Understanding Your Thyroid Gland
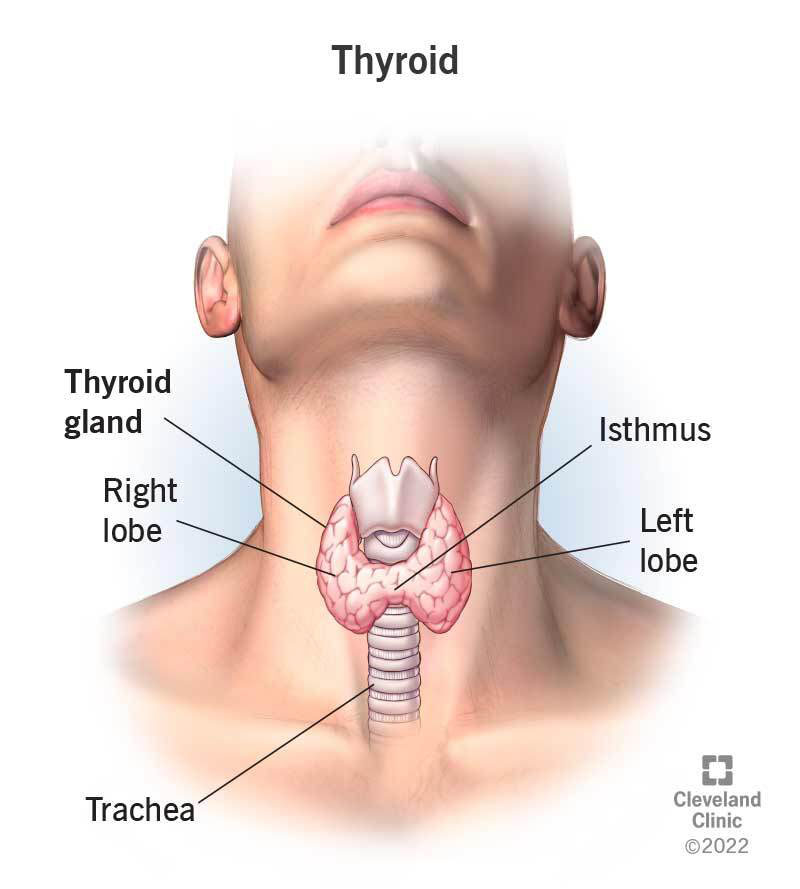
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ positioned at the front of your neck, just below the Adam’s apple.
This essential endocrine gland produces hormones that regulate your body’s metabolism, controlling how your cells use energy from food.
The thyroid consists of two lobes connected by a central portion called the isthmus, and when functioning properly, it plays a crucial role in maintaining your overall health and wellbeing.
While everyone has a thyroid gland, not everyone experiences thyroid-related health issues.
However, when problems do arise, they typically fall into two main categories that require different types of medical attention and treatment approaches.
This might help: Which Endocrinologist in Singapore Should You Consider?
Types of Thyroid Problems Requiring Treatment
Hormone Production Disorders
Thyroid hormone imbalances occur when your gland produces either too much or too little of the essential hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
These conditions significantly impact your quality of life and require prompt medical intervention.
Hyperthyroidism develops when your thyroid becomes overactive, producing excessive amounts of thyroid hormones.
This condition affects approximately 70% of cases through an autoimmune disorder called Graves’ disease, where your body’s immune system mistakenly stimulates the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism occurs when your thyroid gland cannot produce sufficient hormones to meet your body’s metabolic needs.
The most common cause is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, another autoimmune condition where your immune system attacks and damages the thyroid tissue.
Related article: Diabetes Treatment in Singapore: Types, Risks
Thyroid Nodules and Structural Problems
Thyroid nodules are growths or lumps that develop within the thyroid gland.
These can be solid or fluid-filled and vary considerably in size.
Fortunately, medical research shows that over 90% of thyroid nodules are benign (non-cancerous), but proper evaluation remains essential to rule out malignancy.
