Fertility challenges affect many couples in Singapore, with approximately 1 in 6 Singaporean couples experiencing difficulties conceiving.
Understanding the available fertility testing options can be crucial for those struggling to start a family. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about fertility assessments in Singapore, from initial consultations to specialized testing procedures and treatment options.
Understanding Fertility Assessments
A fertility assessment differs significantly from pre-conception screening. While pre-conception screening helps ensure couples are in good health before attempting pregnancy, a fertility assessment specifically targets couples who have been trying unsuccessfully to conceive. These assessments aim to identify specific barriers preventing successful conception or causing recurrent miscarriages.
Fertility doctors in Singapore conduct these assessments, which are typically simple, short processes for both partners. The evaluation helps pinpoint specific factors affecting fertility, which is essential since pregnancy requires both partners’ reproductive systems to function optimally.
When to Consider Fertility Testing
Timing is critical when considering fertility testing. Medical professionals generally recommend seeking fertility testing under these circumstances:
- You and your partner have been trying to conceive naturally for more than 12 months without success
- You’re a woman over 35 years old who has been trying to conceive for more than six months
- You experience irregular or absent menstrual cycles
- You’ve experienced multiple miscarriages
- You have a history of testicular issues or injuries (for men)
- You have known health conditions that might affect fertility, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders
- You’re concerned about egg or sperm quality due to age or lifestyle factors (smoking, alcohol consumption, or obesity)
- You’re considering assisted reproductive techniques like in vitro fertilization (IVF)
You might be interested: A Comprehensive Guide to In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) in Singapore
The age factor is particularly significant for women. As a woman ages, her chances of conception decrease substantially. This is why doctors recommend seeking help after 12 months of trying if the woman is under 36, but after just 6 months if she is 36 or older.
Common Causes of Infertility
Understanding the potential causes of infertility helps couples approach testing with appropriate expectations. Fertility challenges can stem from female factors, male factors, or a combination of both.
Male Infertility Factors
Male infertility typically results from issues with either healthy sperm production or sperm delivery to the egg.
Problems with sperm production include:
- Low sperm count, reducing the chances of fertilization
- Poor sperm motility (the ability of sperm to move efficiently)
- Abnormal sperm morphology (shape and structure)
- Low testosterone levels, sometimes manifesting as decreased facial or body hair and gynaecomastia (enlargement of male breast tissue)
Read more: Male Infertility in Singapore: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Issues with sperm delivery include:
- Erectile dysfunction during sexual intercourse
- Blockages in the sperm ducts that prevent proper sperm transport
- Varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum that can increase temperature and compromise sperm quality)
- Retrograde ejaculation (where semen enters the bladder instead of emerging through the penis)
Related article: Erectile Dysfunction Treatment in Singapore
Female Infertility Factors

Female infertility typically stems from one of three main issues: problems producing healthy eggs, difficulties transporting eggs from the ovaries to the womb, or challenges with the fertilized egg implanting in the uterine lining.
Related article: Menopause Treatment Singapore
Common causes include:
- Ovulation disorders: Hormonal imbalances (often stress-induced or caused by conditions like PCOS) can disrupt the regular ovulation cycle
- Blocked fallopian tubes: This prevents eggs from reaching the womb to meet sperm for fertilization
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, potentially affecting fertility
- Uterine abnormalities: Fibroids, polyps, or structural variations in the uterus can interfere with implantation
- Age-related decline: Egg quantity and quality naturally decrease as women age, particularly after 35
The ability of a fertilized egg to implant itself successfully in the uterine lining is another critical factor. When a woman has fibroids, endometriosis, polyps, or cysts on her womb lining, the surface area available for implantation decreases, reducing the chances of successful pregnancy.
You might be interested: Egg Freezing in Singapore
What to Expect During a Fertility Assessment
A comprehensive fertility assessment typically involves several components to evaluate both partners’ reproductive health. Here’s what couples can expect:
1. Comprehensive Medical History
The first step involves detailed history-taking from both partners. The fertility specialist will ask about:
- Existing medical conditions
- Duration of time trying to conceive
- Frequency of sexual intercourse
- Previous pregnancies or reproductive experiences
- Menstrual cycle regularity (for women)
- Lifestyle factors that might impact fertility
While some questions may seem personal, providing accurate information is essential for proper assessment. Most fertility specialists recommend that couples attend the first consultation together, though if schedules conflict, it’s advisable for the woman to see the gynecologist first to avoid delays.
