What Are Heart Palpitations?
Heart palpitations are a sensation of an irregular, fast, or forceful heartbeat. The experience varies between individuals.
Some people describe palpitations as fluttering, skipped beats, or an extra hard or fast heart rhythm. These sensations can be felt in the chest, neck, or throat regions.
Heart palpitations are common in all age groups, though they tend to occur more frequently in females, especially during pregnancy or menopause. However, they can happen to anyone regardless of age and gender.
Related article: Health Screening in Singapore
Symptoms of Heart Palpitations
The most common symptoms associated with heart palpitations include a fluttering sensation in the chest, along with a pounding or racing heartbeat.
Some people may experience a slow heartbeat instead, while others notice missing beats or extra beats that feel irregular.
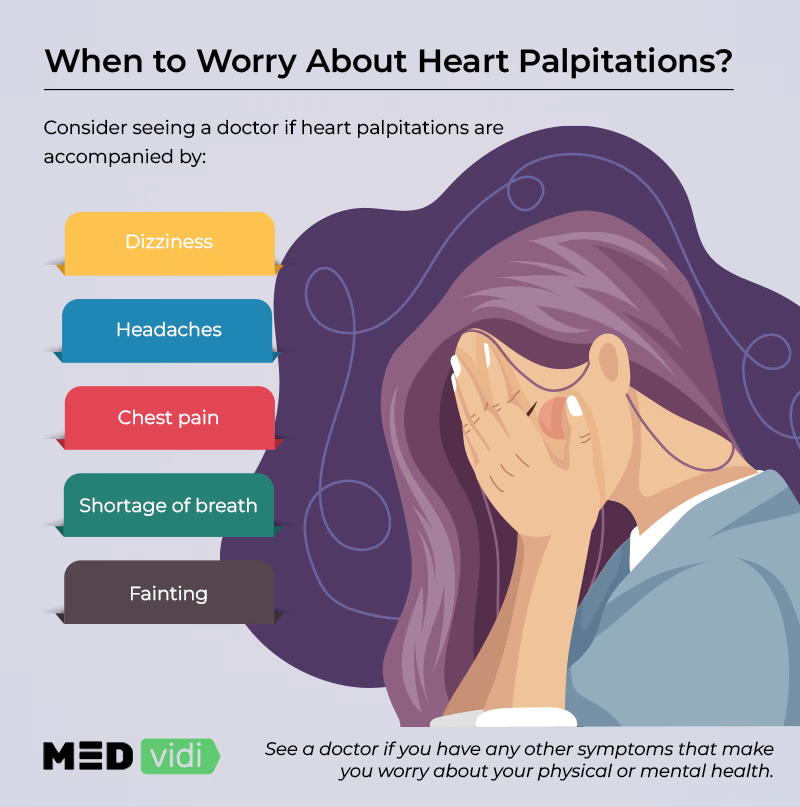
These sensations may be accompanied by chest discomfort, shortness of breath, light-headedness, or even a fainting sensation.
These symptoms typically last from a few seconds to several minutes.
While most cases are harmless, it’s important to consult a doctor if you’re concerned about your palpitations, especially if they persist for longer periods or are accompanied by other concerning symptoms.
Related article: Best JB Health Screening Clinics for Singaporeans
When to Seek Emergency Help
- Severe chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Unusual sweating
- Loss of consciousness
Additionally, it’s crucial to consult a doctor without delay if you have pre-existing heart conditions or a family history of sudden death.
This will help: Which Cardiologist in Singapore Should You Consider? (Sort by Reviews)
Causes of Heart Palpitations
Non-Serious Causes
Heart palpitations often have benign causes, particularly among women and younger patients.
Men and older patients are more likely to experience palpitations caused by arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), but many triggers are completely harmless.
Benign heart palpitations can be triggered by stress and anxiety, including panic attacks that cause temporary but intense heart rate changes.
Lifestyle factors play a significant role, with excessive caffeine consumption, alcohol consumption, energy drinks, and nicotine all being common culprits.
Certain medications, particularly stimulant medications such as weight loss pills and cough and cold medicines, can also trigger palpitations.
Physical factors that may cause harmless palpitations include fever, dehydration, low blood sugar, low blood pressure, and low potassium levels.
Extreme physical activity and excessive excitement can also trigger these sensations.
