What is Bariatric Surgery?

Bariatric surgery, also known as metabolic surgery or weight loss surgery, is a surgical intervention for obesity that has proven to be more effective than lifestyle, dietary, and medical interventions in managing obesity.
This type of surgery modifies different parts of the gastrointestinal (digestive) tract to bring about weight loss.
According to the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, patients who were severely obese lose at least half of their excess weight through bariatric surgery.
These procedures work by either reducing the amount of food you can eat or reducing the nutrients you can absorb.
It’s important to understand that bariatric surgery produces significant and sustainable weight loss results for improving one’s health.
It is not a cosmetic surgery but rather a medical intervention aimed at addressing obesity and its related health complications.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide to Losing Weight in Singapore
Types of Bariatric Surgery
There are four main types of minimally invasive bariatric surgery procedures available in Singapore:
1. Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding (LAGB)
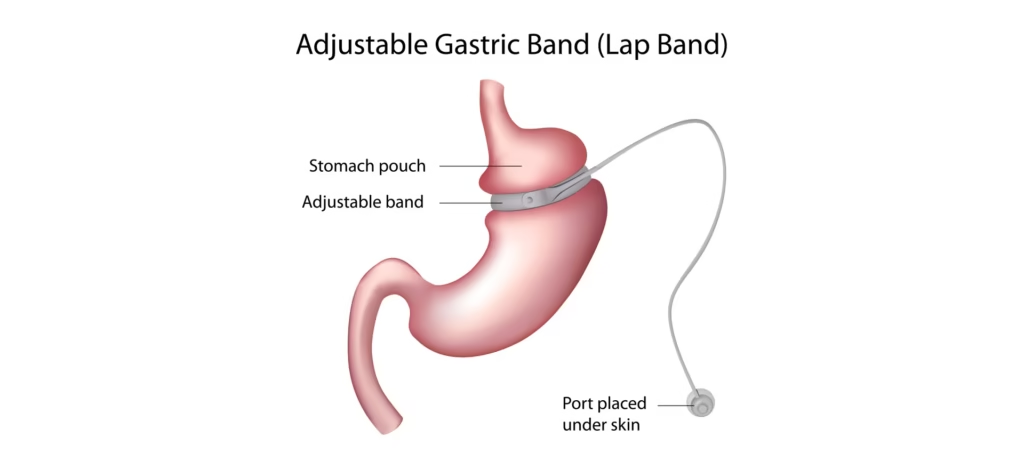
This is a restrictive surgery used to manage morbid obesity that places an inflatable band over the top portion of the stomach, dividing it into two sections and creating a small pouch on top of the main stomach connected by a small channel.
The procedure slows down the passage of food into the main stomach, consequently reducing food intake, and allows control of the opening to the main stomach by inflating or deflating the band with a port implanted under the skin.
This surgery is reversible, as the band and port can be removed if no longer needed.
Related article: Comprehensive Guide to Colonoscopy in Singapore
2. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy (LSG)
This restrictive procedure permanently reduces the size of your stomach to about 25% of its original size by creating a tube-like or “sleeve” remnant through stapling and excising the stomach along its outer edge.
The surgery removes the part of the stomach called the fundus that produces an appetite-stimulating hormone called ghrelin, resulting in more rapid emptying of food from the stomach and leading to changes in intestinal hormones.
This procedure is not reversible and is sometimes performed as the first step in a series of weight loss surgeries.
3. Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (LRYGB)
This restrictive/malabsorptive procedure reduces the size of your stomach to a small pouch of about 30 mL by clipping off a section of it, then directly attaches this small pouch to the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach and the upper end of the small intestine.
The surgery causes food to go straight into the small pouch and then into the small intestine, reducing the amount of fat and calories absorbed from food and helping suppress hunger while creating changes in gut bacteria and gut hormones.
This procedure is difficult to reverse but can be done if medically necessary.