Recognizing Thyroid Disorder Symptoms
Signs of Overactive Thyroid (Hyperthyroidism)
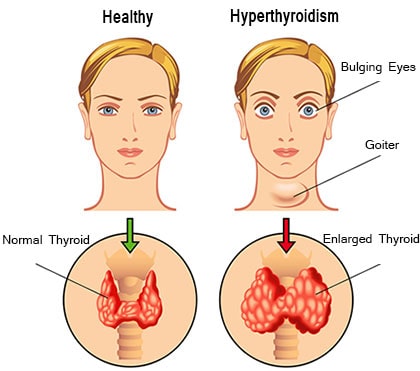
When your thyroid produces too much hormone, you may experience unexplained weight loss despite maintaining a normal or increased appetite.
Other common symptoms include rapid or irregular heartbeat with palpitations, excessive nervousness, anxiety, and restlessness.
Many people also develop hand tremors and muscle weakness, along with increased sensitivity to heat and excessive sweating.
Women may notice changes in their menstrual patterns, while sleep disturbances and persistent restlessness are frequently reported.
Digestive issues such as diarrhea often occur, and in cases of Graves’ disease, bulging eyes may develop. Additionally, an enlarged thyroid gland may become visible as swelling in the neck.
You might like: Type 1 Diabetes Treatment in Singapore: Causes, Risks
Signs of Underactive Thyroid (Hypothyroidism)

When your thyroid cannot produce adequate hormones, persistent fatigue and sluggishness are typically the first symptoms to appear.
Unexplained weight gain often follows, accompanied by increased sensitivity to cold temperatures.
Physical changes may include dry, pale skin and brittle hair, while digestive issues manifest as constipation and overall digestive slowdown.
Facial puffiness and swelling throughout the body are common, along with a hoarse voice that develops gradually.
Many people experience muscle aches, weakness, and joint stiffness, while mental health symptoms such as depression and memory problems frequently occur.
Women may notice irregular or heavy menstrual periods, and a slowed heart rate is often detected during medical examinations.
You might be interested: Type 2 Diabetes Treatment in Singapore: Symptoms, Risks
Thyroid Nodule Warning Signs
Most thyroid nodules develop without causing noticeable symptoms; however, larger nodules may create visible swelling in the neck area.
When symptoms do occur, they typically include difficulty swallowing or breathing, along with hoarseness or other voice changes.
Some people experience pain or tenderness at the base of the neck, and if the nodule produces excess hormones, symptoms similar to hyperthyroidism may develop.
When to Seek Professional Thyroid Treatment
Choosing the Right Specialist
The type of thyroid problem you have determines which medical specialist can provide the most appropriate care:
For Hormone-Related Issues: Consult a family physician, internist, or endocrinologist (hormone specialist) who can diagnose and manage thyroid hormone imbalances through medication and ongoing monitoring.
For Thyroid Nodules or Lumps: See an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist or a head and neck surgeon who has specific training in thyroid surgery and can evaluate whether surgical intervention is necessary.
For Complex Cases: Some patients require care from both an endocrinologist and a surgeon, particularly when thyroid nodules coexist with hormone regulation problems.
You might like: Gestational Diabetes Treatment in Singapore
Risk Factors Requiring Attention
Certain factors increase your likelihood of developing thyroid disorders:
- Gender: Women are five times more likely than men to develop thyroid problems
- Age: Risk increases significantly after age 60
- Family History: Genetic predisposition to thyroid or autoimmune diseases
- Previous Radiation Exposure: Particularly to the neck area
- Autoimmune Conditions: Having other autoimmune disorders
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes can trigger thyroid dysfunction
- Iodine Intake: Both deficiency and excess can affect thyroid function
- Certain Medications: Some drugs can impact thyroid function
This might be helpful: Diabetes Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Comprehensive Thyroid Diagnostic Process
Initial Consultation and Examination
Your thyroid specialist will begin with a thorough medical history review, focusing on:
- Duration and progression of symptoms
- Family history of thyroid or autoimmune diseases
- Previous radiation exposure or medical treatments
- Current medications and supplements
- Changes in weight, energy levels, or mood
The physical examination includes careful palpation of your neck to assess thyroid size, texture, and detect any nodules. Your doctor may also examine your eyes, heart rate, reflexes, and skin condition for signs of thyroid dysfunction.