Even seemingly innocent triggers like eating too much chocolate can cause temporary heart palpitations in some individuals.
This might help: Diabetes Myths Debunked: Separating Fact from Fiction
Hormonal Causes
Hormonal changes can significantly trigger heart palpitations in many people.
Pregnancy often causes palpitations due to the dramatic hormonal shifts and increased blood volume that occur during this time.
Similarly, menopause can trigger palpitations as estrogen and other hormone levels fluctuate, making this a common experience for women during this life transition.
Related article: Menopause Treatment Singapore
Health Conditions
Several underlying health conditions may cause heart palpitations that require medical attention.
Anemia, which reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen, can cause the heart to work harder and create palpitation sensations. Thyrotoxicosis, or an overactive thyroid, speeds up the body’s metabolism and can cause rapid or irregular heartbeats.
Electrolyte imbalances affect the heart’s electrical system and can trigger various types of palpitations.
Additionally, diabetes can cause palpitations through blood sugar fluctuations and potential complications affecting the cardiovascular system.
More information: Diabetes Treatment in Singapore: Types, Risks
Serious Causes of Heart Palpitations
Of greater concern are heart palpitations caused by cardiac arrhythmias. These occur when there is a short-circuit in the electrical impulses controlling your heartbeat, causing it to beat too rapidly, too slowly, or irregularly.
When you have arrhythmia, your heartbeat either goes very fast, over 100 beats a minute (tachycardia) or very slow, less than 60 beats a minute (bradycardia).
Types of Cardiac Arrhythmias
1. Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
This is a prevalent arrhythmia in young adults. SVT is experienced as a sudden burst of rapid heartbeats that begin and end abruptly, lasting for seconds or hours. SVT is usually not life-threatening.
2. Atrial Fibrillation
This fast and irregular palpitation occurs in the atria or upper chambers of the heart and could last a few minutes to an hour. Atrial fibrillation arrhythmias could become chronic and lead to stroke. It is seldom life-threatening, but the heart palpitations could indicate underlying coronary artery disease or heart valve disorders.
3. Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Ventricular tachycardia is a very rapid, but regular heartbeat of 100 beats or more a minute occurring in the lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart.
Sustained heart palpitations lasting more than 30 seconds are considered a medical emergency. They could indicate pre-existing heart diseases such as coronary artery disease or heart valve disorders.
4. Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)
If ventricular tachycardia is left untreated, it will lead to a life-threatening condition called ventricular fibrillation, characterized by very fast and very irregular heartbeats.
It usually precedes a heart attack. You could lose consciousness within seconds and die within minutes.
Other Serious Conditions
More serious conditions and diseases that can cause heart palpitations include:
- Heart valve problems
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Congenital heart disabilities
How to Tell the Difference Between Serious and Non-Serious Palpitations
How can you determine if your palpitations are being caused by something serious or if you just need to cut down on coffee?
If the palpitations are few and far between, they’re probably not serious.
Be aware of what you are doing when the palpitations occur by considering your recent activities:
- Did you finish an intense workout?
- Have you had enough water during the day?
- Have you consumed caffeine, alcohol, or nicotine recently?
Keep track of what your palpitations feel like and if you have any other symptoms.
Click a pen or tap a finger to be aware of what your heart rhythm is doing. Is there anything else abnormal about your body? Do you feel dizzy, sweaty, or confused? Note down your heart rhythm and symptoms so you can better describe them to your doctor.
Why See a Heart Specialist for Palpitations?
In one study, researchers found that more than 80% of patients with palpitations have heart arrhythmias as the cause. Seeing a heart specialist will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of any arrhythmia that might be present.
How Your Cardiologist Diagnoses Palpitations
In most cases of palpitations, your cardiologist will perform a series of tests:
- ECG (Electrocardiogram): A 12-lead ECG will provide details on the electrical rhythm and wiring of the heart.
- Echocardiogram: A heart ultrasound will look for any underlying heart structure problems that could cause palpitations.
- Holter Monitoring: An ambulatory ECG monitor will be attached for a number of days to record your heart rhythm while you are at home or exercising.
- Blood Tests: To exclude problems like anemia, thyroid issues, and electrolyte imbalances.
Other tests may also be done:
- Electrophysiological (EP) Study: An invasive procedure that examines the heart’s electrical activity and determines abnormal heart rhythms.