This might help: Health Screening in Singapore
4. Laparoscopic Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch
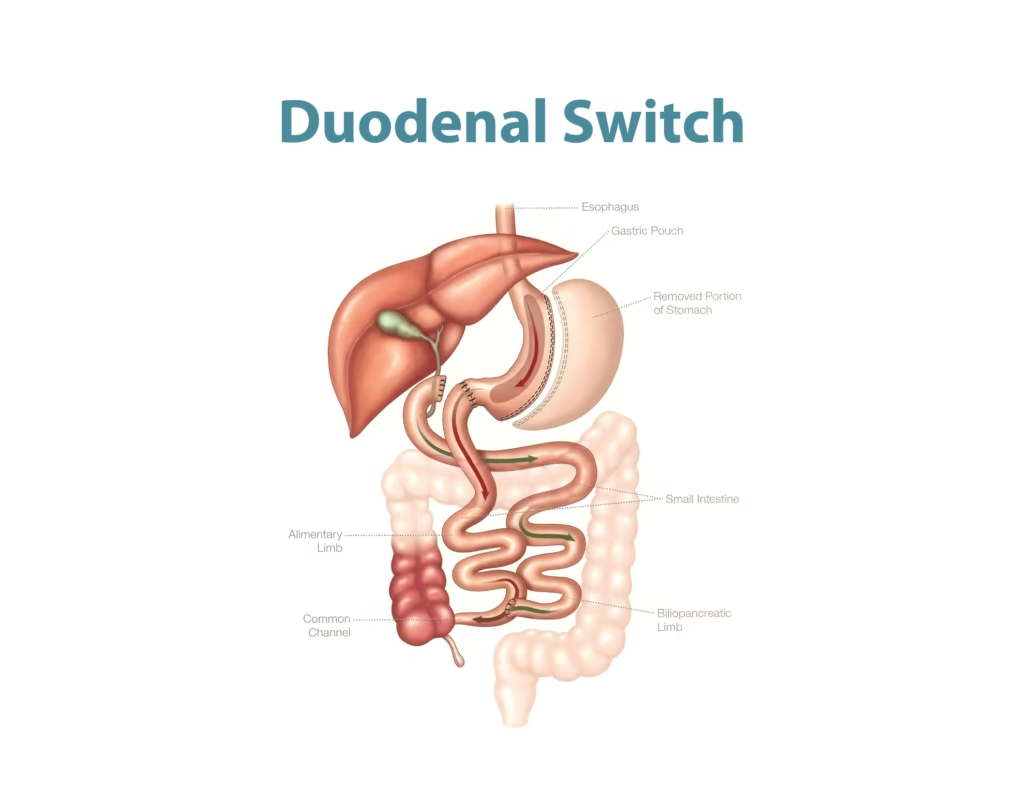
This restrictive/malabsorptive surgery reduces the stomach to about 25% of its original size, similar to sleeve gastrectomy, and clips the middle section of the small intestine while attaching the last part of the small intestine directly to the duodenum.
The procedure reattaches the separated middle section to the end of the intestine, bypassing most of the small intestine, and is performed in two steps: first a sleeve gastrectomy, then the bypassing procedure.
This surgery limits both food intake and the absorption of calories and nutrients.
You might like: Best JB Health Screening Clinics for Singaporeans
Why Consider Bariatric Surgery?
Bariatric surgery can successfully manage weight and greatly improve obesity-associated disorders, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, high cholesterol, heart disease and stroke, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood).
Weight loss surgery can help you enjoy a better quality of life and a longer lifespan.
Studies have found that severely obese individuals who have had bariatric surgery are at 30% lower risk of death from obesity-related conditions than those who did not undergo the surgery.
Research shows that bariatric surgery consistently results in greater and longer-lasting weight loss compared to exercising, dieting, and taking medications alone.
Most studies demonstrate that more than 90% of severely obese patients successfully maintain 30% of total weight loss following bariatric surgery.
Read more: Type 2 Diabetes Treatment in Singapore: Symptoms, Risks
Eligibility Criteria for Bariatric Surgery
According to the Ministry of Health’s Clinical Practice Guidelines, bariatric surgery is recommended for:
- Patients with a BMI > 37.5 kg/m²
- Patients with a BMI > 32.5 kg/m² with medical conditions or complications as a result of obesity
- Patients who have failed significant lifestyle and medical therapy attempts at weight loss
For Asian patients specifically, the minimum BMI for bariatric surgery is 32.5, though in select cases, patients with BMI 30 to 32.5 who have severe obesity-related medical conditions may be considered.
It’s important to note that bariatric surgery may not be suitable for everyone who is severely overweight.
You need to meet certain medical requirements and be willing to make lifelong lifestyle changes to benefit from the surgery.
You might like: Homeopathy in Singapore
The Bariatric Surgery Process
Pre-Surgery Assessment
Before your surgery, you can expect a comprehensive medical assessment of your current condition.
This evaluation will examine factors such as your present weight and body composition, pre-existing medical conditions, dietary habits, lifestyle habits (including smoking and alcohol intake), activity level, previous surgeries, and family history of obesity.