You might like: Cushing Syndrome Treatment: Causes, Symptoms
Essential Diagnostic Tests
| Test Type | Purpose | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid Function Test (TFT) | Assess hormone levels | TSH, Free T4, Free T3 levels |
| Thyroid Ultrasound | Visualize gland structure | Nodule size, number, characteristics |
| Fine Needle Aspiration (FNAC) | Evaluate nodule cells | Benign vs. malignant determination |
| Thyroid Antibody Tests | Detect autoimmune causes | Anti-TPO, Anti-thyroglobulin levels |
| Radioactive Iodine Scan | Assess gland function | Hot vs. cold nodule activity |
Advanced Imaging Studies
For complex cases, additional imaging may include:
- CT or MRI Scans: Detailed visualization of large goiters or suspected cancer
- PET Scans: Evaluation of potential cancer spread
- Nuclear Medicine Studies: Assessment of thyroid function and metabolism
Comprehensive Treatment Options in Singapore
Medical Management of Hormone Disorders
Hypothyroidism Treatment: The primary treatment involves hormone replacement therapy using synthetic levothyroxine tablets.
This medication must be taken on an empty stomach, typically in the morning, to ensure optimal absorption.
Regular blood tests every 6-12 months monitor hormone levels and guide dosage adjustments.
Most patients require lifelong treatment, but with proper management, they can maintain normal energy levels and quality of life.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment Options:
- Anti-thyroid Medications: Drugs like methimazole or propylthiouracil reduce hormone production and typically show improvement within 6-12 weeks.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This treatment selectively destroys overactive thyroid cells and often provides permanent resolution, though it may lead to hypothyroidism requiring hormone replacement.
- Beta-blockers: These medications help control symptoms like rapid heartbeat and tremors while other treatments take effect.
Surgical Treatment: When Surgery is Necessary
Thyroid surgery may be recommended based on the “4 C’s” criteria:
Cancer or Suspected Cancer: Any confirmed or highly suspicious malignant nodule requires surgical removal to prevent spread and ensure complete treatment.
Compression: Large goiters or nodules that press against the windpipe, esophagus, or blood vessels causing breathing or swallowing difficulties.
Control: When hyperthyroidism cannot be managed with medications or radioactive iodine, surgical removal helps control hormone overproduction.
Cosmesis: Some patients choose surgery for large, visible goiters that affect their appearance and self-confidence.
Types of Thyroid Surgery
Hemithyroidectomy: Removal of one thyroid lobe, typically preserving normal hormone production and avoiding the need for hormone replacement therapy.
Total Thyroidectomy: Complete removal of both thyroid lobes, necessary for cancer cases or bilateral disease.
Patients require lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Lymph Node Dissection: Additional removal of nearby lymph nodes when cancer has spread or is suspected to have spread.
Innovative Echotherapy Treatment
Echotherapy represents a cutting-edge, non-invasive treatment option for selected patients with benign thyroid nodules. This procedure uses high-intensity focused ultrasound to destroy abnormal tissue without surgical incisions.
Echotherapy Benefits:
- No surgical cuts, wounds, or permanent scars
- Performed under sedation without general anesthesia
- Preserves normal thyroid function
- 45-minute to 1-hour treatment duration
- Same-day procedure with quick recovery
Echotherapy Criteria:
- Confirmed benign (non-cancerous) nodules
- Nodule size between 1-4 centimeters
- Patients not suitable for conventional surgery
- Absence of suspicious cancer features
Understanding Treatment Costs in Singapore
Insurance Coverage and Financial Planning
Most thyroid treatments in Singapore are covered through a combination of:
- Integrated Shield Plans: Private insurance coverage for specialist consultations and procedures
- Medisave: Government health savings account for eligible medical expenses
- MediClaim: Additional insurance benefits for outpatient and surgical procedures
Procedural Fee Guidelines
The Ministry of Health has established fee benchmarks for thyroid procedures:
| Procedure | Estimated Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Fine Needle Biopsy | $900 |
| Hemithyroidectomy | $8,450 |
| Total Thyroidectomy | $11,750 |
| Thyroid Function Tests | $100-200 |
| Thyroid Ultrasound | $200-300 |
Additional hospital costs include operating theater fees, ward charges, anesthesia, laboratory processing, and surgical consumables. Private room charges vary based on accommodation level chosen.