- Implantable Loop Recorder: In some cases, your cardiologist may insert an implantable loop recorder to verify the causes of palpitations. This small monitoring device is fitted underneath the skin and may stay under the chest for up to 3 years to keep your heart under surveillance.
You might be interested: Comprehensive Guide to Coronary Angioplasty in Singapore
Treatment and Management of Heart Palpitations
Since most cases of heart palpitation are never life-threatening, treatment may include home remedies or no intervention at all. However, if your heart palpitations are concerning, treatment will depend on the underlying cause.
Medications
Doctors would normally prescribe oral medications such as beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers to slow down heart rates in arrhythmias.
Procedures
For supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation arrhythmias, catheter ablation – a non-surgical procedure using radiofrequency energy – is a possible cure.
Heart valve disorders will require surgery.
Prevention and Management of Heart Palpitations
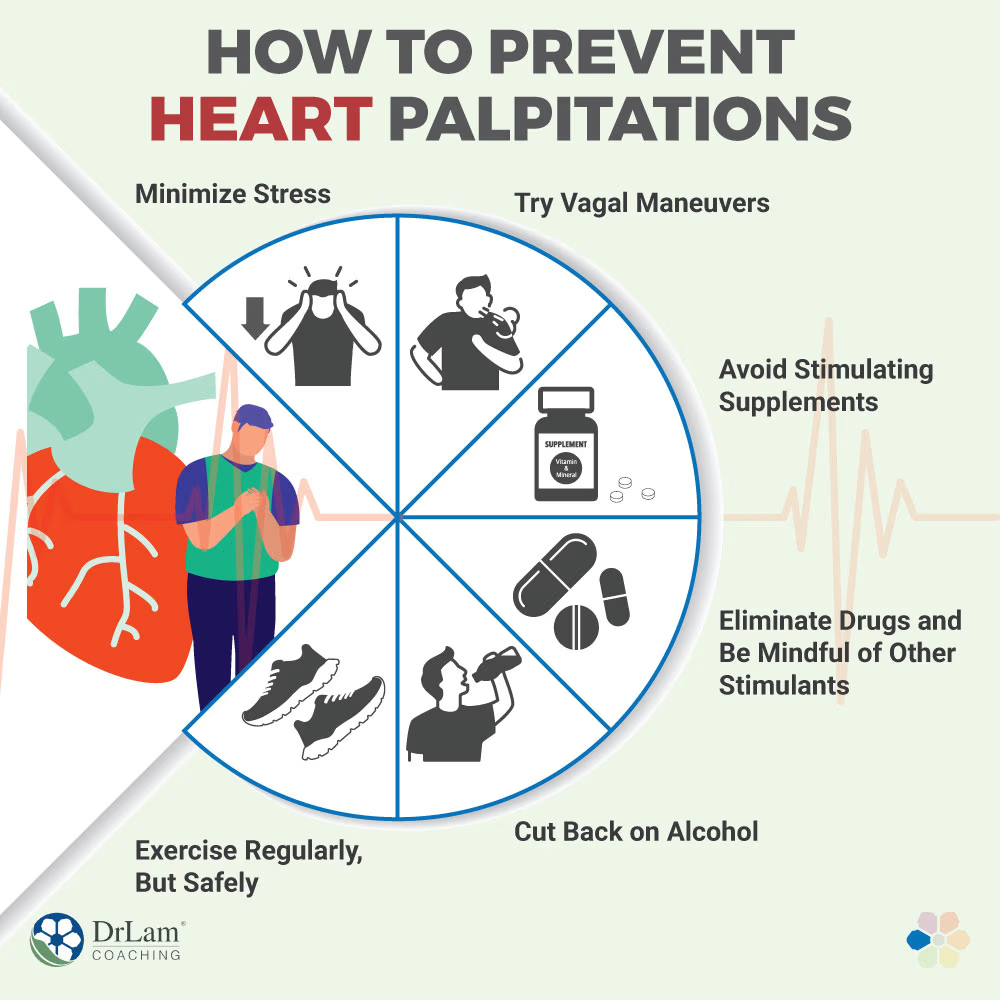
Most cases of heart palpitations can be prevented by understanding their triggers and actively avoiding them. Here are some general lifestyle tips to reduce palpitations:
- Limit or abstain from alcohol intake: Alcohol can trigger palpitations in many individuals.