You will undergo several medical checks and investigations to identify existing health risks, such as heart conditions.
Your medical team will provide recommendations for exercise and dietary programs to kickstart your weight loss journey before surgery.
They will also identify eating patterns such as eating disorders or stress eating habits and create customized meal plans for your needs.
This might help: Which Cardiologist in Singapore Should You Consider? (Sort by Reviews)
The Surgery
Most bariatric surgeries in Singapore are performed laparoscopically (keyhole surgery).
This approach offers smaller scars, faster recovery, less pain, and better cosmetic outcomes compared to conventional surgery methods.
Patients typically spend two to three days in the hospital after laparoscopic procedures.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery
After bariatric surgery, laparoscopic procedures generally have a recovery time of 2-3 weeks.
Patients are typically ready to return to work within three to four weeks.
Close follow-up is critical, especially in the first year, and after the first year, patients will need to see their doctor between one to four times annually.
Patients are required to take supplements as the procedure may affect absorption of vitamins and minerals.
Average weight loss of around four kilograms per month is normal.
In general, patients lose 20 to 40 kilograms over six months to two years, though some super obese people may lose up to 70 kilograms.
Risks and Complications
Bariatric surgery is considered generally safe, but like all major surgeries, it carries some risks:
Short-term Risks
Short-term risks include infection, excessive bleeding, adverse reactions to anesthesia, blood clots and deep vein thrombosis, intestinal leaks in staple lines or joints, and lung or breathing problems.
Long-term Complications
Long-term complications may include bowel obstruction, dumping syndrome (causing diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting), vitamin and nutrient deficiencies, gallstones, hernias, ulcers, and saggy or loose skin from extreme weight loss.
Two complications that require particular attention are:
Obstruction:
When the connection between your stomach and intestines becomes narrowed, leading to a blockage preventing bowel movement. This can be an emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
Dumping Syndrome:
Occurs when food or liquid enters the small intestines too quickly in large amounts, leading to diarrhea and cramps within 10 to 30 minutes after eating.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
In Singapore, bariatric surgery can cost anywhere from SGD $20,000 to $30,000, depending on the complexity of the surgery and any additional hospitalization fees. This amount typically includes:
- Surgeon’s fees
- Hospital fees
However, it does not include follow-up fees for the procedure.
Weight loss surgeries are not covered by all insurers in Singapore. To understand what financing options are available for your condition, it’s recommended to speak with healthcare providers for a detailed breakdown of the financing terms before opting for bariatric surgery.
Common Myths About Bariatric Surgery
Myth 1: After surgery, I can eat all I want and not gain weight.
Reality: Bariatric surgery helps you feel full after smaller meals, but you still need to adhere to dietary rules and exercise. Without proper diet and exercise, you may not lose enough weight.
Myth 2: Anyone dissatisfied with their weight can have bariatric surgery.
Reality: There are specific BMI requirements and patients must have tried other weight loss methods without success.
Myth 3: Bariatric surgery is dangerous.
Reality: While all surgeries have risks, modern advances have reduced these considerably. The benefits of bariatric surgery typically far outweigh the risks of mortality from obesity-related conditions.
Myth 4: Weight loss and health improvement are immediate after surgery.
Reality: It takes time for the effects to be seen, with average weight loss of around 4 kg per month being normal. Close follow-up is essential for successful outcomes.
Myth 5: Bariatric surgery always involves stomach stapling.
Reality: There are various forms of bariatric surgery, from adjustable gastric banding (which doesn’t involve cutting or stapling) to procedures that use stapling techniques.
Myth 6: My nutrition will be severely affected after surgery.
Reality: While nutritional supplements are typically required, your surgeon and dietitian will work together to help you plan meals that support good nutrition and health.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between gastric sleeve and gastric bypass?
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) reduces the size of your stomach to about 25% of its original size by removing a large portion of it.
This is primarily a restrictive procedure that limits food intake and reduces hunger hormone production.
Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) creates a small stomach pouch and connects it directly to the middle portion of the small intestine, bypassing the rest of the stomach and upper portion of the small intestine.
It works through both restriction (smaller stomach) and malabsorption (bypassing part of the digestive tract).
Gastric bypass typically results in greater weight loss (average 60% of excess weight) compared to sleeve gastrectomy (average 40% of excess weight) but may have more nutritional implications due to the malabsorptive component.
How much weight will I lose after bariatric surgery?