2. Physical Examinations
Both partners typically undergo appropriate physical examinations to identify any conditions that might affect fertility. For women, this often includes a pelvic examination.
This might be helpful: Testosterone Replacement Therapy in Singapore: Symptoms, Causes, Benefits
3. Ultrasound of the Woman’s Reproductive Organs
An ultrasound scan helps check for abnormalities in the woman’s reproductive organs, such as:
- Fibroids (benign tumors in the uterus)
- Polyps (small growths in the uterus)
- Endometriotic masses (tissue similar to the uterine lining growing outside the uterus)
- Ovarian cysts
- Structural abnormalities of the uterus
The ultrasound can be performed either trans-abdominally (across the abdomen) or trans-vaginally (through the vagina), depending on what provides the clearest visualization of the reproductive organs. Trans-vaginal ultrasounds generally provide more detailed images but may cause mild discomfort.
This assessment is particularly important for women who have never been examined by a gynecologist, as they may have undetected gynecological issues.
Related article: Endometriosis Treatment in Singapore
4. Female Hormone Testing
Blood tests check for hormone levels that might affect fertility, including:
Basic Hormonal Profile:
- Day 3-5 FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) level
- Day 3-5 LH (Luteinizing Hormone) level
- Day 3-5 E2 (Estradiol) level
- Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) level – indicates egg reserve
Additional Specialized Hormone Tests (if needed):
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) level
- Prolactin level
- DHEAS level
- Testosterone level
- Insulin level (fasting)
These tests help identify any hormonal imbalances that might interfere with ovulation or other aspects of fertility.
5. Egg Reserve Testing
For women concerned about their egg supply, particularly those over 35 or with a family history of early menopause, specific tests evaluate egg reserve:
- Antral Follicle Count: This transvaginal ultrasound counts the small follicles (2-8mm) in the ovaries, providing a snapshot of egg reserve.
- AMH Blood Test: Anti-Müllerian Hormone testing provides an accurate indication of ovarian reserve and can be done at any point in the menstrual cycle.
6. Ovulation Testing
Several methods help determine if and when a woman is ovulating:
- Urine LH Tests: Self-administered tests that detect the LH surge occurring 24-36 hours before ovulation
- Ultrasound Monitoring: Tracking follicle growth through several ultrasounds during the menstrual cycle
- Progesterone Level Testing: Blood test approximately 7 days after ovulation to confirm whether ovulation occurred
7. Fallopian Tube Assessment
One critical test for women is the Hysterosalpingogram (HSG), which evaluates the patency (openness) of the fallopian tubes. This 15-30 minute procedure involves:
- Inserting a small catheter through the vagina into the cervix and uterus
- Injecting medical dye through the catheter
- Taking X-rays or ultrasound images to visualize the flow of dye through the uterus and fallopian tubes
If the dye flows freely through the tubes and spills into the abdominal cavity, the tubes are open. If the dye stops, this might indicate a blockage, although sometimes tube spasms can create false results.
8. Semen Analysis for Men
Male fertility testing primarily centers on semen analysis. The procedure involves:
- Collecting a semen sample after 2-5 days of abstinence
- Laboratory analysis of sperm count, motility (movement), and morphology (shape)
- Assessment of semen volume and other parameters
The sample can be produced at the clinic or at home, provided it reaches the laboratory within 1-2 hours of collection. It’s important to use a laboratory specializing in fertility testing that adheres to World Health Organization standards.