- Reduce or cut down caffeine intake: Coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate can all contribute to palpitations.
- Quit smoking: Nicotine is a stimulant that can increase heart rate.
- Keep a food diary: List down food triggers, such as spices or specific foods that seem to coincide with your palpitations.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and meditation to help keep your focus on controlling your body and breathing, which helps regulate your heartbeat.
- Splash of cold water: You can help slow your heartbeat by lowering your body temperature. Try splashing cold water on your face, putting your face in a basin of cold water, or placing a cold towel on your neck.
- Ensure adequate sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep daily.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can trigger palpitations.
Common Myths About Heart Palpitations
Myth: “I had heart palpitations the other day, which means I have atrial fibrillation.”
FALSE. Palpitations are a very non-specific symptom. They can be due to atrial fibrillation or a variety of other arrhythmias such as tachycardia and premature ventricular contractions.
If you experience frequent or prolonged episodes of palpitations, or are having symptoms such as chest pain or dizziness, you should see a doctor to find out the exact cause.
Myth: “It is dangerous for my heart to skip a beat.”
FALSE. The sensation of skipped or missing heartbeats is normal. These irregularities in the heartbeat can be scary but are not typically dangerous.
They usually occur when someone is excited, stressed, or has had caffeine, alcohol, or certain cold medications.
Myth: “I only had one or two episodes of atrial fibrillation, so it will not come back.”
FALSE. Atrial fibrillation is almost always a recurrent condition that needs lifelong treatment to minimize symptoms and prevent stroke and heart failure. In the beginning, episodes of atrial fibrillation usually occur sporadically and end on their own.
These are called paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. However, if these episodes occur more frequently and over a longer period of time, you should talk to your cardiologist to find the best treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common triggers for heart palpitations?
Common triggers include stress, anxiety, caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, and certain medications.
Physical factors like fever, anemia, low blood sugar, and thyroid problems can also cause palpitations. Many people experience palpitations during pregnancy or menopause due to hormonal changes.
How long do heart palpitations typically last?
Heart palpitations usually last from a few seconds to several minutes. If palpitations persist for longer than 30 seconds and are accompanied by symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or loss of consciousness, seek immediate medical attention.
Can heart palpitations be prevented?
Many cases of heart palpitations can be prevented by avoiding known triggers.
This includes limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, quitting smoking, managing stress through relaxation techniques, getting adequate sleep, staying hydrated, and avoiding stimulant medications when possible.
Are heart palpitations more common in certain age groups?
Heart palpitations can occur in people of all ages. However, women and younger patients typically experience palpitations due to benign causes, while men and older patients are more likely to have palpitations caused by arrhythmias or other cardiac conditions.
How do doctors diagnose the cause of heart palpitations?
Diagnosis typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Doctors may order tests such as an ECG, echocardiogram, Holter monitoring, blood tests, and in some cases, an electrophysiological study or implantable loop recorder to determine the exact cause of palpitations.
What’s the difference between normal heart palpitations and those requiring medical attention?
Normal palpitations are infrequent, brief, and not accompanied by other symptoms. They often occur after exercise, stress, or caffeine consumption.
Palpitations requiring medical attention typically last longer, occur frequently, or are accompanied by symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, or fainting.
Can anxiety cause heart palpitations?
Yes, anxiety is one of the most common causes of heart palpitations. During anxiety or panic attacks, the body’s fight-or-flight response triggers the release of stress hormones that can increase heart rate and cause palpitations.
Managing anxiety through relaxation techniques, therapy, or medication can help reduce these episodes.
Are there any home remedies that can help with heart palpitations?
Several home remedies may help manage heart palpitations, including deep breathing exercises, splashing cold water on your face, maintaining good hydration, avoiding triggers like caffeine and alcohol, and practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga or meditation.
What types of medications are used to treat heart palpitations?
For palpitations caused by arrhythmias, doctors may prescribe medications such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers to slow down heart rate.
Other medications may be prescribed depending on the specific type of arrhythmia or underlying condition causing the palpitations.
Can heart palpitations be a sign of a heart attack?
While most heart palpitations are not signs of a heart attack, they can sometimes indicate serious cardiac conditions.
If palpitations are accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, unusual sweating, or loss of consciousness, seek emergency medical help immediately as these could be signs of a heart attack or another serious condition.