Weight loss varies depending on the procedure, your starting weight, and how well you follow post-surgical recommendations. Generally:
- After sleeve gastrectomy, patients lose an average of 40% of their excess weight
- After gastric bypass, patients lose an average of 60% of their excess weight
Most patients lose between 20-40 kg over six months to two years, with average weight loss of about 4 kg per month being typical. Some patients with higher starting weights may lose up to 70 kg.
What can I eat after bariatric surgery?
Your diet will progress through several phases after surgery, beginning with clear liquids for the first few days, followed by pureed foods for several weeks, then soft foods for a period of time, and a gradual return to solid foods.
Long-term dietary guidelines typically include eating small, frequent meals, chewing food thoroughly, avoiding high-calorie liquids and foods high in sugar and fat, focusing on protein-rich foods, taking recommended vitamin and mineral supplements, and staying hydrated with water.
A dietitian will work with you to develop a personalized meal plan that ensures adequate nutrition.
How long is the recovery period?
For laparoscopic bariatric procedures, most patients stay in the hospital for 2-3 days, return to normal activities within 2-3 weeks, and return to work within 3-4 weeks.
Full recovery and adjustment to the new digestive system can take several months, and weight loss continues over 12-24 months.
Recovery from open surgery procedures, which are less common, typically takes longer, with patients needing more time before returning to normal activities.
Will I need to take supplements after bariatric surgery?
Yes, most bariatric surgery patients need to take vitamin and mineral supplements for life because the reduced size of the stomach limits food intake, some procedures particularly affect nutrient absorption, and specific deficiencies are common without supplementation.
Common supplements include multivitamins, calcium with vitamin D, vitamin B12, iron, and additional supplements based on individual needs.
Regular blood tests will help your healthcare team monitor your nutrient levels and adjust supplements as needed.
Does bariatric surgery cure diabetes?
Bariatric surgery can lead to significant improvement or remission of type 2 diabetes in many patients, with this effect often seen even before significant weight loss occurs, suggesting metabolic changes beyond those attributable to weight loss alone.
Studies show that up to 80% of patients with type 2 diabetes experience remission after gastric bypass, while about 60% experience remission after sleeve gastrectomy, with results typically better in patients with shorter duration of diabetes.
However, not all patients experience complete remission, and some may see their diabetes return years after surgery, particularly if they regain weight or have had diabetes for many years before surgery.
Will I have loose skin after losing weight?
Many patients do experience loose or sagging skin after significant weight loss from bariatric surgery, with factors influencing the amount of loose skin including the amount of weight lost, age, genetics, smoking history, sun exposure history, and how quickly the weight is lost.
Some patients choose to have body contouring procedures to remove excess skin after reaching their weight loss goals, usually 12-18 months after bariatric surgery.
Can weight return after bariatric surgery?
Yes, weight regain is possible after bariatric surgery, though most patients maintain significant weight loss long-term, with studies showing more than 90% of patients maintain at least 30% of their total weight loss.
Some weight regain of 5-10% of lost weight is common 2-5 years after surgery, with factors contributing to weight regain including not following dietary guidelines, lack of regular physical activity, development of maladaptive eating behaviors, stretching of the stomach pouch over time, and hormonal adaptations.
For patients who experience significant weight regain, revisional surgery may be considered.
Is bariatric surgery right for me?
Determining if bariatric surgery is appropriate requires a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. Consider bariatric surgery if:
- Your BMI is 37.5 or higher (for Asian patients)
- Your BMI is 32.5 or higher with obesity-related conditions
- You’ve tried other weight loss methods without success
- You’re willing to make lifelong lifestyle changes
- You’re committed to regular follow-up care
Bariatric surgery is a tool to help with weight loss, not a quick fix or magic solution. Success depends heavily on your commitment to changing eating habits, increasing physical activity, and following medical advice.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgery offers a proven, effective approach to significant weight loss for those with severe obesity, particularly when lifestyle modifications and medications haven’t been effective.
The procedures available in Singapore provide different options to meet individual needs, with laparoscopic techniques offering faster recovery and less scarring.
While bariatric surgery carries risks like any major surgery, for many patients, the benefits of improved health, reduced obesity-related conditions, and enhanced quality of life far outweigh these risks.
The key to success is a commitment to lifelong lifestyle changes and regular medical follow-up.
If you’re considering bariatric surgery, consult with specialized healthcare providers who can assess your specific situation, explain all options in detail, and help you make an informed decision about whether this approach is right for you.