Advanced Fertility Testing Options
If initial testing doesn’t provide clear answers, couples might require more specialized tests:
Hysteroscopy
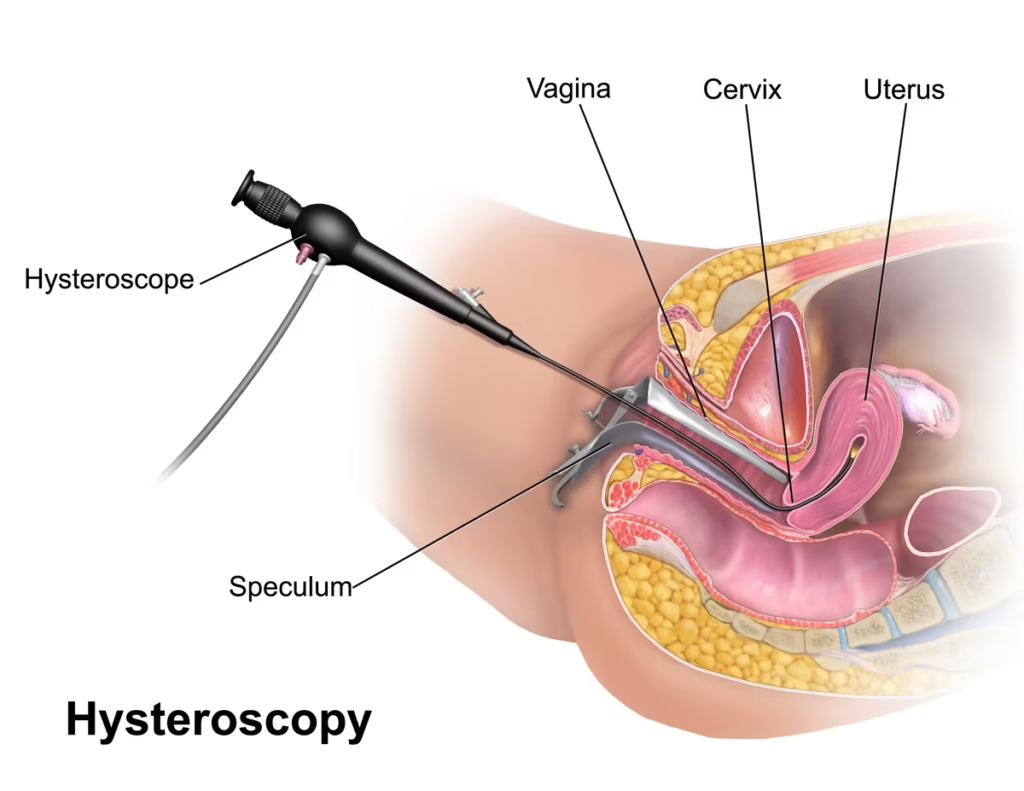
This procedure allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity:
- A small scope with a camera is inserted through the cervix into the uterus
- The doctor can examine the uterine cavity and identify abnormalities like polyps or fibroids
- Minor surgical corrections can often be performed during the same procedure
- Usually performed under mild anesthesia
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
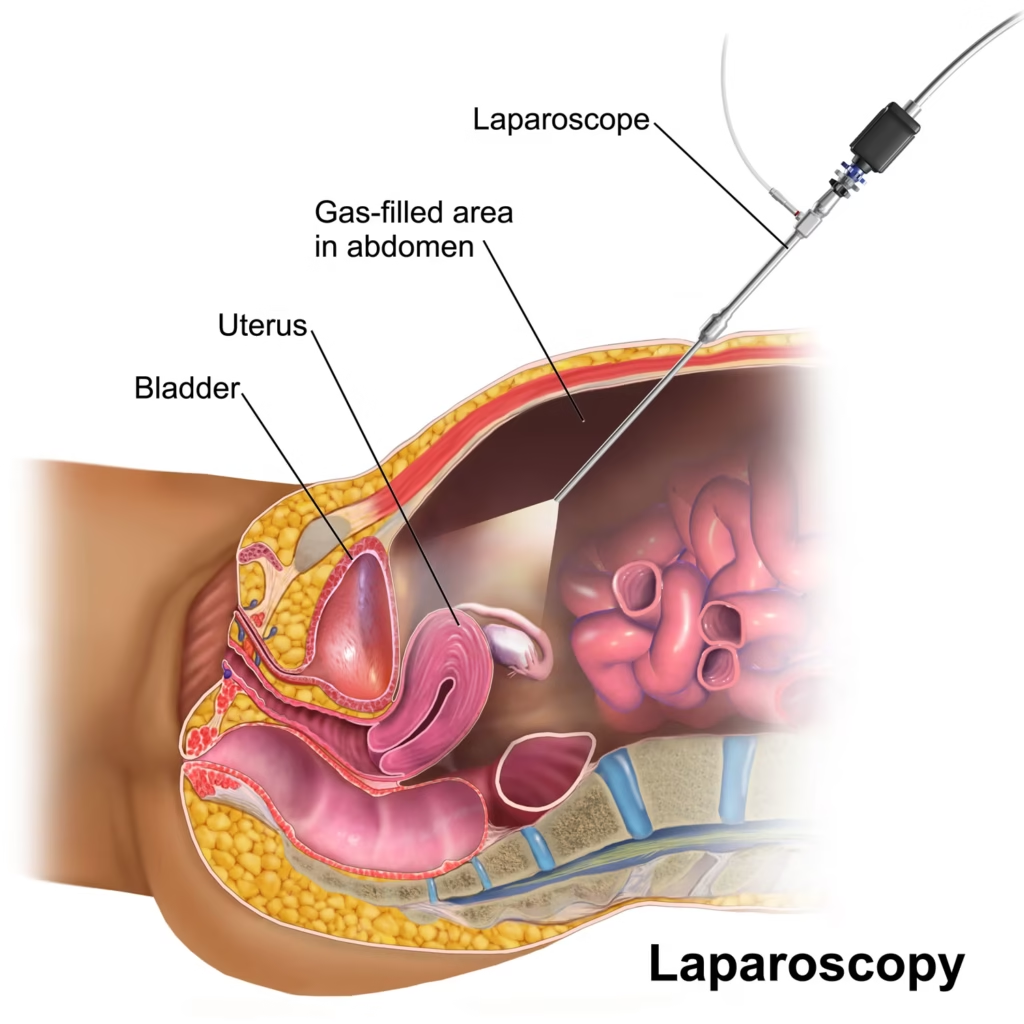
This surgical procedure provides a comprehensive view of the reproductive organs:
- Performed under general anesthesia
- A scope is inserted through a small incision near the navel
- The abdominal cavity is inflated with CO2 gas to improve visibility
- The doctor can examine the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries
- Blue dye can be injected through the cervix to check fallopian tube patency
- Corrective surgery for conditions like endometriosis or adhesions can often be performed simultaneously
Treatment Options After Fertility Assessment
Based on test results, the fertility specialist will discuss appropriate treatment options. Contrary to common belief, IVF isn’t always the first or only recommendation. Treatment approaches might include:
Lifestyle Modifications
For some couples, simple lifestyle changes can significantly improve fertility:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Reducing alcohol consumption and eliminating smoking
- Managing stress
- Timing intercourse to coincide with the fertile window (1-2 days before ovulation)
- Taking appropriate supplements (like folic acid for women)
Medical Treatments
Depending on the underlying cause, medical interventions might include:
- Medication to stimulate ovulation
- Hormone therapy to address imbalances
- Surgical procedures to correct structural issues (removing fibroids or polyps, unblocking fallopian tubes, etc.)