Outpatient vs. Inpatient Care
Outpatient Procedures:
- Diagnostic tests and consultations
- Fine needle aspirations
- Echotherapy treatments
- Post-surgical follow-up appointments
Inpatient Procedures:
- Thyroid surgery requiring 1-3 day hospital stays
- Post-surgical monitoring and recovery
- Management of surgical complications
Post-Treatment Care and Long-term Management
Follow-up Monitoring
Regular follow-up care ensures optimal treatment outcomes:
- Medication Patients: Blood tests every 6-12 months to monitor hormone levels
- Surgical Patients: Wound care, voice assessment, calcium level monitoring
- Cancer Patients: Imaging studies and tumor marker surveillance
Lifestyle Considerations
Dietary Recommendations:
- Maintain adequate iodine intake through iodized salt and seafood
- Limit goitrogenic foods if consuming large quantities
- Take thyroid medications on an empty stomach
- Avoid calcium and iron supplements within 4 hours of thyroid medication
Activity and Recovery:
- Gradual return to normal activities after surgery
- Voice rest and protection for the first weeks post-surgery
- Regular exercise to maintain healthy metabolism
- Stress management to support overall thyroid health
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need surgery for my thyroid nodule?
Not all thyroid nodules require surgical removal. The decision depends on several factors including nodule size, biopsy results, symptoms caused by the nodule, and your personal preferences. Most small, benign nodules can be monitored with regular ultrasounds without immediate intervention.
How do I choose the right thyroid surgeon in Singapore?
Look for surgeons with specialized head and neck training, extensive experience with thyroid procedures, and affiliations with reputable medical institutions.
Consider factors like surgical volume, complication rates, patient outcomes, and communication style when making your decision.
What is my expected recovery time after thyroid surgery?
Most patients stay in the hospital for 2-3 days after surgery and require about one week of recovery time in Singapore for international patients.
Complete healing typically takes 2-4 weeks, during which you should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities.
Is thyroxine replacement therapy necessary after surgery?
This depends on the type of surgery performed. Patients who undergo hemithyroidectomy (removal of one lobe) often maintain normal thyroid function without medication.
However, those requiring total thyroidectomy will need lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Will thyroid hormone replacement affect my weight or fertility?
When properly calibrated and monitored, thyroid hormone replacement should not negatively impact your weight, fertility, or cause hair loss.
In fact, correcting thyroid hormone deficiency often improves these aspects of health.
Can thyroid nodules be prevented?
Since the exact causes of thyroid nodules remain unclear, complete prevention is not possible. However, maintaining good thyroid health through adequate iodine intake, avoiding smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing stress may help reduce your risk.
How accurate is fine needle aspiration biopsy?
FNAC is highly accurate for diagnosing thyroid nodules, with a success rate of over 95% for determining whether nodules are benign or malignant.
The procedure is well-tolerated and causes no more discomfort than a routine blood test.
What are the risks of thyroid surgery?
Modern thyroid surgery performed by experienced surgeons has very low complication rates.
Potential risks include temporary or permanent changes in voice, low calcium levels (hypoparathyroidism), bleeding, and infection.
Your surgeon will discuss specific risks based on your individual case.
How often should I have thyroid function tests?
The frequency depends on your condition and treatment.
Patients on hormone replacement therapy typically need testing every 6-12 months once stable levels are achieved.
Those with thyroid nodules may require annual monitoring, while patients with thyroid cancer need more frequent surveillance.
Is echotherapy available for all thyroid nodules?
Echotherapy is only suitable for specific cases involving benign nodules between 1-4 cm in size. Patients must be confirmed to have non-cancerous nodules through proper testing, and the treatment is typically reserved for those who are not good candidates for conventional surgery.
What should I expect during my first thyroid consultation?
Your initial consultation will include a comprehensive medical history review, physical examination of your neck and thyroid gland, discussion of symptoms, and planning for appropriate diagnostic tests.
The appointment typically takes 45-60 minutes and may include scheduling for blood tests and imaging studies.
How long does it take to see improvement with thyroid treatment?
Improvement timelines vary by treatment type.
Patients starting hormone replacement therapy often feel better within 4-6 weeks, while those receiving anti-thyroid medications may see symptom improvement within 6-12 weeks.
Surgical patients typically experience immediate resolution of compression symptoms but may need time for complete healing.
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders are highly treatable conditions that affect millions of people worldwide.
Singapore offers world-class medical care for all types of thyroid problems, from simple hormone imbalances to complex surgical cases.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can restore your quality of life and prevent serious complications.
If you suspect you may have a thyroid problem, don’t delay in seeking professional evaluation.
With the right medical team and treatment plan, you can effectively manage your thyroid condition and maintain excellent health for years to come.

