanism of GERD remains the same worldwide, dietary patterns and lifestyle factors in Singapore may influence symptom triggers.
The multicultural cuisine, including spicy foods common in local dishes, may contribute to symptoms in susceptible individuals.
However, the medical understanding and treatment approaches align with international standards.