Assisted Reproductive Techniques
For more complex fertility challenges, options include:
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Prepared sperm is inserted directly into the uterus close to the time of ovulation
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory, with resulting embryos transferred to the uterus
Read more: A Comprehensive Guide to In-Vitro Fertilisation (IVF) in Singapore
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is directly injected into an egg, often used for male factor infertility
It’s worth noting that according to some specialists, only about 20-30% of patients seeking fertility help ultimately require IVF. Many couples achieve pregnancy through less invasive methods.
Where to Get Fertility Testing in Singapore
Fertility testing services are available through various healthcare providers in Singapore:
Public Hospitals
- Generally more affordable and potentially partially subsidized
- May have longer waiting times for appointments
- Often provide comprehensive services
Private Hospitals and Specialized Fertility Clinics
- Typically offer faster appointment scheduling
- Provide more personalized care and attention
- May have specialized equipment and expertise
- Usually come with higher costs
General Practitioners (GPs)
- Can provide basic fertility assessments
- May order initial blood tests or semen analysis
- Will refer to specialists for more comprehensive testing
Costs of Fertility Testing in Singapore
The cost of fertility testing in Singapore varies widely depending on several factors:
- Whether tests are conducted at public or private facilities
- The specific tests required
- Whether testing is done individually or as part of a comprehensive package
- Insurance coverage (some plans may cover certain fertility tests)
Couples should consider discussing costs with their healthcare provider before proceeding with testing, as some comprehensive fertility packages may offer better value than individual tests.
How to Boost Natural Fertility
While undergoing fertility testing, couples can take several steps to enhance their natural fertility:
1. Understand Your Fertile Window
- Track ovulation using home ovulation predictor kits or apps
- Engage in intercourse 1-2 days before expected ovulation
- Maintain regular sexual activity (2-3 times weekly) throughout the cycle
2. Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle
- Maintain a healthy weight (both underweight and overweight conditions can impact fertility)
- Eliminate smoking, which significantly reduces fertility in both men and women
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Reduce caffeine intake
- Exercise moderately (excessive exercise can sometimes impact fertility)
3. Optimize Nutrition
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Consider prenatal vitamins or supplements (women should take 400mcg of folic acid daily)
- Some evidence suggests that certain traditional Chinese medicine approaches may support fertility, though consult a healthcare provider first
FAQ: Fertility Testing in Singapore
How long should we try to conceive naturally before seeking fertility testing?
If the woman is under 35, doctors generally recommend trying for 12 months before seeking testing. For women 35 and older, it’s advisable to seek help after 6 months of trying. However, if you have known fertility risk factors (irregular periods, history of reproductive conditions, etc.), consider consulting a specialist sooner.
Can I perform any fertility tests at home?
Yes, some basic fertility testing can be done at home:
- Ovulation predictor kits that detect LH surges
- Basal body temperature tracking to identify ovulation patterns
- Some at-home hormone tests, including AMH testing for egg reserve
- At-home sperm tests for basic sperm count assessment
However, home tests have limitations and aren’t as comprehensive or reliable as clinical evaluations. They should complement, not replace, professional fertility assessments.
Is a fertility test painful?
Most fertility tests cause minimal discomfort:
- Blood tests involve a brief needle prick
- Ultrasounds (even transvaginal ones) typically cause only mild discomfort
- HSG (fallopian tube assessment) may cause cramping during the procedure
- Semen analysis involves no pain
If you’re concerned about discomfort, discuss this with your doctor, who can suggest ways to make your experience more comfortable.
Should both partners get tested simultaneously?
Yes, fertility experts strongly recommend that both partners undergo testing simultaneously. Since fertility challenges can stem from male factors, female factors, or a combination of both, comprehensive testing of both partners provides the clearest picture and avoids unnecessary delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Can my GP perform fertility testing?
General practitioners can conduct initial fertility assessments and order basic tests like hormone blood work. However, for comprehensive fertility evaluation, your GP will likely refer you to a gynecologist, fertility specialist, or urologist (for male testing). GPs serve as an excellent first point of contact in your fertility journey.
Does insurance cover fertility testing in Singapore?
Coverage varies widely depending on your insurance plan. Some plans cover diagnostic testing, particularly when linked to specific medical conditions, while others offer limited or no coverage. Check with your insurance provider about specific coverage details before proceeding with testing.
How long does a complete fertility assessment take?
A comprehensive fertility assessment typically spans several weeks to complete all necessary tests. Initial consultations and basic tests might be completed in a few days, but hormone testing often requires specific timing within the menstrual cycle. Follow-up appointments to discuss results and treatment plans typically occur 2-4 weeks after testing begins.
What’s the difference between fertility testing and IVF preparation?
Fertility testing is a diagnostic process to identify potential causes of infertility, while IVF preparation involves specific protocols to prepare for in vitro fertilization treatment. Fertility testing often precedes any treatment decisions, including whether IVF is necessary. Not all couples who undergo fertility testing will require IVF.
Can men freeze sperm in Singapore?
Yes, sperm freezing (cryopreservation) is available in Singapore through fertility clinics and hospitals. This option might be considered by men facing medical treatments that could affect fertility, those traveling frequently, or those wanting to preserve fertility for future family planning.
What happens after a fertility assessment?
After completing all tests, you’ll meet with your fertility specialist to discuss:
- Test results and any identified fertility challenges
- Recommended treatment options based on your specific situation
- Lifestyle modifications that might improve fertility
- Next steps in your fertility journey
The specialist will create a personalized plan tailored to your needs and preferences.
Conclusion
Fertility testing provides valuable insights for couples struggling to conceive, opening doors to appropriate treatments and interventions. In Singapore, couples have access to comprehensive testing options through both public and private healthcare channels.
Remember that fertility challenges are common—affecting up to one in six Singaporean couples—and seeking professional help is both normal and advisable. The sooner you identify potential fertility barriers, the sooner you can address them and move forward on your path to parenthood.
While the fertility journey can be emotionally challenging, Singapore’s advanced healthcare system offers numerous resources, technologies, and supportive professionals to guide couples through this process. With proper assessment, many couples overcome fertility challenges and achieve their dream of starting or expanding their family.